Redis vs Memcached
Redis In-Memory Datastore
Redis is a data structure server. It is open-source, networked, in-memory, and stores keys with optional durability. The development of Redis has been sponsored by Pivotal Software since May 2013; before that, it was sponsored by VMware. According to the monthly ranking by DB-Engines.com, Redis is the most popular key-value store. The name Redis means REmote DIctionary Server. - wiki
Redis Usages:
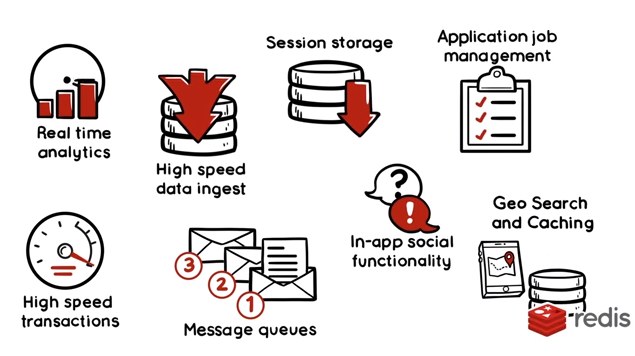
Redis - preset data types:
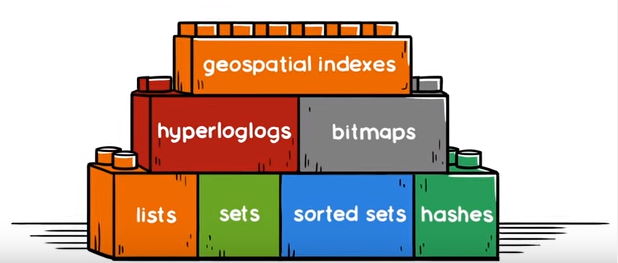
Picture credit - RedisLabs
The following description is from http://redis.io/topics/introduction
Redis is an open source, BSD licensed, advanced key-value cache and store. It is often referred to as a data structure server since keys can contain strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps and hyperloglogs.
You can run atomic operations on these types, like appending to a string; incrementing the value in a hash; pushing an element to a list; computing set intersection, union and difference; or getting the member with highest ranking in a sorted set.
In order to achieve its outstanding performance, Redis works with an in-memory dataset. Depending on your use case, you can persist it either by dumping the dataset to disk every once in a while, or by appending each command to a log. Persistence can be optionally disabled, if you just need a feature-rich, networked, in-memory cache.
Redis also supports trivial-to-setup master-slave asynchronous replication, with very fast non-blocking first synchronization, auto-reconnection with partial resynchronization on net split.
Memcached (Mem-Cache-D) or Redis? It's a question that nearly always comes up in any discussion about performance out of a database-driven Web application. When performance needs to be improved, caching is often the first step we take, and Memcached and Redis are typically the two major candidates for enhancing the performance.
While the two cache engines share a number of similarities, they also have important differences. Redis, the newer and more versatile of the two, is almost always the better choice though there are some benchmark testings showing Redis is worse to Memcached with multi gets at high volumes.
- Both Memcached and Redis are in-memory.
- key-value data stores.
- They both belong to the NoSQL family.
- Both are based on the same key-value data model.
- They both keep all data in RAM, which makes them useful as a caching layer.
- In terms of performance, the two data stores are also remarkably similar, exhibiting almost identical characteristics (and metrics) with respect to throughput and latency.
The first is for caching small and static data, such as HTML code fragments. Memcached's internal memory management, while not as sophisticated as Redis, Memcached is more efficient because Memcached will consume comparatively less memory resources for metadata.
However, we'll almost always want to use Redis. By using Redis as a cache, we gain a lot of power such as the ability to fine-tune cache contents and durability.
Radis is better in almost every aspect of cache management. Redis also employs more sophisticated approaches to memory management and eviction candidate selection.
Caches employ a mechanism called data eviction to delete old data from memory in order to make room for new data. Memcached's data eviction mechanism uses an LRU (Least Recently Used) algorithm and somewhat arbitrarily evicts data that's similar in size to the new data. Redis, by contrast, allows for fine-grained control over eviction though a choice of six different eviction policies. Redis also employs more sophisticated approaches to memory management and eviction candidate selection.
So, we may want to choose the Redis because of its broader functional and convenient features.
Redis In-Memory Datastore
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization