Design Patterns
- Singleton Pattern
Intent
The Singleton pattern ensures a class has only one instance, and provides a global point of access to it.
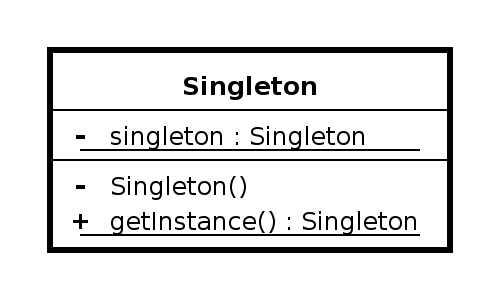
A Singleton is an elegant way of maintaining global state, but we should always question whether we need global state. Singleton pattern offers several advantages over global variables because it does the following:
- Enforces that only one instance of the class can be instantiated.
- Allows control over the allocation and destruction of the object.
- Provides thread-safe access to the object's global state.
- Prevents the global namespace from being polluting.
Let's think about a class which has private constructor.
It becomes a class that can't be instantiated because it has private constructor.
class MyClass {
private:
MyClass(){}
};
We need to have an instance of the class to call it, but we can't have an instance because no other class can't instantiate it. We can use the constructor from an object of type MyClass but we can never instantiate that object because no other object can use:
new MyClass();So, we should find a way of using a static method.
Here is an example code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton *getInstance();
private:
Singleton(){}
static Singleton* instance;
};
Singleton* Singleton::instance = 0;
Singleton* Singleton::getInstance()
{
if(!instance) {
instance = new Singleton();
cout << "getInstance(): First instance\n";
return instance;
}
else {
cout << "getInstance(): previous instance\n";
return instance;
}
}
int main()
{
Singleton *s1 = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton *s2 = Singleton::getInstance();
return 0;
}
Output from the run:
getInstance(): First instance getInstance(): previous instance
Singleton pattern limits the instantiation of a class to
We can modify the design of the code with the following constraints:
- We do not want the singleton by copied so that there is only one instance. This can be achieved by declaring a private copy constructor and a private assignment operator.
- The getInstance() method should return a reference rather than a pointer. This blocks a client from deleting the object. Also, by making destructor private, we can achieve the same effect.
The revised code looks like this:
#include <iostream>
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton& getInstance();
private:
Singleton() {std::cout << "Ctor\n";};
~Singleton() {std::cout << "Dtor\n";};
Singleton(const Singleton&);
const Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&);
};
Singleton& Singleton::getInstance()
{
static Singleton instance;
return instance;
}
int main()
{
Singleton &s1; = Singleton::getInstance();
Singleton &s2; = Singleton::getInstance();
return 0;
}
The revised version is not thread safe because there could be a race condition during the initialization of the static Singleton, Singleton& Singleton::getInstance(). But we can make the method thread safe by adding a mutex lock:
Singleton& Singleton::getInstance()
{
Mutex mutex;
ScopedLock(&mutex;); // to unlock mutex on exit
static Singleton instance;
return instance;
}
In 2009, the authors of the original design patterns said the only pattern they would consider removing from the original list is Singleton. This is because it is essentially a way to store global data and tends to be an indicator of poor design.
There are several alternatives to the Singleton pattern:
- dependency injection
- Monostate pattern
- session context
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization