Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
Minikube defaults to 1024MB of memory and 1 CPU. Running Minikube with the default resource configuration results in insufficient resource errors during this tutorial. To avoid these errors, start Minikube with the following settings:
$ minikube start --memory 2048 --cpus=2 minikube v1.9.2 on Darwin 10.13.3 KUBECONFIG=/Users/kihyuckhong/.kube/config Using the hyperkit driver based on existing profile Starting control plane node m01 in cluster minikube Restarting existing hyperkit VM for "minikube" ... Preparing Kubernetes v1.18.0 on Docker 19.03.8 ... Enabling addons: dashboard, default-storageclass, storage-provisioner Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube"
- What is StatefuleSet?
- Why StatefuleSet is used?
- How it's different from Deployment?
StatefulSets make it easier to deploy stateful applications into our Kubernetes cluster.
StatefulSet is used to manage stateful applications:
- It manages the deployment and scaling of a set of Pods.
- It provides guarantees about the ordering and uniqueness of these Pods.
- However, unlike a Deployment, a StatefulSet maintains a sticky identity (i.e. id-0, id-1, id-2 and so on) for each of their Pods. Replica Pods of MySQL, for example, are not identical. These pods are created from the same spec, but are not interchangeable: each has a persistent identifier that it maintains across any rescheduling.
- The persistent identifiers are:
- predictable pod name : mypod-0, mypod-1, ... instead of hash (mypod-c0238feaje)
- fixed endpoint / individual dns name: (mypod-0-svc2)
- StatefulSets currently require a Headless Service to be responsible for the network identity of the Pods. We are responsible for creating this Service.
- StatefulSets do not provide any guarantees on the termination of pods when a StatefulSet is deleted. To achieve ordered and graceful termination of the pods in the StatefulSet, it is possible to scale the StatefulSet down to 0 prior to deletion.
- The storage for a given Pod must either be provisioned by a PersistentVolume Provisioner based on the requested storage class, or pre-provisioned by an admin.
StatefulSets are intended to be used with stateful applications and distributed systems. However, in order to demonstrate the basic features of a StatefulSet, we will deploy a simple web application using a StatefulSet.
The following web.yaml creates a Headless Service ("nginx"), to publish the IP addresses of Pods in the StatefulSet, web:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: nginx
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: k8s.gcr.io/nginx-slim:0.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
- A Headless Service, named nginx, is used to control the network domain.
- The Headless service is created by explicitly specifying None for the cluster IP (.spec.clusterIP). So, for headless Services, a cluster IP is not allocated.
- The StatefulSet, named web, has a Spec that indicates that 3 replicas of the nginx container will be launched in unique Pods.
- pod selector: we must set the .spec.selector field of a StatefulSet to match the labels of its .spec.template.metadata.labels.
- The volumeClaimTemplates will provide stable storage using PersistentVolumes provisioned by a PersistentVolume Provisioner. Kubernees creates one PersistentVolume for each volumeClaimTemplates. In our case, each Pod will receive a single PersistentVolume with a default StorageClass and 1 Gib of provisioned storage.
- When a Pod is (re)scheduled onto a node, its volumeMounts mount the PersistentVolumes associated with its PersistentVolume Claims. Note that, however, the PersistentVolumes associated with the Pods' PersistentVolume Claims are not deleted when the Pods, or StatefulSet are deleted. This must be done manually
- When the StatefulSet Controller creates a Pod, it adds a label, statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name, that is set to the name of the Pod. This label allows you to attach a Service to a specific Pod in the StatefulSet.
We will need to use two terminal windows.
In the first terminal, use kubectl get to watch ('-w') the creation of the StatefulSet's Pods with selector flag ('-l').
$ kubectl get pods -w -l app=nginx
In the second terminal, use kubectl apply to create the Headless Service and StatefulSet defined in the web.yaml:
$ kubectl apply -f web.yaml service/nginx created statefulset.apps/web created
We get the following output from the watch:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 Pending 0 3s web-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s web-0 1/1 Running 0 20s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 2s web-1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s web-1 1/1 Running 0 4s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 2s web-2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s web-2 1/1 Running 0 4s
Ordered Pod Creation: for a StatefulSet with 3 replicas, when Pods are being deployed,
they are created sequentially, in order from {0 1 2} as we can see from the output of the kubectl get command in the first terminal.
Note that the web-1 Pod is not launched until the web-0 Pod is Running and Ready. Same to the web-2 against the web-1.
The command above creates three Pods, each running an nginx webserver. To verify that they were created successfully, let's get the nginx Service and the web StatefulSet:
$ kubectl get service nginx NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nginx ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 4m $ kubectl get statefulset web NAME READY AGE web 3/3 5m37s
Pods in a StatefulSet have a unique ordinal index and a stable network identity.
Let's examine the Pod's Ordinal Index from the StatefulSet's Pods:
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 1/1 Running 0 22m web-1 1/1 Running 0 22m web-2 1/1 Running 0 22m
The Pods in a StatefulSet have a sticky, unique identity. This identity is based on a unique ordinal index that is assigned to each Pod by the StatefulSet controller. The Pods' names take the form <statefulset name>-<ordinal index>. Since the web StatefulSet has three replicas, it creates three Pods, web-0, web-1, and web-2.
Each Pod has a stable hostname based on its ordinal index.
We can use kubectl exec to execute the hostname command in each Pod:
$ for i in {0..2}; do kubectl exec web-$i -- sh -c hostname; done
web-0
web-1
web-2
We may want to use kubectl run to execute a container (busybox) that provides the nslookup command from the dnsutils package. Using nslookup on the Pods' hostnames, we can examine their in-cluster DNS addresses as shown below:
$ kubectl run -it --image busybox:1.28 my-dns-test-pod --restart=Never --rm If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. / # for i in 0 1 2;do nslookup web-$i.nginx;echo;echo '---';done Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-0.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.10 web-0.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-1.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.11 web-1.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-2.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.12 web-2.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- / #
While we are making progress, we may want to check the following table, in our case, the first row.
| Cluster Domain | Service(ns/name) | StatefulSet | StatefulSet Domain | Pod DNS | Pod Hostname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cluster.local | default/nginx | default/web | nginx.default.svc.cluster.local | web-0.default.svc.cluster.local ... | web-0 ... |
| cluster.local | foo/nginx | foo/web | nginx.foo.svc.cluster.local | web-0.foo.svc.cluster.local ... | web-0 ... |
| kube.local | foo/nginx | foo/web | nginx.foo.svc.kube.local | web-0.foo.svc.kube.local ... | web-0 ... |
- CNAME of the Headless Service : nginx.default.svc.cluster.local (note: "nginx" is the service name - my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local)
- SRV records of the Pods : web-0.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local, web-1.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local, and web-2.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local
$ kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-0 1/1 Running 0 62m 172.17.0.10 minikube <none> <none> web-1 1/1 Running 0 61m 172.17.0.11 minikube <none> <none> web-2 1/1 Running 0 61m 172.17.0.12 minikube <none> <none>
The CNAME of the headless service points to SRV records (one for each Pod that is Running and Ready). The SRV records point to A record entries that contain the Pods' IP addresses.
When the Pods restarted, the Pods' ordinals, hostnames, SRV records, and A record names have not changed, but the IP addresses associated with the Pods may change. Let's use kubectl delete to delete all the Pods in the StatefulSet, and wait for the StatefulSet to restart them, and for both Pods to transition to Running and Ready:
$ kubectl delete pod -l app=nginx pod "web-0" deleted pod "web-1" deleted pod "web-2" deleted $ kubectl get pod -l app=nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 1/1 Running 0 22s web-1 1/1 Running 0 20s web-2 1/1 Running 0 18s
Use kubectl exec and kubectl run to view the Pods hostnames and in-cluster DNS entries:
$ for i in 0 1 2; do kubectl exec web-$i -- sh -c 'hostname'; done web-0 web-1 web-2 $ kubectl run -it --image busybox:1.28 my-dns-test-pod --restart=Never --rm If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. / # for i in 0 1 2;do nslookup web-$i.nginx;echo;echo '---';done Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-0.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.2 web-0.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-1.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.4 web-1.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: web-2.nginx Address 1: 172.17.0.8 web-2.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local --- / #
Notice that the IPs of the Pods have changed. This is why it is important not to configure other applications to connect to Pods in a StatefulSet by IP address.
If we need to find and connect to the active members of a StatefulSet, we should query the CNAME of the Headless Service (nginx.default.svc.cluster.local).
From the busybox:
/ # nslookup nginx.default.svc.cluster.local Server: 10.96.0.10 Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local Name: nginx.default.svc.cluster.local Address 1: 172.17.0.8 web-2.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local Address 2: 172.17.0.4 web-1.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local Address 3: 172.17.0.2 web-0.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local
The SRV records associated with the CNAME will contain only the Pods in the StatefulSet that are Running and Ready.
If our application already implements connection logic that tests for liveness and readiness, we can use the SRV records of the Pods ( web-0.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local, web-1.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local, and web-2.nginx.default.svc.cluster.local), as they are stable, and our application will be able to discover the Pods' addresses when they transition to Running and Ready.
Let's get the PersistentVolumeClaims for web-0, web-1, and web-2:
$ kubectl get pvc -l app=nginx NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE www-web-0 Bound pvc-1568146b-82ee-4658-969b-e4afbd660701 1Gi RWO standard 107m www-web-1 Bound pvc-d0505e50-ac97-4263-92ac-29d3ce97f2c1 1Gi RWO standard 107m www-web-2 Bound pvc-5a021388-5272-416b-825f-0883d2d4ff06 1Gi RWO standard 107m
The StatefulSet controller created three PersistentVolumeClaims that are bound to three PersistentVolumes. As the cluster used in this post is configured to dynamically provision PersistentVolumes, the PersistentVolumes were created and bound automatically.
The NGINX webservers, by default, will serve an index file at /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html. The volumeMounts field in the StatefulSets spec ensures that the /usr/share/nginx/htmll directory is backed by a PersistentVolume.
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "nginx"
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: k8s.gcr.io/nginx-slim:0.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
Write the Pods' hostnames to their index.html files :
$ for i in 0 1 2; do kubectl exec web-$i -- sh -c 'echo $(hostname) > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html'; done
Then, verify that the NGINX webservers are serving the hostnames:
$ for i in 0 1 2; do kubectl exec -it web-$i -- curl localhost; done web-0 web-1 web-2
Let's test if the pods are serving the right hostname even after rescheduled.
As we've done before we need to delete the pods and wait for the StatefulSet resume them. Then, we check if they are still serving the same host:
$ kubectl delete pod -l app=nginx pod "web-0" deleted pod "web-1" deleted pod "web-2" deleted $ kubectl get pod -l app=nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 1/1 Running 0 22s web-1 1/1 Running 0 19s web-2 1/1 Running 0 12s
Once again, we can see the "web-0" came up first.
This time, we don't have to write the host to the index.html because it is supposed be in the PersistentVolumes. All we need to do is to run "curl":
$ for i in 0 1 2; do kubectl exec -it web-$i -- curl localhost; done web-0 web-1 web-2
As we can see from the output, even though web-0, web-1 and web-2 were rescheduled, they continue to serve their hostnames because the PersistentVolumes associated with their PersistentVolumeClaims are remounted to their volumeMounts. No matter what node web-0and web-1 are scheduled on, their PersistentVolumes will be mounted to the appropriate mount points.
Scaling a StatefulSet refers to increasing or decreasing the number of replicas. This is accomplished by updating the replicas field. We can use kubectl scale:
$ kubectl scale sts web --replicas=5 statefulset.apps/web scaled $ kubectl get pod -l app=nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 1/1 Running 0 7m25s web-1 1/1 Running 0 7m22s web-2 1/1 Running 0 7m15s web-3 1/1 Running 0 17s web-4 1/1 Running 0 11s
The StatefulSet controller scaled the number of replicas. As with StatefulSet creation, the StatefulSet controller created each Pod sequentially with respect to its ordinal index, and it waited for each Pod's predecessor to be "Running" and "Ready" before launching the subsequent Pod.
$ kubectl scale sts web --replicas=2 statefulset.apps/web scaled $ kubectl get pod -l app=nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 1/1 Running 0 9m24s web-1 1/1 Running 0 9m21s
The controller deleted one Pod at a time, in reverse order with respect to its ordinal index, and it waited for each to be completely shutdown before deleting the next.
Get the StatefulSet's PersistentVolumeClaims:
$ kubectl get pvc -l app=nginx NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE www-web-0 Bound pvc-1568146b-82ee-4658-969b-e4afbd660701 1Gi RWO standard 3h49m www-web-1 Bound pvc-d0505e50-ac97-4263-92ac-29d3ce97f2c1 1Gi RWO standard 3h49m www-web-2 Bound pvc-5a021388-5272-416b-825f-0883d2d4ff06 1Gi RWO standard 3h49m www-web-3 Bound pvc-0b6247ee-80a8-4808-9bf9-23455734be15 1Gi RWO standard 3m www-web-4 Bound pvc-9c6c1d1a-88c6-48dd-bcc3-33862db7650e 1Gi RWO standard 2m55s
There are still five PersistentVolumeClaims (pvc-*, ...) and five PersistentVolumes (www-web-*, ...) - the PersistentVolumes mounted to the Pods of a StatefulSet are not deleted when the StatefulSet's Pods are deleted. This is still true when Pod deletion is caused by scaling the StatefulSet down.
The StatefulSet controller supports automated updates.
The strategy used is determined by the spec.updateStrategy field of the StatefulSet API Object.
This feature can be used to upgrade the container images, resource requests and/or limits, labels, and annotations of the Pods in a StatefulSet.
There are two valid update strategies, RollingUpdate which is the default and another updateStrategy is OnDelete.
Let's patch the web StatefulSet to change the container image:
$ kubectl patch statefulset web --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/image", "value":"gcr.io/google_containers/nginx-slim:0.8"}]'
statefulset.apps/web patched
The RollingUpdate update strategy will update all Pods in a StatefulSet, in reverse ordinal order, while respecting the StatefulSet guarantees.
Let's patch the web StatefulSet to apply the RollingUpdate update strategy:
$ kubectl patch statefulset web -p '{"spec":{"updateStrategy":{"type":"RollingUpdate"}}}'
statefulset.apps/web patched (no change)
$ kubectl get po -l app=nginx -w web-2 1/1 Terminating 0 18m web-2 0/1 Terminating 0 18m web-2 0/1 Terminating 0 18m web-2 0/1 Terminating 0 18m web-2 0/1 Terminating 0 18m web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-2 1/1 Running 0 2s web-1 1/1 Terminating 0 20m web-1 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-1 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-1 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-1 1/1 Running 0 2s web-0 1/1 Terminating 0 20m web-0 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-0 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-0 0/1 Terminating 0 20m web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-0 1/1 Running 0 2s
The Pods in the StatefulSet are updated in reverse ordinal order. The StatefulSet controller terminates each Pod, and waits for it to transition to Running and Ready prior to updating the next Pod.
Note that, even though the StatefulSet controller will not proceed to update the next Pod until its ordinal successor is Running and Ready, it will restore any Pod that fails during the update to its current version. Pods that have already received the update will be restored to the updated version, and Pods that have not yet received the update will be restored to the previous version. In this way, the controller attempts to continue to keep the application healthy and the update consistent in the presence of intermittent failures.
Get the Pods to view their container images:
$ for p in 0 1 2; do kubectl get po web-$p --template '{{range $i, $c := .spec.containers}}{{$c.image}}{{end}}'; echo; done
gcr.io/google_containers/nginx-slim:0.8
gcr.io/google_containers/nginx-slim:0.8
gcr.io/google_containers/nginx-slim:0.8
StatefulSet supports both Non-Cascading and Cascading deletion. In a Non-Cascading Delete, the StatefulSet's Pods are not deleted when the StatefulSet is deleted. In a Cascading Delete, both the StatefulSet and its Pods are deleted.
$ kubectl delete statefulset web statefulset.apps "web" deleted
By default, when we delete a StatefuleSet, it deletes the pods as well ("--cascade=true"). To keep the pods, we can append "--cascade=false":
$ kubectl delete sts web --cascade=false
For some distributed systems, the StatefulSet ordering guarantees are unnecessary and/or undesirable. These systems require only uniqueness and identity.
To address this, we'll use .spec.podManagementPolicy as shown below (web-parallel.yaml):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "nginx"
podManagementPolicy: "Parallel"
replicas: 5
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: k8s.gcr.io/nginx-slim:0.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
In one terminal, watch the Pods in the StatefulSet with kubectl get po -l app=nginx -w while running kubectl apply -f web-parallel.yaml on another terminal:
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-3 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-3 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-4 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-4 0/1 Pending 0 0s web-1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s web-3 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s web-4 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s web-1 1/1 Running 0 3s web-2 1/1 Running 0 3s web-3 1/1 Running 0 5s web-4 1/1 Running 0 5s web-0 1/1 Running 0 6s
Parallel pod management tells the StatefulSet controller to launch or terminate all Pods in parallel, and not to wait for Pods to become Running and Ready or completely terminated prior to launching or terminating another Pod.
Same thing happens when we scale the StatefuleSet with kubectl scale statefulset/web --replicas=3 or delete the set with kubectl delete sts web.
Note that the default pod management is set to OrderedReady which tells the StatefulSet controller to respect the ordering.
To continue to play with StatefulSet, please check https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/stateful-application/basic-stateful-set/
And these:
- Explains why we need the stateful set, MySQL example: Kubernetes Tutorial: Why do you need StatefulSets in Kubernetes?
- Explains difference between regular pod deploy (stateless) and the stateful set deploy, MySQL example:
Kubernetes StatefulSet simply explained | Deployment vs StatefulSet
The two main characteristics of a statefuleset compared with a regular deployment:
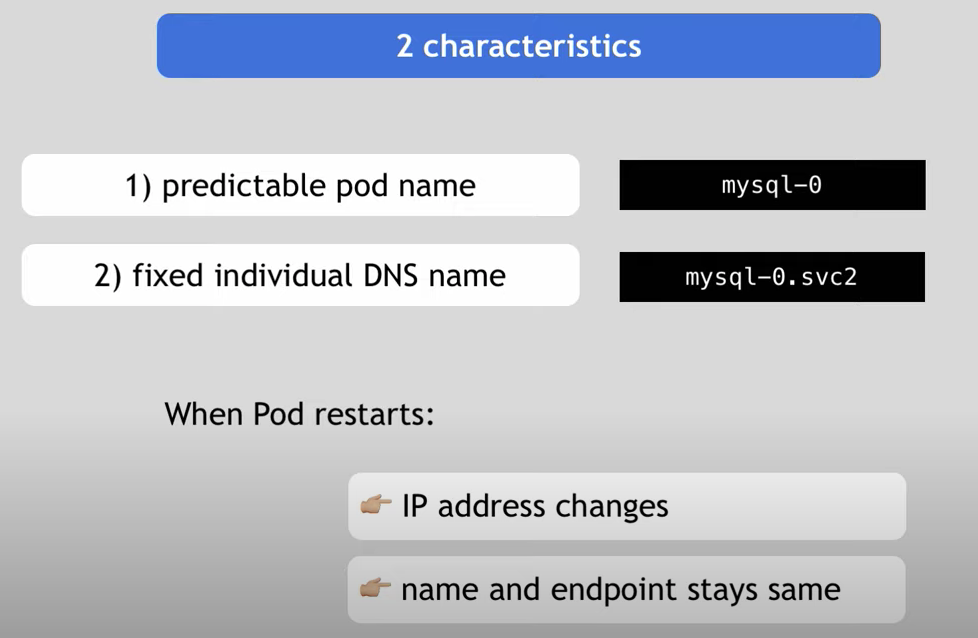
"Stateful applications are not perfect for containerized environment"
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization