Docker & Kubernetes - Helm Chart v2/v3
- What is Helm?
- What are Helm Charts?
- How to use them?
- What is Tiller?
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. It packages Kubernetes yaml files into a chart. The chart is usually pushed into Helm repositories.
For Kubernetes, it is equivalent to yum, apt, or homebrew. There are great and Kubernetes ready apps in public repository waiting for us to use.
Helm charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources. A Helm chart describes how to manage a specific application on Kubernetes.
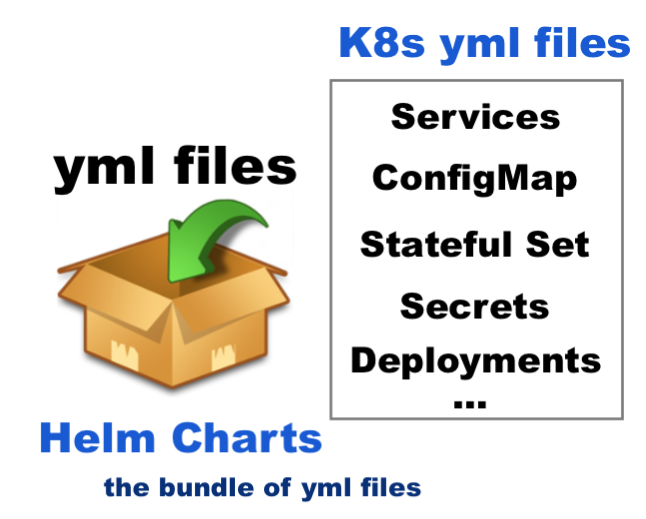 It consists of metadata that describes the application, plus the infrastructure needed to operate it in terms of the standard Kubernetes primitives.
Each chart references one or more container images that contain the application code to be run.
It consists of metadata that describes the application, plus the infrastructure needed to operate it in terms of the standard Kubernetes primitives.
Each chart references one or more container images that contain the application code to be run.
Helm charts contains at least these two elements:
- A description of the package (chart.yml).
- One or more templates, which contains Kubernetes manifest files.
Despite the fact we can run application containers using the Kubernetes command line (kubectl), the easiest way to run workloads in Kubernetes is using the ready-made Helm charts. Helm charts simply indicate to Kubernetes:
- how to perform the application deployment
- how to manage the container clusters
One other reason we need to use Helm is that it's a templating engine. Suppose we have several apps to deploy to Kubernetes cluster but when we look at the yaml files they are not that different from each other, probably, the app name and image name are the difference among all the yaml files. A typical sample looks like this:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-app-comtainer
image: my-app-image
port: 3000
Most of the value are the same. So, here are the things we can do with the templating engine:
- Define a common blueprint for all our microservices.
- Replacing the vaules dynamically.
- So, our yamls can be converted something like this:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: {{ .Values.name }} spec: containers: - name: {{ .Values.container.name }} image: {{ .Values.container.name }} port: {{ .Values.container.port }}
So, instead of having multiple yaml files, we have only one yaml file called vaules.yaml. We can replace the vaules during our build pipeline on the fly. As another use case, we can easily deploy our app to Kubernetes cluster across different environments such as dev, staging, and prod.
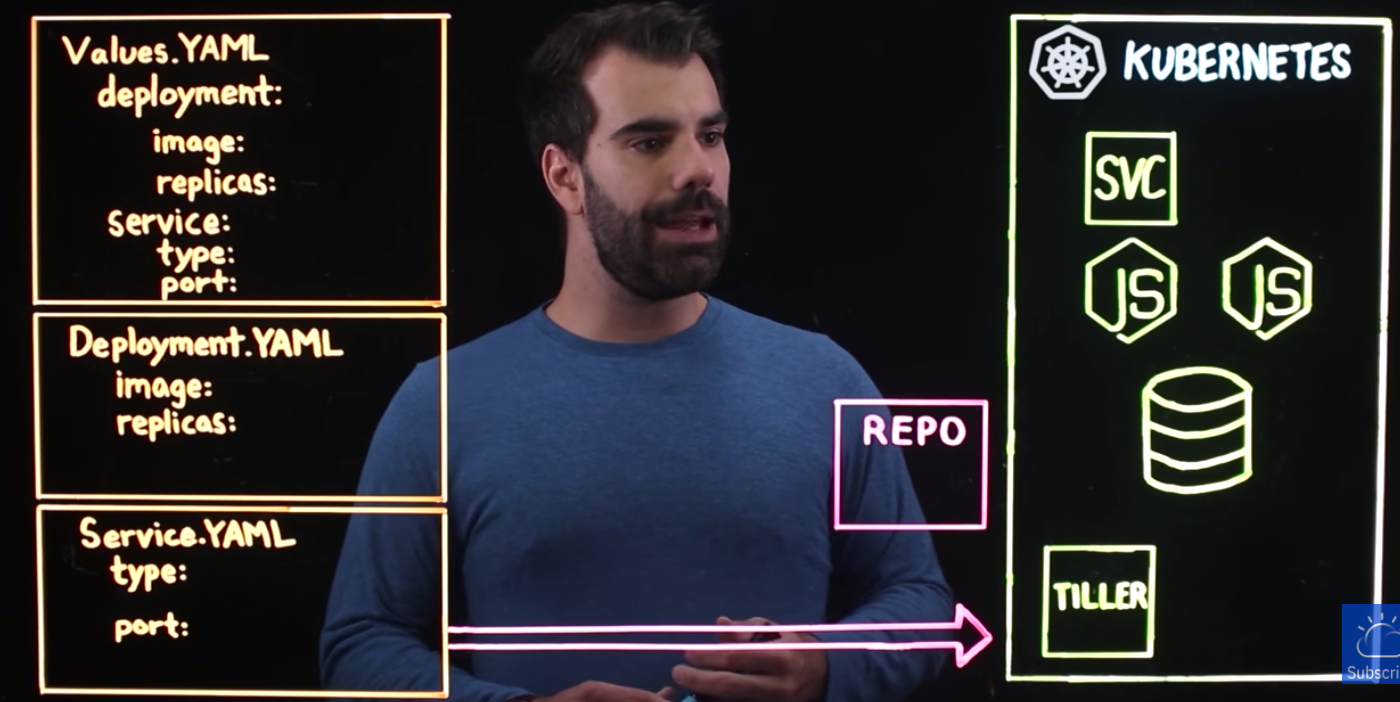
source: What is Helm?
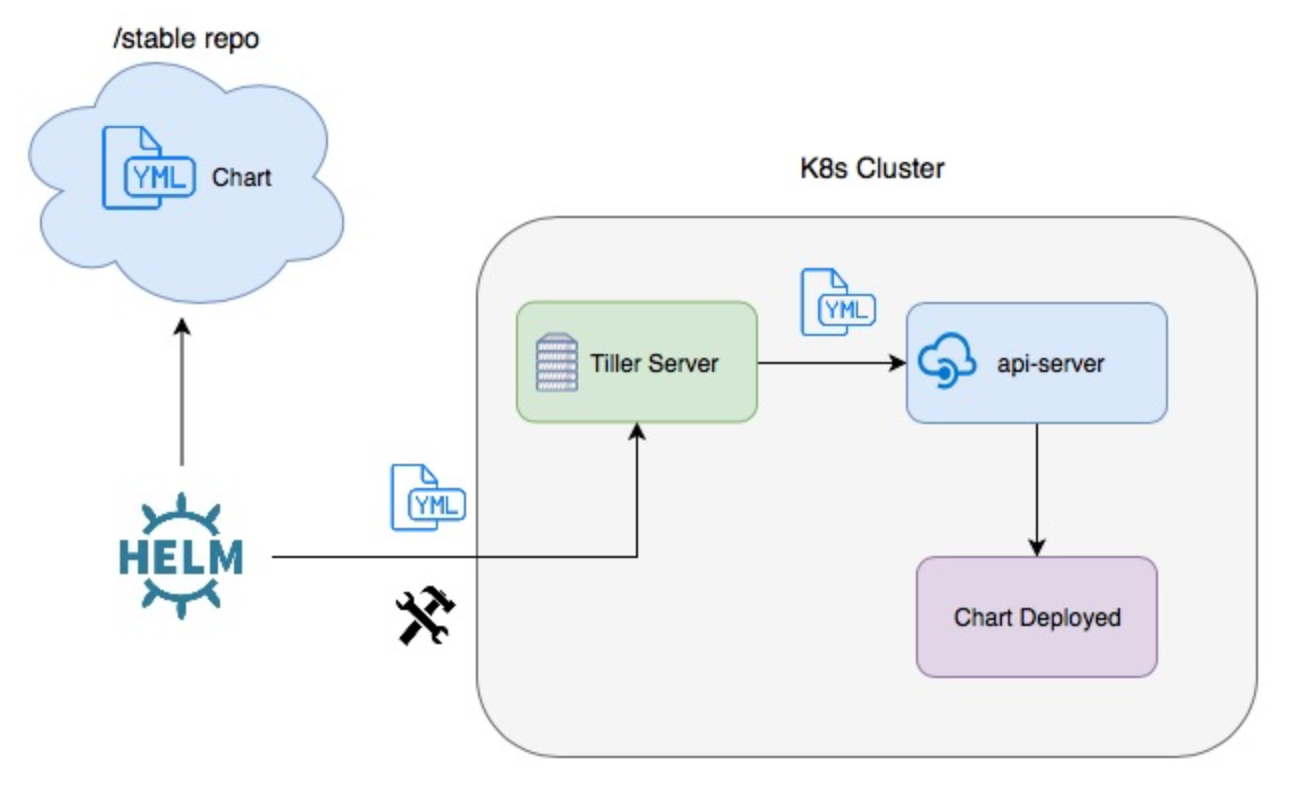
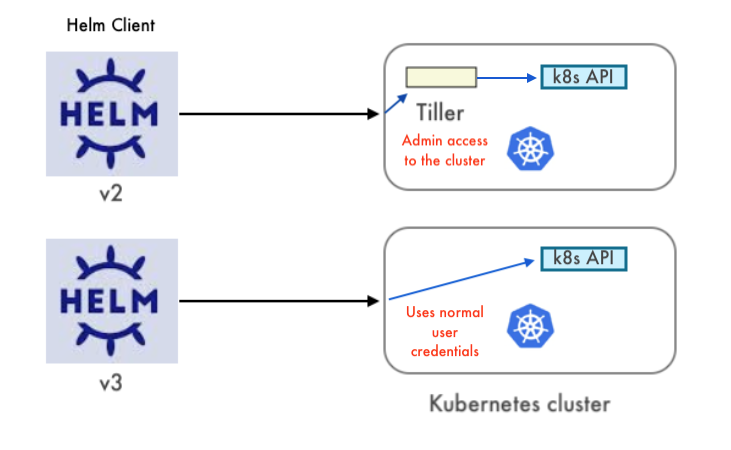
source: Packaging Applications for Kubernetes. Note the diagram applies only up to Helm 2 but not Helm 3.
In Helm 3, Tiller will be removed (Helm 3 Preview: Charting Our Future – Part 2: A Gentle Farewell to Tiller) because the tiller inside a K8s cluster has too much poewr such as CREATE/UPDATE/DELETE and it causes some security issues. So, the Helm 3 client library will communicate directly with the Kubernetes API server not via Tiller.
Terminology:
- Charts are the package format used by Helm. They define a set of resources to be deployed to a Kubernetes cluster. Functionally, charts are comparable to an apt, yum or homebrew.
- Repositories are locations where charts can be collected and distributed. They’re similar in function to apt or rpm repositories.
- A Releases represent an instance of a chart running in a Kubernetes cluster. If a chart is installed multiple times into the same Kubernetes cluster, it will be given a unique release with a corresponding name each time.
- In other words, Helm is used to install charts into Kubernetes clusters. The installation of a chart creates a release. To locate Helm charts for deployment, one would search a Helm chart repository.
Helm chart directory structure looks like this:
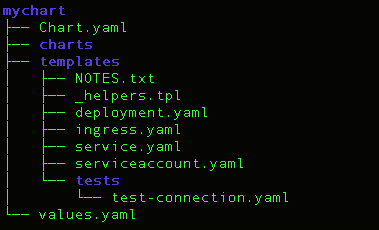
That's exactly the following command creates:
$ helm create mychart Creating mychart
- The top folder mychart: the name of the chart.
- Chart.yaml: meta info about the chart such as name, version, and dependencies etc.
- charts/ folder: There is initially empty and it allows us to add dependent charts that are needed to deploy our application.
- tempaltes/ folder: stores the actual yaml files.
Athelm install mychart, the template files will be filled with the values from values.yaml. The most important part of the chart is the template directory. It holds all the configurations for our application that will be deployed into the cluster. As we can see, this application has a basic deployment, ingress, service, and service account. This directory also includes a tests/ directory which includes a test for a connection into the app. - values.yaml: values for the template files.
The template files collect deployment information from this values.yaml file.
So, to customize our Helm chart, we need to edit the values file.
The default vaules can be overridden, for example:$ helm install --values=my-new-values.yaml mychart
- Kubernetes must be installed. The latest stable release of Kubernetes is recommended since Kubernetes versions prior to 1.6 have limited or no support for role-based access controls (RBAC).
- Helm will figure out where to install Tiller by reading our Kubernetes configuration file ($HOME/.kube/config) which is the same file that kubectl uses.
- To find out which cluster Tiller would install to, we can run
kubectl config current-contextorkubectl cluster-info: - We'll mostly use Helm v2 and then v3 in later sections of this post.
$ minikube start Starting local Kubernetes v1.10.0 cluster... Starting VM... Getting VM IP address... Moving files into cluster... Setting up certs... Connecting to cluster... Setting up kubeconfig... Starting cluster components... Kubectl is now configured to use the cluster. Loading cached images from config file.
$ kubectl config current-context minikube $ kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes master is running at https://192.168.99.100:8443 CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.99.100:8443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
There are two parts to Helm: The Helm client and the Tiller server.
To install Helm on MacOS:
$ brew install kubernetes-helm
$ helm version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.16.10", GitCommit:"bceca24a91639f045f22ab0f41e47589a932cf5e", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Error: could not find tiller
The easiest way to install tiller into the cluster is simply to run helm init.
This will validate that helm's local environment is set up correctly (and set it up if necessary).
$ helm init $HELM_HOME has been configured at /Users/kihyuckhong/.helm. Tiller (the Helm server-side component) has been installed into your Kubernetes Cluster. Please note: by default, Tiller is deployed with an insecure 'allow unauthenticated users' policy. To prevent this, run `helm init` with the --tiller-tls-verify flag. For more information on securing your installation see: https://v2.helm.sh/docs/securing_installation/
Note that we just setup the helm backend (Tiller) as a deployment on our minikube instance and
it will connect to whatever cluster kubectl connects to by default (kubectl config view).
$ kubectl config view
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority: /Users/kihyuckhong/.minikube/ca.crt
server: https://192.168.99.100:8443
name: minikube
contexts:
- context:
cluster: minikube
user: minikube
name: minikube
current-context: minikube
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: minikube
user:
client-certificate: /Users/kihyuckhong/.minikube/client.crt
client-key: /Users/kihyuckhong/.minikube/client.key
Now that we confirmed kubectl is pointed at our minikube.
Once it connects, it will install tiller into the kube-system namespace.
After helm init, we should be able to run kubectl get pods --namespace kube-system and see Tiller running.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ... tiller-deploy-6fd8d857bc-8pj74 1/1 Running 1 10h
Once Tiller is installed, running helm version should show us both the client and server version:
$ helm version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.16.10", GitCommit:"bceca24a91639f045f22ab0f41e47589a932cf5e", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Server: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.16.10", GitCommit:"bceca24a91639f045f22ab0f41e47589a932cf5e", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Just to make sure, let's verify again if our Tiller is setup properly as a deployment on our minikube instance:
$ kubectl describe deploy tiller-deploy --namespace=kube-system
Name: tiller-deploy
Namespace: kube-system
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 05 Oct 2020 15:19:03 -0700
Labels: app=helm
name=tiller
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 2
Selector: app=helm,name=tiller
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=helm
name=tiller
Service Account: tiller
Containers:
tiller:
Image: gcr.io/kubernetes-helm/tiller:v2.16.10
Ports: 44134/TCP, 44135/TCP
Host Ports: 0/TCP, 0/TCP
Liveness: http-get http://:44135/liveness delay=1s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Readiness: http-get http://:44135/readiness delay=1s timeout=1s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment:
TILLER_NAMESPACE: kube-system
TILLER_HISTORY_MAX: 0
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: tiller-deploy-76989fbdf6 (1/1 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 45m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set tiller-deploy-76989fbdf6 to 1
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 44m deployment-controller Scaled down replica set tiller-deploy-6fd89dcdc6 to 0
At this point, helm cli configured to use minikube since tiller has been setup and deployed to minikube to interact with the k8s api!
To deploy a new package to our cluster, use the helm install command. At its simplest, it takes only one argument: the name of the chart. In this section, we'll use a chart from the repo.
$ helm repo list NAME URL stable https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com local http://127.0.0.1:8879/charts $ helm search mariadb NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION stable/mariadb 7.3.14 10.3.22 DEPRECATED Fast, reliable, scalable, and easy to use open... stable/phpmyadmin 4.3.5 5.0.1 DEPRECATED phpMyAdmin is an mysql administration frontend
Let's deploy the stable/mariadb:
$ helm install stable/mariadb WARNING: This chart is deprecated NAME: affable-toucan LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 16 14:26:11 2021 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: DEPLOYED RESOURCES: ==> v1/ConfigMap NAME DATA AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master 1 2s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave 1 2s affable-toucan-mariadb-tests 1 2s ==> v1/Pod(related) NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master-0 0/1 Pending 0 2s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave-0 0/1 Pending 0 2s ==> v1/Secret NAME TYPE DATA AGE affable-toucan-mariadb Opaque 2 2s ==> v1/Service NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE affable-toucan-mariadb ClusterIP 10.98.221.99 <none> 3306/TCP 1s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave ClusterIP 10.107.13.73 <none> 3306/TCP 1s ==> v1/StatefulSet NAME READY AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master 0/1 1s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave 0/1 1s NOTES: This Helm chart is deprecated Given the `stable` deprecation timeline (https://github.com/helm/charts#deprecation-timeline), the Bitnami maintained Helm chart is now located at bitnami/charts (https://github.com/bitnami/charts/). The Bitnami repository is already included in the Hubs and we will continue providing the same cadence of updates, support, etc that we've been keeping here these years. Installation instructions are very similar, just adding the _bitnami_ repo and using it during the installation (`bitnami/` instead of `stable/ `) ```bash $ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami $ helm install my-release bitnami/<chart> # Helm 3 $ helm install --name my-release bitnami/<chart> # Helm 2 ``` To update an exisiting _stable_ deployment with a chart hosted in the bitnami repository you can execute ```bash $ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami $ helm upgrade my-release bitnami/<chart> ``` Issues and PRs related to the chart itself will be redirected to `bitnami/charts` GitHub repository. In the same way, we'll be happy to answer questions related to this migration process in this issue (https://github.com/helm/charts/issues/20969) created as a common place for discussion. Please be patient while the chart is being deployed Tip: Watch the deployment status using the command: kubectl get pods -w --namespace default -l release=affable-toucan Services: echo Master: affable-toucan-mariadb.default.svc.cluster.local:3306 echo Slave: affable-toucan-mariadb-slave.default.svc.cluster.local:3306 Administrator credentials: Username: root Password : $(kubectl get secret --namespace default affable-toucan-mariadb -o jsonpath="{.data.mariadb-root-password}" | base64 --decode) To connect to your database: 1. Run a pod that you can use as a client: kubectl run affable-toucan-mariadb-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --image docker.io/bitnami/mariadb:10.3.22-debian-10-r27 --namespace default --command -- bash 2. To connect to master service (read/write): mysql -h affable-toucan-mariadb.default.svc.cluster.local -uroot -p my_database 3. To connect to slave service (read-only): mysql -h affable-toucan-mariadb-slave.default.svc.cluster.local -uroot -p my_database To upgrade this helm chart: 1. Obtain the password as described on the 'Administrator credentials' section and set the 'rootUser.password' parameter as shown below: ROOT_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace default affable-toucan-mariadb -o jsonpath="{.data.mariadb-root-password}" | base64 --decode) helm upgrade affable-toucan stable/mariadb --set rootUser.password=$ROOT_PASSWORD
During installation, the helm client will print useful information about which resources were created, what the state of the release is, and also whether there are additional configuration steps we can or should take.
Now the mariadb chart is installed. Note that installing a chart creates a new release object. The release above is named affable-toucan. (If we want to use our own release name, we can simply use the --name flag on helm install.)
Helm does not wait until all of the resources are running before it exits.
To keep track of a release's state, or to re-read configuration information, we can use helm status:
$ helm status affable-toucan LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 16 14:26:11 2021 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: DEPLOYED RESOURCES: ==> v1/ConfigMap NAME DATA AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master 1 5m58s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave 1 5m58s affable-toucan-mariadb-tests 1 5m58s ==> v1/Pod(related) NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master-0 1/1 Running 0 5m58s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave-0 1/1 Running 0 5m58s ==> v1/Secret NAME TYPE DATA AGE affable-toucan-mariadb Opaque 2 5m58s ==> v1/Service NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE affable-toucan-mariadb ClusterIP 10.98.221.99 <none> 3306/TCP 5m57s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave ClusterIP 10.107.13.73 <none> 3306/TCP 5m57s ==> v1/StatefulSet NAME READY AGE affable-toucan-mariadb-master 1/1 5m57s affable-toucan-mariadb-slave 1/1 5m57s ... $ helm status affable-toucan LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 16 14:26:11 2021 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: DEPLOYED ...
When it is time to uninstall or delete a release from the cluster, use the helm delete command:
$ helm delete affable-toucan release "affable-toucan" deleted
This will remove the release from the cluster. We can see all of our currently deployed releases with the helm list command:
$ helm list
As we can see from the output above, the affable-toucan release was deleted.
However, Helm always keeps records of what releases happened. Need to see the deleted releases? helm list --deleted shows those, and helm list --all shows all of the releases (deleted and currently deployed, as well as releases that failed):
$ helm list --deleted NAME REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION NAMESPACE affable-toucan 1 Tue Mar 16 14:26:11 2021 DELETED mariadb-7.3.14 10.3.22 default
Using Helm repositories is a recommended practice (Helm repositories are optional), however, we can deploy a Helm chart to a Kubernetes cluster directly from the filesystem. There is no requirement that a Helm chart must be uploaded to a Helm repository before being deployed to a cluster.
Let's play with our initial chart (mychart) which Helm creates an nginx deployment, by default. Note that we create the chart earlier with the helm create command:
$ helm create mychart
We will use NodePort service type, so we need to change the value in mychart/values.yaml for the service type:
From:
service: type: ClusterIP
To:
service: type: NodePort
Deploy the package:
$ helm install mychart -n bogo NAME: bogo LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 16 14:55:26 2021 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: DEPLOYED RESOURCES: ==> v1/Deployment NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE bogo-mychart 0/1 1 0 1s ==> v1/Pod(related) NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE bogo-mychart-5c78cbfc6b-p7fsm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s ==> v1/Service NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE bogo-mychart NodePort 10.99.92.18880:30018/TCP 1s ==> v1/ServiceAccount NAME SECRETS AGE bogo-mychart 1 1s NOTES: 1. Get the application URL by running these commands: export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services bogo-mychart) export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}") echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT $ kubectl get all NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/bogo-mychart-5c78cbfc6b-p7fsm 1/1 Running 0 2m38s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/bogo-mychart NodePort 10.99.92.188 80:30018/TCP 2m39s service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 49d NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/bogo-mychart 1/1 1 1 2m39s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/bogo-mychart-5c78cbfc6b 1 1 1 2m38s
The minikube service command will open a browser for us:
$ minikube service bogo-mychart |-----------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL | |-----------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | default | bogo-mychart | http/80 | http://192.168.64.11:30018 | |-----------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| Opening service default/bogo-mychart in default browser...
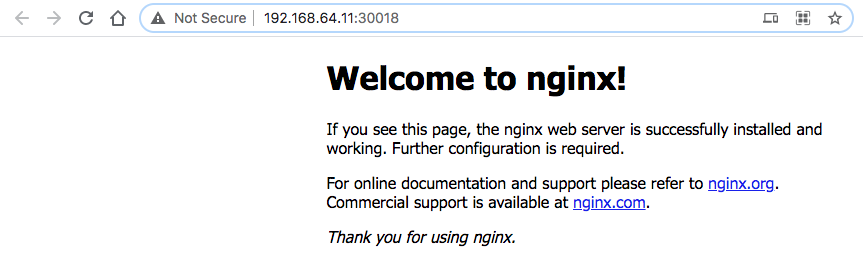
We can check the release:
$ helm ls NAME REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION NAMESPACE bogo 1 Tue Mar 16 14:55:26 2021 DEPLOYED mychart-0.1.0 1.0 default
To delete the release:
$ helm del bogo release "bogo" deleted $ helm ls $
We may want to have both versions of Helm on our Mac since some applications do no support v3 yet. To update an application installed with Helm v2 needs to be uninstalled with Helm v2, and then reinstalled with Helm v3.
$ brew uninstall helm $ brew uninstall helm@2 $ brew uninstall helm@3 $ brew install helm@2 $ brew install helm $ ls /usr/local/opt/helm@2/bin helm tiller $ ls /usr/local/opt/helm@3/bin helm $ ln -sf /usr/local/opt/helm@2/bin/tiller /usr/local/bin/tiller $ ln -sf /usr/local/opt/helm@2/bin/helm /usr/local/bin/helm2 $ ln -sf /usr/local/opt/helm@3/bin/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
Chect the versions:
$ helm2 version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.17.0", GitCommit:"a690bad98af45b015bd3da1a41f6218b1a451dbe", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Server: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.17.0", GitCommit:"a690bad98af45b015bd3da1a41f6218b1a451dbe", GitTreeState:"clean"}
$ helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.5.3", GitCommit:"041ce5a2c17a58be0fcd5f5e16fb3e7e95fea622", GitTreeState:"dirty", GoVersion:"go1.16.2"}
- To create new chart named mysql:
$ helm create mysql Creating mysql $ tree mysql mysql ├── Chart.yaml ├── charts ├── templates │ ├── NOTES.txt │ ├── _helpers.tpl │ ├── deployment.yaml │ ├── hpa.yaml │ ├── ingress.yaml │ ├── service.yaml │ ├── serviceaccount.yaml │ └── tests │ └── test-connection.yaml └── values.yaml
- Helm, by default, creates an nginx deployment.
We're going to customize it to create a Helm Chart to deploy mysql on Kubernetes cluster. Also, we'll add new deployment (mysql/templates/deployment.yaml):
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: {{ include "mysql.fullname" . }} spec: selector: matchLabels: app: {{ include "mysql.name" . }} template: metadata: labels: app: {{ include "mysql.name" . }} spec: containers: - name: {{ .Chart.Name }} image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag }}" imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }} env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD value: {{ .Values.mysql_root_password }} ports: - containerPort: {{ .Values.service.port }} name: mysql volumes: - name: mysql-persistent-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: {{ .Values.persistentVolumeClaim }} -
Also, we need to create PVC which is used in deployment (mysql/templates/persistentVolumeClaim.yaml):
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: {{ .Values.persistentVolumeClaim }} spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 1Gi -
Helm runs each file in the templates/ directory through Go template rendering engine. Now, we want to create mysql/templates/service.yaml to connect to the mysql instance:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: {{ include "mysql.fullname" . }} spec: ports: - port: {{ .Values.service.port }} selector: app: {{ include "mysql.name" . }} clusterIP: None -
It's time to update mysql/values.yaml to populate the chart's templates:
# Default values for mysql. # This is a YAML-formatted file. # Declare variables to be passed into your templates. image: repository: mysql tag: 5.6 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent nameOverride: "" fullnameOverride: "" serviceAccount: # Specifies whether a service account should be created create: false # The name of the service account to use. # If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template name: mysql_root_password: password service: type: ClusterIP port: 3306 persistentVolumeClaim: mysql-data-disk ingress: enabled: false annotations: {} # kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx # kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true" hosts: - host: chart-example.local paths: [] tls: [] # - secretName: chart-example-tls # hosts: # - chart-example.local autoscaling: enabled: false resources: {} # We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious # choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little # resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following # lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'. # limits: # cpu: 100m # memory: 128Mi # requests: # cpu: 100m # memory: 128Mi - Here is the updated directory structure:
$ tree mysql mysql ├── Chart.yaml ├── charts ├── templates │ ├── NOTES.txt │ ├── _helpers.tpl │ ├── deployment.yaml │ ├── hpa.yaml │ ├── ingress.yaml │ ├── persistentVolumeClaim.yaml │ ├── service.yaml │ ├── serviceaccount.yaml │ └── tests │ └── test-connection.yaml └── values.yaml
- Render the chart templates locally and check if everything is correct:
$ helm template mysql --- # Source: mysql/templates/persistentVolumeClaim.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: mysql-data-disk spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 1Gi --- # Source: mysql/templates/service.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: RELEASE-NAME-mysql spec: ports: - port: 3306 selector: app: mysql clusterIP: None --- # Source: mysql/templates/deployment.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: RELEASE-NAME-mysql spec: selector: matchLabels: app: mysql template: metadata: labels: app: mysql spec: containers: - name: mysql image: "mysql:5.6" imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD value: password ports: - containerPort: 3306 name: mysql volumes: - name: mysql-persistent-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: mysql-data-disk --- # Source: mysql/templates/tests/test-connection.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: "RELEASE-NAME-mysql-test-connection" labels: helm.sh/chart: mysql-0.1.0 app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql app.kubernetes.io/instance: RELEASE-NAME app.kubernetes.io/version: "1.16.0" app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm annotations: "helm.sh/hook": test-success spec: containers: - name: wget image: busybox command: ['wget'] args: ['RELEASE-NAME-mysql:3306'] restartPolicy: Never - Execute the
helm installcommand to deploy our mysql chart in the Kubernetes cluster:helm install [NAME] [CHART] [flags]
$ helm install mysql-rel mysql NAME: mysql-rel LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Sep 6 16:16:45 2020 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 NOTES: 1. Get the application URL by running these commands: export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=mysql,app.kubernetes.io/instance=mysql-rel" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use your application" kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:80
We can get a bash shell running in the MySQL container and take a look around. Just exec bash against the mysql pod:$ kubectl exec -it mysql-rel-7557ff844d-9rhdh -- bash root@mysql-rel-7557ff844d-9rhdh:/#
- Note that installing a Helm chart creates a new release object, in our case, it is named mysql-rel. To check the state:
$ helm status mysql-rel NAME: mysql-rel LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Sep 6 16:16:45 2020 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 ...
- To do an install or an upgrade, we can use
helm upgradecommand:$ helm upgrade --install mysql-rel mysql Release "mysql-rel" has been upgraded. Happy Helming! NAME: mysql-rel LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Sep 6 17:40:36 2020 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 2 NOTES: 1. Get the application URL by running these commands: export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=mysql,app.kubernetes.io/instance=mysql-rel" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use your application" kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:80 $ helm ls NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION mysql-rel default 2 2020-09-06 17:40:36.90264 -0700 PDT deployed mysql-0.1.0 1.16.0 - To clean everything up, we can delete the release:
$ helm del mysql-rel release "mysql-rel" uninstalled $ helm ls NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
For more information, please check Using Helm
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization