Design Patterns
- Strategy Pattern
bogotobogo.com site search:
Strategy Pattern
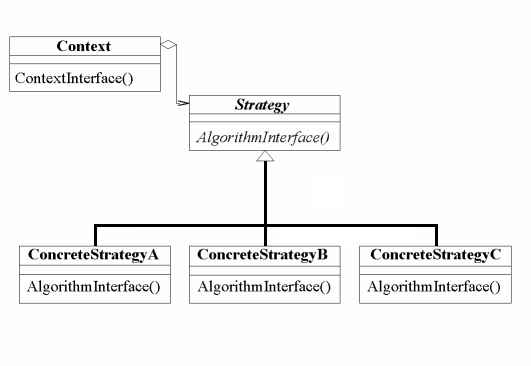
Intent
The strategy pattern is intended to provide a means to define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one as an object, and make them interchangeable. The strategy pattern lets the algorithms vary independently from clients that use them.
Sample 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SortBehavior
{
public:
virtual void sort() const = 0;
};
class Merge: public SortBehavior
{
public:
virtual void sort() const {
cout << "Merge sort()\n";
}
};
class Quick: public SortBehavior {
public:
virtual void sort() const {
cout << "Quick sort()\n";
}
};
class Heap: public SortBehavior
{
public:
virtual void sort() const {
cout << "Heap sort()\n";
}
};
class SearchBehavior
{
public:
virtual void search() const = 0;
};
class Sequential: public SearchBehavior
{
public:
virtual void search() const {
cout << "Sequential search()\n";
}
};
class BinaryTree: public SearchBehavior
{
public:
virtual void search() const {
cout << "BinaryTree search()\n";
}
};
class HashTable: public SearchBehavior
{
public:
virtual void search() const {
cout << "HashTable search()\n";
}
};
// Context
class Collection
{
private:
SortBehavior* m_sort;
SearchBehavior* m_search;
public:
Collection(){}
void set_sort(SortBehavior* s){
m_sort = s;
}
void set_search(SearchBehavior* s){
m_search = s;
}
void sort() const {
m_sort->sort();
}
void search() const {
m_search->search();
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Merge merge;
Quick quick;
Heap heap;
Sequential sequential;
BinaryTree binaryTree;
HashTable hashTable;
Collection colA;
colA.set_sort(&merge;);
colA.sort();
Collection colB;
colB.set_search(&binaryTree;);
colB.search();
return 0;
}
Output from the run:Merge sort() BinaryTree search()
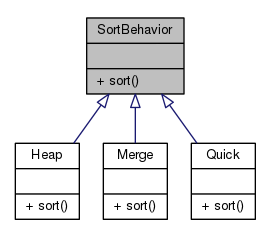
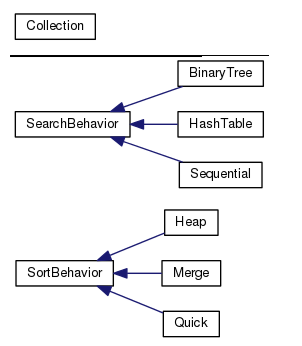
- We have two interfaces: SortBehavior and SearchBehavior along with corresponding classes that implement each concrete behavior.
- With the design, other types of objects can reuse our search and sort behaviors because these behaviors are no longer hidden away in our Collection classes.
- And we can add new behaviors without modifying any of our existing behavior classes.
- We put instance variables hold a pointer to a specific behavior at runtime.
class Collection { private: SortBehavior* m_sort; SearchBehavior* m_search; - Using the pointers, we can implement the each behavior
void sort() const { m_sort->sort(); } void search() const { m_search->search(); } - Rather than handling the sort behavior itself, the Collection object delegates that behavior to the object pointed by m_sort.
colA.set_sort(&merge;); colA.sort(); => Collection::m_sort->sort(); ==> virtual void sort() const{ cout << "Merge sort()\n"; } - We do not care what kind of collection object it is, all we care about is that it knows how to sort()
- Actually, we've created system using composition giving us a lot more flexibility. Not only does it let us encapsulate a family of algorithm into their own set of classes, but it also let us change behavior at runtime as long as the object we're composing with implements the correct behavior interface.
Sample 2
In this sample, we have two ways of recording contact information: stream & database. The two classes (StreamRecord and DatabaseRecord share the same interface for their own implementation of recording data via baseclass member function store() which has all the shared implementation methods (actually, api).
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Record
{
public:
virtual void start_record() = 0;
virtual void store_field(const string &name;, const string &value;) = 0;
virtual void finish_record() = 0;
virtual ~Record() { }
};
struct ContactData
{
string first_name, last_name, phone, email;
};
class ContactRecorder
{
public:
ContactRecorder(Record *a) : m_Record(a)
{
assert(a != 0);
}
void store(const ContactData &data;)
{
assert(m_Record != 0);
m_Record->start_record();
m_Record->store_field("first name", data.first_name);
m_Record->store_field("last name", data.last_name);
m_Record->store_field("phone", data.phone);
m_Record->store_field("email", data.email);
m_Record->finish_record();
}
private:
Record *m_Record;
};
class StreamRecord : public Record
{
public:
StreamRecord(ostream &s;, const string &record;_name = string())
: m_ostream(s), m_record_name(record_name)
{ }
void start_record() { m_ostream << m_record_name << "( "; }
void store_field(const string &name;, const string &value;)
{
m_ostream << name << ": " << value << "; ";
}
void finish_record() { m_ostream << ")" << endl; }
void set_record_name(const string &name;) { m_record_name = name; }
private:
ostream &m;_ostream;
string m_record_name;
};
class MySql {};
class DatabaseRecord : public Record
{
public:
DatabaseRecord() : m_dbConnection(new MySql) {}
void start_record() { cout << "start transaction\n"; }
void store_field(const string &name;, const string &value;)
{ cout << "insert into table\n"; }
void finish_record() { cout << "finish transaction\n"; }
private:
MySql *m_dbConnection;
};
int main()
{
ContactData data = {"Black", "Smith", "415-675-1874", "adams@email.com"};
StreamRecord sRecord(std::cout);
ContactRecorder contact(&sRecord;);
contact.store(data);
DatabaseRecord dbRecord;
ContactRecorder contact2(&dbRecord;);
contact2.store(data);
return 0;
}
Output:
( first name: Black; last name: Smith; phone: 415-675-1874; email: smith@email.com; ) start transaction insert into table insert into table insert into table insert into table finish transaction
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization