Design Patterns
- Template Method Pattern
Intent
Define the skeleton of an algorithm in an operation, deferring some steps to subclasses. Template Method lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an algorithm without changing the algorithm's structure.
This pattern is all about creating a template for an algorithm. So, what's a template?
It's just a method; it's a method that defines an algorithm as a set of steps. One or more of these steps is defined to be abstract and implemented by a subclass. This ensures the algorithm's structure stays unchanged while subclasses provide some part of the implementations.
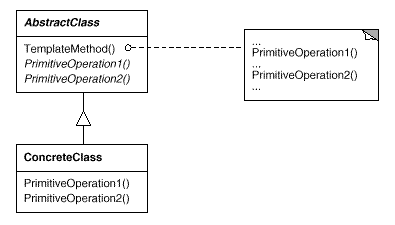
Let's look at the diagram above.
- The AbstractClass contains the template method. The abstract versions of the operations used in the template method.
- There may be many ConcreteClasses, each implementing the full set of operations required by the template method.
- The ConcreteClasses implements the abstract operations, which are called when the templateMethod() needs them.
- The template method makes use of the primativeOperations to implement an algorithm. It is decoupled from the actual implementation of these operations.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class AbstractClass
{
public:
void templateMethod() {
primitiveOperation1();
primitiveOperation2();
concreteOperation();
hook();
}
virtual void primitiveOperation1() = 0;
virtual void primitiveOperation2() = 0;
void concreteOperation() {
cout << "Mandatory Operations for all ConcreteClasses" << endl;
}
virtual void hook() {}
};
class ConcreteClassA : public AbstractClass
{
public:
void primitiveOperation1() {
cout << "primitiveOp1 A" << endl;
}
void primitiveOperation2() {
cout << "primitiveOp2 A" << endl;
}
};
class ConcreteClassB : public AbstractClass
{
public:
void primitiveOperation1() {
cout << "primitiveOp1 B" << endl;
}
void primitiveOperation2() {
cout << "primitiveOp2 B" << endl;
}
void hook() {
cout << "hook() B" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
ConcreteClassA ca;
ConcreteClassB cb;
ca.templateMethod();
cb.templateMethod();
return 0;
}
Output:
primitiveOp1 A primitiveOp2 A Mandatory Operations for all ConcreteClasses primitiveOp1 B primitiveOp2 B Mandatory Operations for all ConcreteClasses hook() B
Let's summarize what's done.
- Note that the templateMethod() defines the sequence of steps, each represented by a method.
- Two of the primitive operations must be implemented by concrete subclasses.
virtual void primitiveOperation1() = 0; virtual void primitiveOperation2() = 0;
- A concrete operation is defined in the abstract class. This one is not declared as virtual so that subclasses can't override it. It may be used in the template method directly, or used by subclasses.
void concreteOperation() { cout << "Mandatory Operations for all ConcreteClasses" << endl; } - We can also have concrete methods that do nothing by default we call these hooks. Subclasses are free to override these but don't have to.
virtual void hook() {}
This example has two concrete classes derived from OperationTemplate class which provides 3 interfaces: read_input(), write_output, and operate(). The two derived classes perform different operations while sharing the same interfaces that template design pattern provides.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <iterator>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
class OperationTemplate
{
public:
typedef std::map<std::string, std::string> Arguments;
public:
bool solve(const Arguments &input;, Arguments &output;)
{
assert(output.empty());
if (!read_input(input)) {
return false;
}
if (!operate()) {
return false;
}
write_output(output);
return true;
}
protected:
virtual bool read_input(const Arguments &input;) = 0;
virtual bool operate() = 0;
virtual void write_output(Arguments &output;) const = 0;
public:
virtual ~OperationTemplate() { }
};
class MathOperation : public OperationTemplate
{
public:
MathOperation(): mx(0), my(0), mOperation(0), mResult(0) { }
private:
bool read_input(const Arguments &input;)
{
Arguments::const_iterator i = input.find("x");
if (input.end() == i) {
return false;
}
std::istringstream in(i->second);
in >> mx;
if (in.fail()) {
return false;
}
i = input.find("y");
if (input.end() == i) {
return false;
}
in.clear();
in.str(i->second);
in >> my;
if (in.fail()) {
return false;
}
i = input.find("operation");
if (input.end() == i || i->second.size() != 1) {
return false;
}
mOperation = i->second[0];
return true;
}
bool operate()
{
switch (mOperation)
{
case '+':
mResult = mx + my;
break;
case '-':
mResult = mx - my;
break;
case '*':
mResult = mx * my;
break;
case '/':
if (0 == my) {
return false;
}
mResult = mx / my;
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
void write_output(Arguments &output;) const
{
std::ostringstream out;
out << mResult;
output.insert(std::make_pair(std::string("result"), out.str()));
}
private:
int mx, my, mResult;
char mOperation;
};
class ListOperation : public OperationTemplate
{
private:
bool read_input(const Arguments &input;)
{
mList.clear();
Arguments::const_iterator i = input.find("array");
if (input.end() == i) {
return false;
}
std::istringstream in(i->second);
typedef std::istream_iterator<int> T;
std::copy(T(in), T(), std::back_inserter(mList));
if (!in.eof()) return false;
return true;
}
bool operate()
{
mList.reverse();
return true;
}
void write_output(Arguments &output;) const
{
std::ostringstream out;
std::copy(mList.begin(), mList.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<int>(out, " "));
output.insert(std::make_pair(std::string("result"), out.str()));
}
private:
std::list<int> mList;
};
int main()
{
map<string, string> myInput, myOutput;
// 10 + 20 = 30
myInput.insert(make_pair("x", "10"));
myInput.insert(make_pair("y", "20"));
myInput.insert(make_pair("operation", "+"));
MathOperation a;
a.solve(myInput, myOutput);
cout << myOutput["result"] << endl;
myInput.clear();
myOutput.clear();
// 1 2 3 4 5 -> 5 4 3 2 1
myInput["array"] = "1 2 3 4 5";
ListOperation b;
b.solve(myInput, myOutput);
cout << myOutput["result"] << endl;
return 0;
}
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization