Design Patterns
- Model View Controller (MVC) Pattern
- Separation of Model from View components makes it possible to implement several user interfaces that reuse the common core business logic.
- Duplication of low-level Model code is eliminated across multiple UI implementations.
- Decoupling of Model and View code results in an improved ability to write unit tests for the core business logic code.
- Modularity of components allows core logic developers and UI developers to work simultaneously without affecting the other.
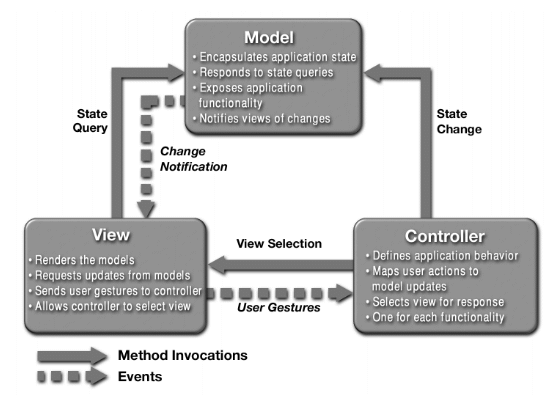
- Model
- Manages the app data and state
- Not concerned with UI or presentation
- Often persists somewhere
- Same model should be reusable, unchanged in different interfaces
- View
- Present the Model to the user in an appropriate interface
- Allows user to manipulate data
- Does not store any data except to cache state
- Easily reusable & configurable to display different data
- Controller
- Intermediary between Model & View
- Updates the view when the model changes
- Updates the model when the user manipulates the view
- Typically where the app logic lives
This pattern decouples changes to how data are manipulated from how they are displayed or stored, while unifying the code in each component. In other words, it's a way of developing apps keeping the data (model) used in the program, and the visual (view) component of the program separate from one another, each interacting only with a controller containing the logic of our program. The view and the model interact only with the controller NEVER with each other.
A triad of three modules linked by the Observer Pattern. The View drives a presentation and elements within the View observe the Model. Elements within the Controller observe the View and Model, and elements within the Model observe the Controller.
In a simple application, the Controller can affect changes to the Model based on user input and also communicate those changes to the View so that the UI can be updated. In real-world applications, however, the View will normally also need to update to reflect additional changes to the underlying Model. This is necessary because changing one aspect of the Model may cause it to update other dependent Model state. This requires Model code to inform the View layer when state changes happen. The Model code, however, cannot statically bind and call the View code. This is where observers come in.
The Observer Pattern is a specific instance of the publish/subscribe paradigm. These techniques define a one-to-many dependency between objects such that a publisher object can notify all subscribed objects of any state changes without depending on them directly.
MVC is often seen in web applications where the view is the HTML or XHTML generated by the app. The controller receives GET or POST input and decides what to do with it, handing over to domain objects (i.e. the model) which contain the business rules and know how to carry out specific tasks such as processing a new subscription, and which hand control to (X)HTML-generating components such as templating engines, XML pipelines, AJAX callbacks, etc.
The MVC model can be found in UI toolkits such as Nokia's Qt, Apple's Cocoa, Java Swing, and MFC library.
When we write an iPhone app, we have to deal with MVC all the time. iPhone SDK Tutorials
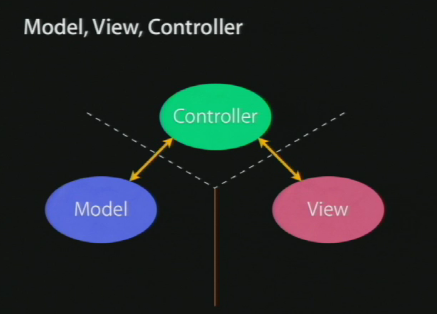
The Model talks to the controller and the controller can manipulate the model. The View can manipulate the Controller and the Controller can set the value of the View state. Note that we do not have any arrow between the Model and the View.
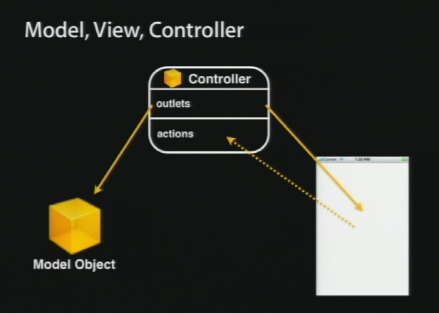
We have a Controller in the middle with Model in the left and the view in the right side. The controller has outlets so that it can talk to the View and Model. The View may have buttons or sliders that can send the actions. Essentially, actions go from the window to the Controller so that the Controller can do whatever it needs.
Models: Content Providers.
Data Managers that are the recommended form of inter-application data sharing.
Views: Activities.
This is the application's primary user interface component. Every individual screen of an Android application is derived from the Activity Java class (android.app.Activity).
They are containers for Views (android.view.View).
Controllers: Services.
These are background components that behave like UNIX daemons and Windows services. They run invisibly and perform ongoing unattended processing.
Python's web service framework also based on MVC.
For more info, visit MVC - Hello World Django.
- Martin Fowler's GUI Architectures
- Qt 5 - Model/View Programming.
Qt's MVC is not exactly follow conventional MVC (if there is any clear cut), but it works wonderfully within Qt's framework. Their Controller is merged into View.
If the view and the controller objects are combined, the result is the model/view architecture. This still separates the way that data is stored from the way that it is presented to the user, but provides a simpler framework based on the same principles. This separation makes it possible to display the same data in several different views, and to implement new types of views, without changing the underlying data structures. To allow flexible handling of user input, we introduce the concept of the delegate. The advantage of having a delegate in this framework is that it allows the way items of data are rendered and edited to be customized.
However, it's worth investigating their approach of using "delegate" with their Model/View pattern. - Qt 5 MVC - ModelView with QListView and QStringListModel
- Qt 5 MVC - ModelView with QTreeView and QDirModel
- Qt 5 MVC - ModelView with QTreeView and QFileSystemModel
- Qt 5 MVC - ModelView with QTableView and QItemDelegate
- Django - RESTful Web Framework (Python)
- Laravel - RESTful Web Framework (PHP)
- Ruby on Rails - RESTful Web Framework (Ruby)
There are MVC patterns that can be found in other programming languages. The followings are my tutorials for Web Services Framework:
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization