MEAN Stack : Building REST API with Node and MongoDB
We'll setup a simple node server, and test REST APIs (GET, POST, DELETE). Then, we'll check the results via Browser and Postman Chrome extension.
The material is based on Build a RESTful API in 5 Minutes with NodeJS - Updated
This tutorial assumes we already have Node installed:
$ node -v v0.10.32 $ npm -v 2.14.1 $ mongo MongoDB shell version: 3.0.6 connecting to: test
Let's make our working directory, NodeREST:
$ mkdir NodeREST $ cd NodeREST
npm init will create a package.json:
$ npm init
Here is the package.json:
{
"name": "noderest",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Let's install Express:
$ npm install express --save
Note that we used --save flag to put it into package.json file.
Let's make server.js:
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
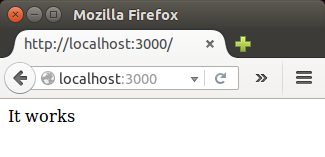
app.get('/', function(req, res) {
res.send('It works');
});
app.listen(3000);
console.log('Listening on port 3000');
Run it:
T$ node server.js Listening on port 3000
We may want to install mongoose which a=is a wrapper for MongoDB and node-restful for our REST API:
$ npm install --save mongoose node-restful
Also, we need body-parser:
$ npm install --save body-parser
nodemon monitors for any changes in our node.js application and automatically restart the server. Let's install it:
$ sudo npm install -g nodemon
Now run nodemon instead of node:
$ nodemon server.js
Then, if we change a code, it will be reflected immediately because nodemon automatically restart the server:
... [nodemon] restarting due to changes... [nodemon] starting `node server.js` ...
Let's modify server.js to setup API:
// Dependencies
var express = require('express');
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
var bodyParser = require('body-parser');
// MongoDB
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/rest_test');
// Express
var app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// Routes
app.use('/api', require('./routes/api'));
// Start server
app.listen(3000);
console.log('Listening on port 3000...');
Note that we add moongoose, body-parser, and routes.
Here is our /routes/api.js:
// Dependencies
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
// Routes
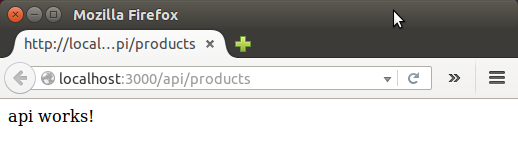
router.get('/products', function(req, res) {
res.send('api works!');
});
// Return router
module.exports = router;
Let's build our models to work with database.
// Dependencies
var restful = require('node-restful');
var mongoose = restful.mongoose;
// Schema
var productSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
sku: String,
price: Number
});
// Return model
module.exports = restful.model('Products', productSchema);
We need to change api.js accordingly:
// Dependencies
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
// Models
var Product = require('../models/product');
// Routes
Product.methods(['get', 'put', 'post', 'delete']);
Product.register(router, '/products');
// Return router
module.exports = router;
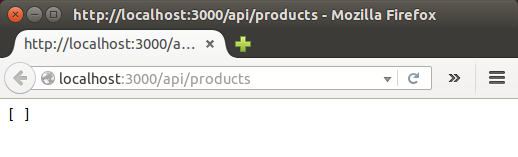
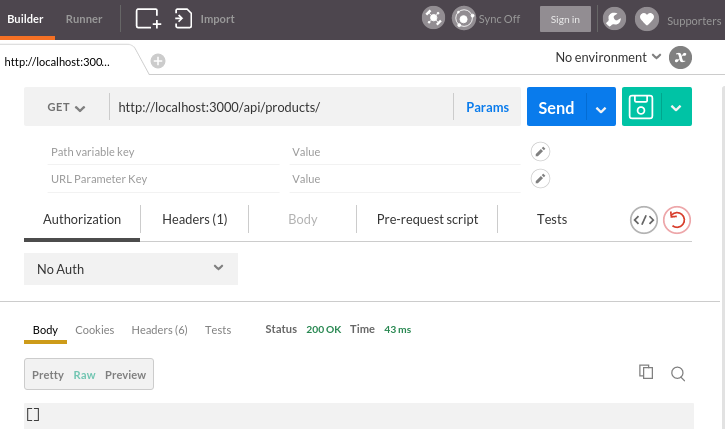
Since we do not have any data, we got empty array of product.
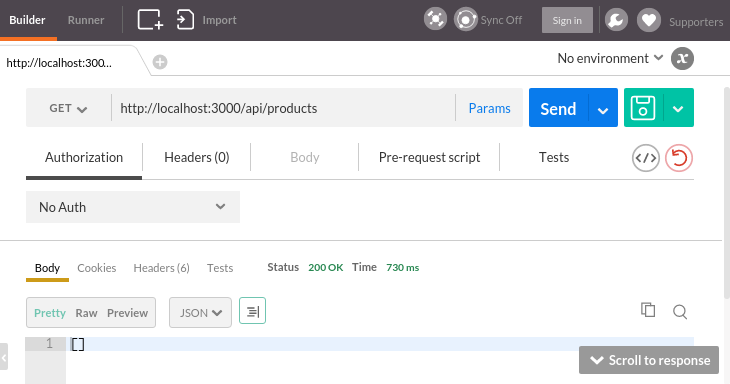
On postman Chrome extensions, we get the same result:
On postman Chrome extensions, we want to fill in data using POST:
{
"name" : "bogotobogo",
"sku" : "qaz1234",
"price" : 12.99
}
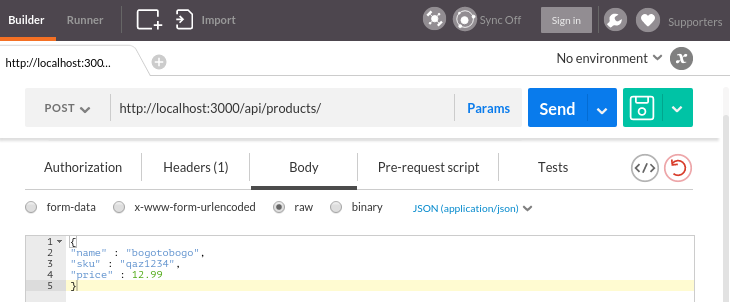
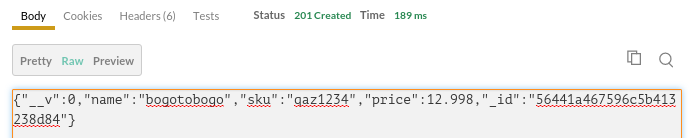
Click "Send", and we can check if it's been really posted on Postman response pane:
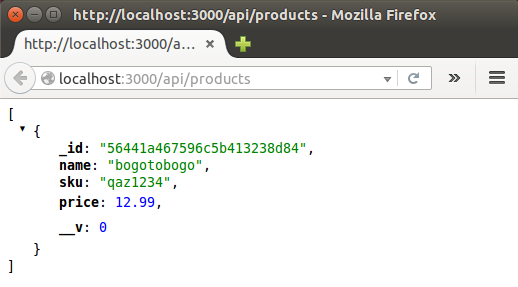
Or we can check via browser:
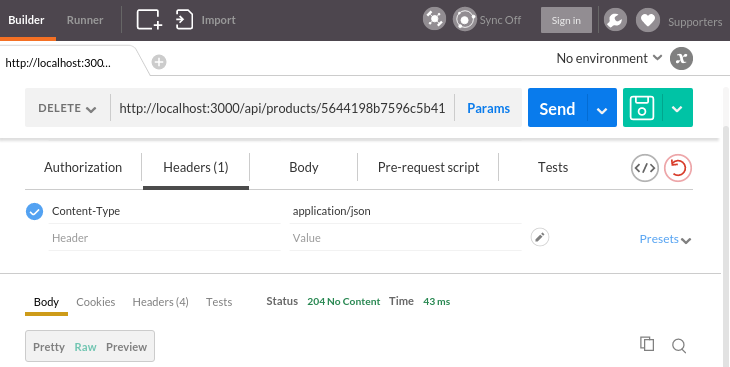
We can delete a record by appending id:

Click "Send", then we get empty list again:
Node.JS
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization