HTML5 Tutorial
- Introduction 2020

In this chapter, we will go over basic HTML elements how they can be changed in HTML5. Some of them will be shorter and briefer while some of them will be longer.
Example we are going to use is Sample.html.
The doctype
<!DOCTYPE html UBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" ttp://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
can just be simple like this.
<!DOCTYPE html>
There is a long history behind doctype but it's related to the backward compatibility and compatibility with among browsers. Anyway, that's the HTML5's doctype.
The root element of an HTML page is <html>.
It looks like this:
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" lang="en" >
It is valid HTML5, however, part of it is not needed anymore in HTML5.
Here the xmlns attribute says that elements in this page are in the XHTML namespace, http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml. But elements in HTML5 are always in this namespace, so we no longer need to declare it explicitly. Our HTML5 page will work exactly the same in all browsers, whether this attribute is present or not.
That leaves us with this root element:
<html lang="en">
The first child of the <html> element is usually the <head> element. The <head> element contains metadata which has information about the page. The <head> element itself hasn't changed in any interesting way in HTML5. But inside of the <head> element is worth looking into.
Let's go back to our example's <head> part.
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>BeforeHTML5</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="SampleStyle.css" />
<link rel="alternate"
type="application/atom+xml"
title="Web Animation"
href="/feed/" />
<link rel="search"
type="application/opensearchdescription+xml"
title="Open Source Web Animation"
href="opensearch.xml" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="/favicon.ico" />
</head>
Then we need to define the document's character encoding since there could be a real security risk if we are not doing it.
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
This tells that the web server thinks it's sending us an HTML document using the UTF-8 character encoding.
In HTML5, the line should work as it is. But it can be changed to:
<meta charset="utf-8" />
But followings are equally valid HTML5:
<META CHARSET=UTF-8> <META CHARSET=UTF-8 /> <META CHARSET="UTF-8"> <META CHARSET="UTF-8" /> <meta charset=utf-8> <meta charset=utf-8 /> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <Meta CHARset=uTf-8>
Now, we have all the minimum requirements for HTML document.
Really? Let's check with the following html. Note that we do not have <head> and <body>. Amazingly, we do not have <html> tag, either!
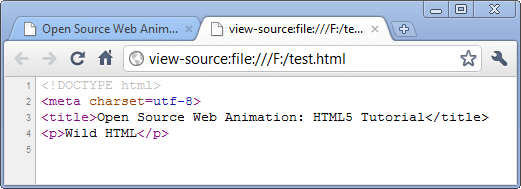
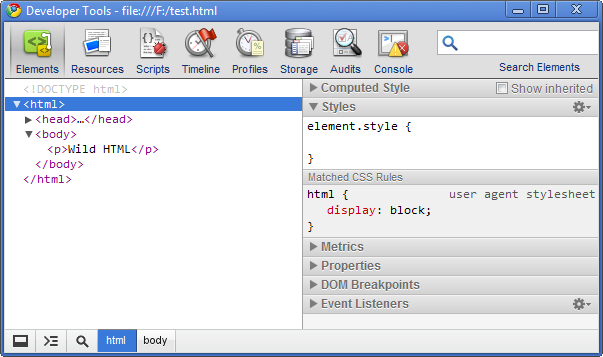
As we see from the Chrome Developer Tools, browsers generate the missing tags for us. HTML5 does not require those tags, however, we shouldn't omit the tags. Though there are couple of reasons, for the interest of maintainability we need to keep those optional elements.
So, here is the minimum maintainable HTML5 document.
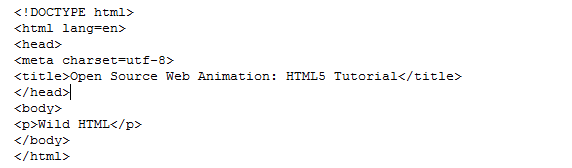
While <a href> is simply pointing to another page, link relation, <link rel> is giving additional information when we are linking to:
- a stylesheet containing CSS rules.
- a feed that contains the same content as this page, but in a standard subscribable format.
- the next chapter of an online book that this page is also a part of.
- a translation of this page into another language.
- the same content as this page, but in PDF format.
rel = "stylesheet"
Let's look at the first link relation in the Sample.html.
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="SampleStyle.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style-original.css" />
rel = "alternate"
<link rel="alternate"
type="application/atom+xml"
title="Web Animation"
href="/feed/" />
We call it feed autodiscovery when <link rel="alternate"> is combined with either the RSS or Atom media type in the type attribute. It allows syndicated feed readers to discover that a site has a news feed of the latest articles. Most browsers also support feed autodiscovery by displaying a special icon next to the URL.
The rel="alternate" link relation has always been a strange hybrid with vague definition. In HTML5, its definition has been clarified and extended to more accurately describe existing web content. Using rel="alternate" in conjunction with type=application/atom+xml indicates an Atom feed for the current page. But we can also use rel="alternate" in conjunction with other type attributes to indicate the same content in another format, like PDF.

Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization