Design Patterns
- Proxy Pattern
Intent
Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
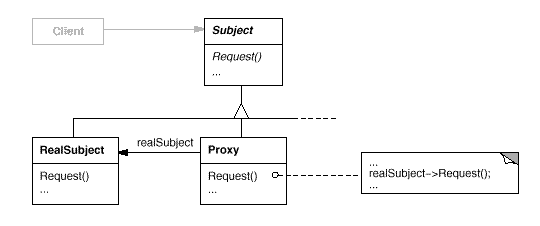
Let's take look at the diagram.
- Both the Proxy and the RealSubject implement the Subject interface. This allows any client to treat the Proxy just like the RealSubject.
- The RealSubject is usually the object that does most of the real work; the Proxy controls access to it.
- The control may be needed if the Subject is running on a remote machine, if the Subject is expensive to create in some way or if access to the subject needs to be protected in some way.
- The Proxy often instantiates or handle the creation of the RealSubject.
- The Proxy keeps a reference (pointer) to the Subject, so it can forward requests to the Subject when necessary.
- In some cases, the Proxy may be responsible for creating and destroying the RealSubject. Clients interact with the RealSubject through the Proxy.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Subject
{
public:
virtual void request() = 0;
virtual ~Subject() {}
};
class RealSubject : public Subject
{
public:
void request() {
cout << "RealSubject.request()" << endl;
}
};
class Proxy : public Subject
{
private:
Subject* realSubject;
public:
Proxy() : realSubject (new RealSubject())
{}
~Proxy() {
delete realSubject;
}
// Forward calls to the RealSubject:
void request() {
realSubject->request();
}
};
int main() {
Proxy p;
p.request();
}
A Proxy provides an interface that forwards function calls to another interface of the same form. A Proxy pattern is useful to modify the behavior of the RealSubject class while still preserving its interface. This is particularly useful if the RealSubject class is in third-party library and hence not easily modifiable directly. There are other use cases of Proxy:
-
Implement lazy instantiation of the RealSubject object
In this case, the RealSubject object is not actually instantiated until a method call is invoked. This can be useful if instantiating the RealSubject object is a heavyweight operation that we wish to defer until absolutely necessary. -
Implement access control to the RealSubject object
We may want to insert a permissions layer between the Proxy and the RealSubject objects to ensure that users can only call certain methods on the RealSubject object if they have appropriate permission. -
Support debug or dry-run modes
This lets us insert debugging statement into the Proxy methods to log all call to the RealSubject object or we can stop the forwarding to certain RealSubject method with a flag to let us call the Proxy in a dry-run mode, such as to turn off writing the object's state to disk. -
Make the RealSubject class to be thread safe
This can be done by adding mutex locking to the methods that are not thread safe. While this may not be the most efficient way to make the underlying class thread safe, it is a useful if we cannot modify the RealSubject. -
Share resources
We could have multiple Proxy objects share the same underlying RealSubject class. This could be used to implement reference counting, for instance. This is, actually, another design pattern called the Flyweight pattern, where multiple objects share the same underlying data to minimize memory. -
Protect against future changes in the RealSubject class
We anticipate that a dependent library will change in the future so we create a proxy wrapper around that API that directly mimics the current behavior. So, when the library changes later, we can preserve the old interface via our proxy object and simply change its underlying implementation to use the new library methods.
With Remote Proxy, the proxy acts as a local representative for an object that lives in a different address space. A method call on the proxy results in the call being transferred over the wire, invoked remotely, and the result being returned back to the proxy and then to the client.
With Virtual Proxy, the proxy acts as a representative for an object that may be expensive to create. The Virtual Proxy often defers the creation of the object until it is needed.
The Virtual Proxy also act as a surrogate for the object before and while it is being created. After that, the proxy delegates requests directly to the RealSubject.
With Protection Proxy, the proxy controls access to an object based on access rights. For instance, if we had an employee object, a Protection Proxy might allow the employee to call certain methods on the object, a manager to call additional methods (like makeBonus()), and a HR employee to call any method on the object.
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization