GCP: Deploying a containerized web application via Kubernetes
We'll learn how to package a web application in a Docker container image, and run that container image on a Kubernetes Engine cluster as a load-balanced set of replicas that can scale to the needs of your users.
To package and deploy our application on Kubernetes Engine, we need to do the followings:
- Package the app into a Docker image
- Run the container locally on the machine (optional)
- Upload the image to a registry
- Create a container cluster
- Deploy the app to the cluster
- Expose the app to the Internet
- Scale up the deployment
- Deploy a new version of the app
Take the following steps to enable the Kubernetes Engine API as we've done in GCP: Kubernetes Quickstart:
- Visit the Kubernetes Engine page in the Google Cloud Platform Console.
- Create or select a project.
- Wait for the API and related services to be enabled. This can take several minutes.

We'll use Google Cloud Shell, which comes
preinstalled with the gcloud, docker, and kubectl command-line tools used
in this tutorial. If we use Cloud Shell, we don’t need to install these command-line tools on our local machine.
To use Google Cloud Shell:
- Go to the Google Cloud Platform Console.
-
Click the Activate Cloud Shell button at the top of the console window.
A Cloud Shell session opens inside a new frame at the bottom of the console and displays a command-line prompt.
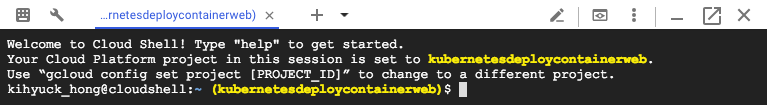
We may want to set the defaults so that we can save time when we use command-line tool:
gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID gcloud config set compute/zone ZONE
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud config set project kubernetesdeploycontainerweb Updated property [core/project]. kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud config set compute/zone us-east4-a Updated property [compute/zone].
Kubernetes Engine accepts Docker images as the application deployment format. To build a Docker image, we need to have an application and a Dockerfile.
For this tutorial, we will deploy a sample web
application called hello-app, a web server written
in Go that responds to all requests with the message
"Hello, World!" on port 80.
The application is packaged as a Docker image, using the Dockerfile that contains instructions on how the image is built. We will use this file to package the application below.
To download the hello-app source code, run the following commands:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/kubernetes-engine-samples
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ cd kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$
Set the PROJECT_ID environment variable in our shell by retrieving the pre-
configured project ID on gcloud by running the command below:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ export PROJECT_ID="$(gcloud config get-value project -q)"
Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-19280]
The value of PROJECT_ID will be used to tag the container image for pushing it
to our private Container Registry.
To build the container image of this application and tag it for uploading, run the following command:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ docker build -t gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v1 .
...
Successfully built 15f56228a80e
Successfully tagged gcr.io/kubernetesdeploycontainerweb/hello-app:v1
This command instructs Docker to build the image using the Dockerfile in the
current directory:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ ls Dockerfile main.go manifests README.md
and tag it with a name, such as gcr.io/my-project/hello-app:v1.
The gcr.io prefix refers to Google Container Registry, where
the image will be hosted. Running this command does not upload the image yet.
We can run docker images command to verify that the build was successful:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE gcr.io/kubernetesdeploycontainerweb/hello-app v1 15f56228a80e 3 minutes ago 10.3MB
Now, we need to upload the container image to a registry so that Kubernetes Engine can download and run it.
First, configure Docker command-line tool to authenticate to Container Registry (we need to run this only once):
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud auth configure-docker
WARNING: Your config file at [/home/kihyuck_hong/.docker/config.json] contains these credential helper entries:
...
Docker configuration file updated.
We can now use the Docker command-line tool to upload the image to our Container Registry:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ docker push gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v1
The push refers to repository [gcr.io/kubernetesdeploycontainerweb/hello-app]
ed7a2efbc124: Pushed
...
To test our container image using our local Docker engine, run the following command:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v1
2018/09/12 21:19:31 Server listening on port 8080
If we're on Cloud Shell, we can can click "Web preview" button on the top right to see our application running in a browser tab.

Otherwise, open a new terminal window (or a Cloud Shell tab) and run to verify if the container works and responds to requests with "Hello, World!":
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ curl http://localhost:8080
Hello, world!
Version: 1.0.0
Hostname: 72b1a02f1d15
Once we've seen a successful response, we can shut down the container by
pressing Ctrl+C in the tab where docker run command is running.
Now that the container image is stored in a registry, we need to create a container cluster to run the container image.
First, we may try to use console to create the cluster.

A cluster consists of a pool of Compute Engine VM instances running Kubernetes, the open source cluster orchestration system that powers Kubernetes Engine.
Once we have created a Kubernetes Engine cluster, we use Kubernetes to deploy applications to the cluster and manage the applications' lifecycle.

We've already create the cluster via console, however, we will run the following command to create a two-node cluster named bogo-hello-cluster via command-line:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud container clusters create bogo-hello-cluster --num-nodes=
2 --zone=us-east4-a
...
kubeconfig entry generated for bogo-hello-cluster.
NAME LOCATION MASTER_VERSION MASTER_IP MACHINE_TYPE NODE_VERSION NUM_NODES STATUS
bogo-hello-cluster us-east4-a 1.9.7-gke.6 35.236.195.6 n1-standard-1 1.9.7-gke.6 2 RUNNING
It may take several minutes for the cluster to be created.

Once the command has completed, run the following command and see the cluster's three worker VM instances:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud compute instances list
NAME ZONE MACHINE_TYPE PREEMPTIBLE INTERNAL_IP EXTERNAL_IP STATUS
gke-bogo-hello-cluster-default-pool-0e1d32c3-4cwl us-east4-a n1-standard-1 10.150.0.6 35.221.25.147 RUNNING
gke-bogo-hello-cluster-default-pool-0e1d32c3-mxqw us-east4-a n1-standard-1 10.150.0.5 35.221.18.79 RUNNING
To deploy and manage applications on a Kubernetes Engine cluster, we must
communicate with the Kubernetes cluster management system. We typically do this
by using the kubectl command-line tool.
Kubernetes represents applications as Pods, which are units that represent a container (or group of tightly-coupled containers). The Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes.
In this tutorial, each Pod
contains only our hello-app container.
The kubectl run command below causes Kubernetes to create a
Deployment named hello-web on our cluster.
The Deployment manages multiple copies of our application, called replicas, and
schedules them to run on the individual nodes in our cluster. In this case, the
Deployment will be running only one Pod of our application.
Run the following command to deploy our application, listening on port 8080:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl run hello-web --image=gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v1
--port 8080
deployment "hello-web" created
To see the Pod created by the Deployment, run the following command:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-web-85455bbc49-xkbqp 1/1 Running 0 44m
By default, the containers we run on Kubernetes Engine are not accessible from the Internet, because they do not have external IP addresses. We must explicitly expose our application to traffic from the Internet, run the following command:
$ kubectl expose deployment hello-web --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080
service "hello-web" exposed
The kubectl expose command above creates a Service
resource, which provides networking and IP support to our application's Pods.
Kubernetes Engine creates an external IP and a Load Balancer (subject to
billing) for our application.
The --port flag specifies the port number configured on the Load Balancer, and
the --target-port flag specifies the port number that is used by the Pod
created by the kubectl run command from the previous step.
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hello-web LoadBalancer 10.59.247.225 35.188.240.248 80:30420/TCP 8m
Once we've determined the external IP address for our application, copy the IP
address. Point our browser to this URL (such as http://35.188.240.248) to check
if our application is accessible.

We add more replicas to our application's Deployment resource by using the
kubectl scale command. To add two additional replicas to our Deployment (for
a total of three), run the following command:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl scale deployment hello-web --replicas=3
deployment "hello-web" scaled
We can see the new replicas running on our cluster by running the following commands:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl get deployment hello-web
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hello-web 3 3 3 3 2h
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~ (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-web-85455bbc49-4xggn 1/1 Running 0 2m
hello-web-85455bbc49-hdcxr 1/1 Running 0 2m
hello-web-85455bbc49-xkbqp 1/1 Running 0 2h
Now, we have multiple instances of our application running independently of
each other and we can use the kubectl scale command to adjust capacity of
our application.
The load balancer we provisioned in the previous step will start routing traffic to these new replicas automatically.
Kubernetes Engine's rolling update mechanism ensures that our application remains up and available even as the system replaces instances of our old container image with our new one across all the running replicas.
We can create an image for the v2 version of our application by building the
same source code and tagging it as v2 (or we can change the "Hello, World!"
string to "Hello, Kubernetes Engine!" before building the image):
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ pwd
/home/kihyuck_hong/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ ls
Dockerfile main.go manifests README.md
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ docker build -t gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v2 .
...
Successfully built f50f178f02e2
Successfully tagged gcr.io/kubernetesdeploycontainerweb/hello-app:v2
Then push the image to the Google Container Registry:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud docker -- push gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-app:v2
Now, apply a rolling update to the existing deployment with an image update:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl set image deployment/hello-web hello-web=gcr.io/${PROJEC
T_ID}/hello-app:v2
deployment "hello-web" image updated
Visit our application again at http://[EXTERNAL_IP],
and observe the changes we made take effect.
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl get service NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE hello-web LoadBalancer 10.59.247.225 35.188.240.248 80:30420/TCP 1h

To avoid incurring charges to our Google Cloud Platform account for the resources used in this tutorial.
After completing this tutorial, follow these steps to remove the following resources to prevent unwanted charges incurring on our account:
-
Delete the Service: This step will deallocate the Cloud Load Balancer created for our Service:
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ kubectl delete service hello-web service "hello-web" deleted -
Wait for the Load Balancer provisioned for the hello-web Service to be deleted: The load balancer is deleted asynchronously in the background when you run
kubectl delete. Wait until the load balancer is deleted by watching the output of the following command:kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud compute forwarding-rules list Listed 0 items. -
Delete the container cluster: This step will delete the resources that make up the container cluster, such as the compute instances, disks and network resources.
kihyuck_hong@cloudshell:~/kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app (kubernetesdeploycontainerweb)$ gcloud container clusters delete bogo-hello-cluster The following clusters will be deleted. - [bogo-hello-cluster] in [us-east4-a] Do you want to continue (Y/n)? Y Deleting cluster bogo-hello-cluster...done. Deleted [https://container.googleapis.com/v1/projects/kubernetesdeploycontainerweb/zones/us-east4-a/clusters/bogo-hello-cluster].
GCP (Google Cloud Platform)
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization