Algorithms - Path Finding
The detailed description of A* algorithm can be found A* Pathfinding for Beginners.
The C++ code below is based on that article, and it's using priority_queue of STL to store sorted list of nodes. When we push( ) an object onto a priority_queue, that object is sorted into the queue according to a comparison function or function object. We can allow the default less template to supply this, or we can provide one of our own as in the code below. The priority_queue ensures that when we look at the top( ) element, it will be the one with the highest priority. When we're done with it, we call pop( ) to remove it and bring the next one into place. Thus, the priority_queue has nearly the same interface as a stack, but it behaves differently. Like stack and queue, priority_queue is an adaptor that is built on top of one of the basic sequences the default sequence being vector.
The program below, gives lower-F the highest priority by overloading operator< of Node class.
Here is a diagram (8x6 grid) used to simulate the description of the tutorial mentioned earlier:
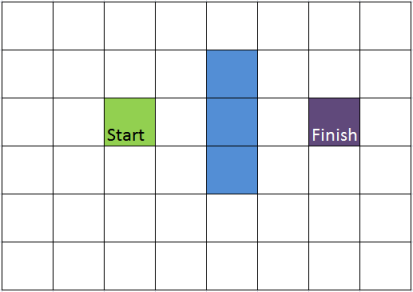
In the code, when NDIR=4, only vertical and horizontal movements are allowed, and when NDIR=8, diagonal movements are allowed.
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int IDIM = 8; // horizontal size of the squares
const int JDIM = 6; // vertical size size of the squares
const int NDIR = 4; // number of possible directions to go at any position
// if NDIR = 4
const int iDir[NDIR] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
const int jDir[NDIR] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
// if NDIR = 8
//const int iDir[NDIR] = {1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1};
//const int jDir[NDIR] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
int squares[IDIM][JDIM];
// list of closed (check-out) nodes
int closedNodes[IDIM][JDIM];
// list of open (not-yet-checked-out) nodes
int openNodes[IDIM][JDIM];
// map of directions (0: East, 1: North, 2: West, 3: South)
int dirMap[IDIM][JDIM];
struct Location
{
int row, col;
Location()
{
row = col = 0;
};
Location(int r, int c)
{
row = r;
col = c;
};
};
class Node
{
// current position
int rPos;
int cPos;
// total distance already travelled to reach the node
int GValue;
// FValue = GValue + remaining distance estimate
int FValue; // smaller FValue gets priority
public:
Node(const Location &loc;, int g, int f)
{rPos = loc.row; cPos = loc.col; GValue = g; FValue = f;}
Location getLocation() const {return Location(rPos,cPos);}
int getGValue() const {return GValue;}
int getFValue() const {return FValue;}
void calculateFValue(const Location& locDest)
{
FValue = GValue + getHValue(locDest) * 10;
}
void updateGValue(const int & i) // i: direction
{
GValue += (NDIR == 8 ? (i % 2 == 0 ? 10 : 14) : 10);
}
// Estimation function for the remaining distance to the goal.
const int & getHValue(const Location& locDest) const
{
static int rd, cd, d;
rd = locDest.row - rPos;
cd = locDest.col - cPos;
// Euclidian Distance
// d = static_cast<int>(sqrt((double)(rd*rd+cd*cd)));
// Manhattan distance
d = abs(rd) + abs(cd);
// Chebyshev distance
//d = max(abs(rd), abs(cd));
return(d);
}
// Determine FValue (in the priority queue)
friend bool operator<(const Node & a, const Node & b)
{
return a.getFValue() > b.getFValue();
}
};
// A-star algorithm.
// The path returned is a string of direction digits.
string pathFind( const Location &locStart; ,
const Location &locFinish; )
{
// list of open (not-yet-checked-out) nodes
static priority_queue<Node> q[2];
// q index
static int qi;
static Node* pNode1;
static Node* pNode2;
static int i, j, row, col, iNext, jNext;
static char c;
qi = 0;
// reset the Node lists (0 = ".")
for(j = 0; j < JDIM; j++) {
for(i = 0; i < IDIM; i++) {
closedNodes[i][j] = 0;
openNodes[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// create the start node and push into list of open nodes
pNode1 = new Node(locStart, 0, 0);
pNode1->calculateFValue(locFinish);
q[qi].push(*pNode1);
// A* search
while(!q[qi].empty()) {
// get the current node w/ the lowest FValue
// from the list of open nodes
pNode1 = new Node( q[qi].top().getLocation(),
q[qi].top().getGValue(), q[qi].top().getFValue());
row = (pNode1->getLocation()).row;
col = pNode1->getLocation().col;
cout << "row, col=" << row << "," << col << endl;
// remove the node from the open list
q[qi].pop();
openNodes[row][col] = 0;
// mark it on the closed nodes list
closedNodes[row][col] = 1;
// stop searching when the goal state is reached
if(row == locFinish.row && col == locFinish.col) {
// drawing direction map
cout << endl;
for(j = JDIM - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
for(i = 0; i < IDIM; i++) {
cout << dirMap[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// generate the path from finish to start from dirMap
string path = "";
while(!(row == locStart.row && col == locStart.col)) {
j = dirMap[row][col];
c = '0' + (j + NDIR/2) % NDIR;
path = c + path;
row += iDir[j];
col += jDir[j];
}
// garbage collection
delete pNode1;
// empty the leftover nodes
while(!q[qi].empty()) q[qi].pop();
return path;
}
// generate moves in all possible directions
for(i = 0; i < NDIR; i++) {
iNext = row + iDir[i];
jNext = col + jDir[i];
// if not wall (obstacle) nor in the closed list
if(!(iNext < 0 || iNext > IDIM - 1 || jNext < 0 || jNext > JDIM - 1 ||
squares[iNext][jNext] == 1 || closedNodes[iNext][jNext] == 1)) {
// generate a child node
pNode2 = new Node( Location(iNext, jNext), pNode1->getGValue(), pNode1->getFValue());
pNode2->updateGValue(i);
pNode2->calculateFValue(locFinish);
// if it is not in the open list then add into that
if(openNodes[iNext][jNext] == 0) {
openNodes[iNext][jNext] = pNode2->getFValue();
q[qi].push(*pNode2);
// mark its parent node direction
dirMap[iNext][jNext] = (i + NDIR/2) % NDIR;
}
// already in the open list
else if(openNodes[iNext][jNext] > pNode2->getFValue()) {
// update the FValue info
openNodes[iNext][jNext] = pNode2->getFValue();
// update the parent direction info, mark its parent node direction
dirMap[iNext][jNext] = (i + NDIR/2) % NDIR;
// replace the node by emptying one q to the other one
// except the node to be replaced will be ignored
// and the new node will be pushed in instead
while(!(q[qi].top().getLocation().row == iNext &&
q[qi].top().getLocation().col == jNext)) {
q[1 - qi].push(q[qi].top());
q[qi].pop();
}
// remove the wanted node
q[qi].pop();
// empty the larger size q to the smaller one
if(q[qi].size() > q[1 - qi].size()) qi = 1 - qi;
while(!q[qi].empty()) {
q[1 - qi].push(q[qi].top());
q[qi].pop();
}
qi = 1 - qi;
// add the better node instead
q[qi].push(*pNode2);
}
else delete pNode2;
}
}
delete pNode1;
}
// no path found
return "";
}
int main()
{
// create empty squares
for(int j = 0; j < JDIM; j++) {
for(int i = 0; i < IDIM; i++) squares[i][j] = 0;
}
// make wall
squares[4][2] = 1;
squares[4][3] = 1;
squares[4][4] = 1;
// starting and ending positions
int iStart = 2,jStart = 3;
int iEnd = 6,jEnd = 3;
cout << "Grid Size (IDIM,JDIM): "<< IDIM<< "," << JDIM << endl;
cout << "Start: " << iStart<<","<< jStart << endl;
cout << "Finish: " << iEnd<<","<< jEnd << endl;
clock_t start = clock();
// get the path
string path = pathFind(Location(iStart, jStart), Location(iEnd, jEnd));
clock_t end = clock();
double time = double(end - start);
cout << "Time (ms): "<< time << endl;
cout << "path: " << path << endl;
// follow the path on the squares and display it
if(path.length() > 0) {
char c;
int m,n;
int i = iStart;
int j = jStart;
squares[i][j] = 2;
for(m = 0; m < path.length(); m++) {
c = path.at(m);
n = atoi(&c;);
i = i + iDir[n];
j = j + jDir[n];
squares[i][j] = 3;
}
squares[i][j] = 4;
// display the squares with the path
for(j = JDIM - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
for(i = 0; i < IDIM; i++) {
if(squares[i][j] == 0)
cout << ".";
else if(squares[i][j] == 1)
cout << "O"; //obstacle
else if(squares[i][j] == 2)
cout << "I"; //Initial
else if(squares[i][j] == 3)
cout << "P"; //path
else if(squares[i][j] == 4)
cout << "F"; //final
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return(0);
}
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization