AWS EC2 Container Service (ECS) & EC2 Container Registry (ECR) | Docker Registry
- Container instances:
- EC2 instances
- Docker daemon
- ECS agents (open source in Github : aws/amazon-ecs-agent)
- Cluster is a logical grouping of container instances that we can place tasks on:
- Collection of resources - resource pool (primarily containers and insances running those insances)
- Scalable
- Grouping of container instances
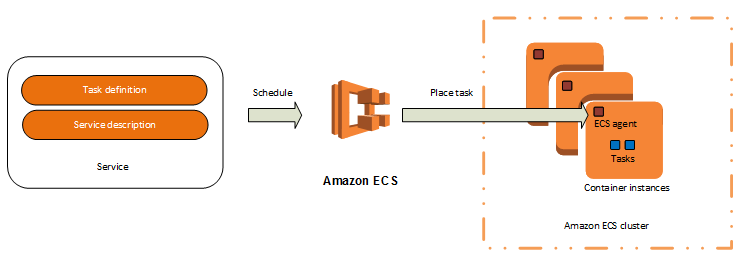
- Task definition is a description of an application that contains one or more container definitions:
- Container definitions (cpu, memory, links to set up channels between containers, ports)
- Volume definitions to persist data between containers
- Task definitions are tracked by names and versions
- Task is an instantiation of a task definition that is running on a container instance:
- Unit of work
- We can run as many containers as we our app needs
- Runs on container instances
- Service is a scheduler that ensures that the specified number of tasks are constantly running and rescheduled on failure, and optionally registered against an Elastic Load Balancing load balancer:
- We just refer task definition and number of tasks we want to run
- ECS handles the deployment and integration with ELB
Here are the benefits of using ECR:
- Security:
- IAM resource based policies
- Cloud Trail audit logs
- Images encrypted at transit and at rest
- Ease of managing and deploying images:
- Tight integration with ECSs
- Integration with Docker toolset
- AWS Management Console and AWS CLI
- Reliability and performance: S3 backed
In this post, we'll deploy a Flask app to AWS ECS.
- Configure repository:
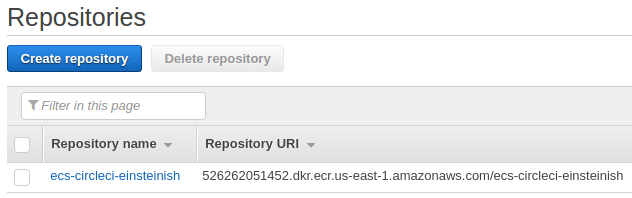
A repository is a place that we store Docker images in Amazon ECR. Every time we push or pull an image from Amazon ECR, we specify the registry and repository location to tell Docker where to push the image to or where to pull it from.

- Build, tag, and push Docker image
If AWS CLI is not installed yet, let's install it. We need AWS CLI because we want to push our Docker image to Repository (ECR). We push the image once we get the login credentials from CLI:- Download the AWS CLI Bundled Installer:
$ curl "https://s3.amazonaws.com/aws-cli/awscli-bundle.zip" -o "awscli-bundle.zip"
- Unzip the package:
$ unzip awscli-bundle.zip
- Run the install executable:
$ sudo ./awscli-bundle/install -i /usr/local/aws -b /usr/local/bin/aws
Now that our repository exists, we can push a Docker image by following these steps:
- Retrieve the docker login command that we can use to authenticate our Docker client to our registry:
$ aws ecr get-login --region us-east-1 docker login -u AWS -p AQECA...AT2 -e none https://526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
- Or we can combine the two previous commands into one command:
$ eval $(aws ecr get-login --region us-east-1) Login Succeeded
-
We need to add a file ./app/requirements.txt:
Flask==0.11.1
And the image has the following (main.py):from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/") def hello(): return "Hello World from Flask in a uWSGI Nginx Docker container with \ Python 2.7 (default)" if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host='0.0.0.0', debug=True, port=80) - Build our Docker image using the following command. For information on building a Docker file from scratch see the instructions here. We can skip this step if our image is already built:
$ docker build -t ecs-circleci-einsteinish . Step 1 : FROM tiangolo/uwsgi-nginx-flask:flask ---> 788ca94b2313 Step 2 : COPY ./app /app ---> Using cache ---> 0666386303c5 Successfully built 0666386303c5
- Let's check if our docker image is correctly built, on local machine:
$ docker run -t ecs-circleci-einsteinish
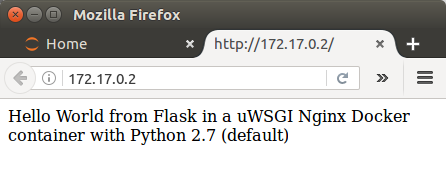
To get the ip of docker on our hostmachine:
$ docker inspect --format '{{ .NetworkSettings.IPAddress }}' $(docker ps -q) 172.17.0.2
We can see it works:
- After the build completes, tag the image so we can push the image to the newly created repository (ECR):
$ docker tag ecs-circleci-einsteinish:latest 526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ecs-circleci-einsteinish:latest
- Run the following command to push this image to the repository:
$ docker push 526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ecs-circleci-einsteinish:latest
- Download the AWS CLI Bundled Installer:
- Create a task definition via JSON
Basically the task definition tells how we want to run the container. The JSON file looks like this:
{ "containerDefinitions": [ { "name": "flask-app-container", "image": "526262051452.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ecs-circleci-einsteinish:latest", "memory": "128", "cpu": "10", "essential": true, "portMappings": [ { "hostPort": "80", "containerPort": "80", "protocol": "tcp" } ], "environment": null, "mountPoints": null, "volumesFrom": null, "hostname": null, "user": null, "workingDirectory": null, "extraHosts": null, "logConfiguration": null, "ulimits": null, "dockerLabels": null } ], "volumes": [], "networkMode": "bridge", "placementConstraints": [], "family": "flask-app-task" }
Task definitions specify various parameters for our application, such as which containers to use and the repositories in which they are located, which ports should be opened on the container instance for our application, and what data volumes should be used with the containers in the task.
We have registered our ECS Task Definition!
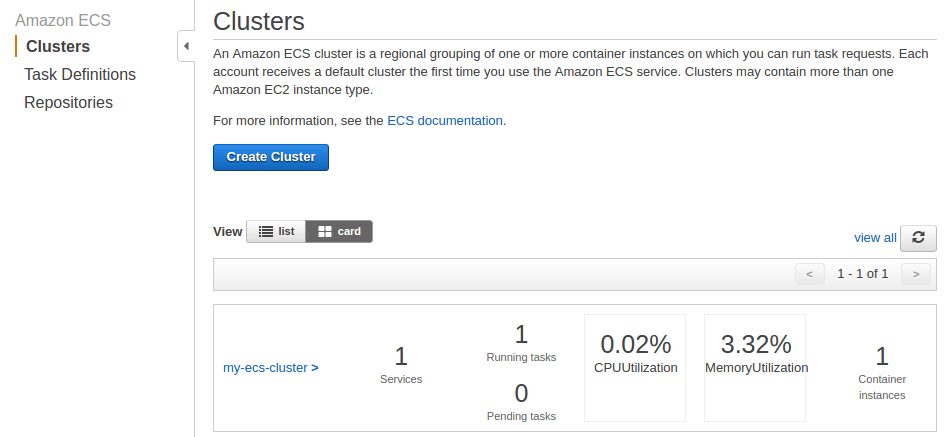
Let's create the ECS cluster. Select Clusters in the left-hand navigation pane:

When we run tasks using Amazon ECS, we place them on a cluster, which is a logical grouping of EC2 instances. Amazon ECS downloads our container images from a registry that we specify, and runs those images on the container instances within our cluster.
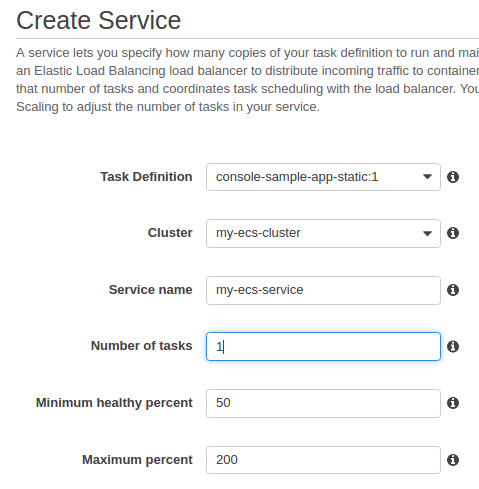
- Create a service
The service describes how we want our task definitions to run.
Amazon ECS allows us to run and maintain a specified number (the "desired count") of instances of a task definition simultaneously in an ECS cluster. This is called a service. If any of our tasks should fail or stop for any reason, the Amazon ECS service scheduler launches another instance of our task definition to replace it and maintain the desired count of tasks in the service.


- Review
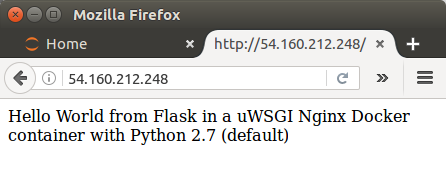
- Output from ECS container:
Go to EC2 instance pane and get the public-ip of the container instance:

Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization