scikit-learn : Features and feature extraction

Machine Learning 101: General Concepts summarized Machine learning as follows:
- Know how to extract features from real-world data in order to perform machine learning tasks.
Feature extraction involves reducing the amount of resources required to describe a large set of data.
When performing analysis of complex data one of the major problems stems from the number of variables involved.
Analysis with a large number of variables generally requires a large amount of memory and computation power, also it may cause a classification algorithm to overfit to training samples and generalize poorly to new samples.
Feature extraction is a general term for methods of constructing combinations of the variables to get around these problems while still describing the data with sufficient accuracy.
- Feature extraction - wiki - Know the basic categories of supervised learning, including classification and regression problems.
- Know the basic categories of unsupervised learning, including dimensionality reduction and clustering.
- Understand the distinction between linearly separable and non-linearly separable data.
"Machine Learning is about building programs with tunable parameters (typically an array of floating point values) that are adjusted automatically so as to improve their behavior by adapting to previously seen data."
The diagram shown below is a typical workflow diagram for using machine learning.
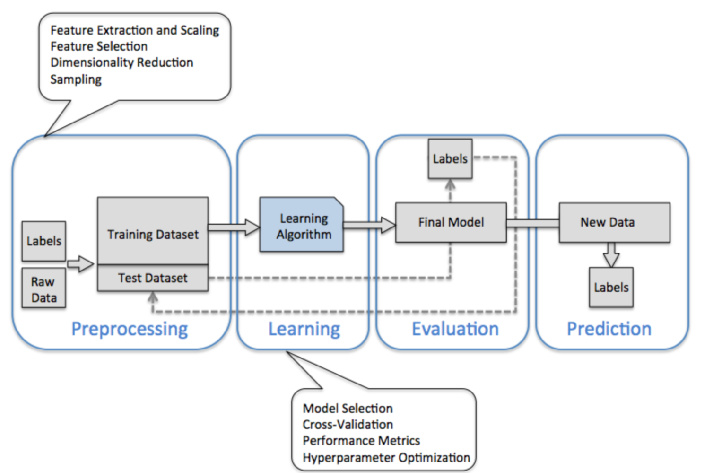
- Preprocessing - getting data into shape
Raw data rarely comes in the form and shape that is necessary for the optimal performance of a learning algorithm.
So, the preprocessing of the data is one of the most crucial steps in any machine learning application. If we take the Iris flower data set in the next section, we could think of the raw data as a series of flower images from which we want to extract meaningful features.
Useful features could be the color, the hue, the intensity of the flowers, the height, and the flower lengths and widths.
Some of the selected features may be highly correlated and therefore redundant to a certain degree. In those cases, dimensionality reduction techniques are useful for compressing the features onto a lower dimensional subspace. Reducing the dimensionality of our feature space has the advantage that less storage space is required, and the learning algorithm can run much faster.
- Training and selecting a predictive model
- Evaluating models and predicting unseen data instances
After we have selected a model that has been fitted on the training data set, we can use the test data set to estimate how well it performs on this unseen data to estimate the generalization error.
If we are satisfied with its performance, we can now use this model to predict new, future data.
It is important to note that the parameters for the previously mentioned procedures such as feature scaling and dimensionality reduction are solely obtained from the training data set, and the same parameters are later reapplied to transform the test data set, as well as any new data samples.
The picture and the description of the process are from "Python Machine Learning by Sebastian Raschka, 2015"
The version numbers of the major Python packages that were used throughout this tutorial are listed below:
- NumPy 1.9.1
- SciPy 0.14.0
- scikit-learn 0.15.2
- matplotlib 1.4.0
- pandas 0.15.2
The scikit-learn API combines a user-friendly interface with a highly optimized implementation of several classification algorithms.
The scikit-learn library offers not only a large variety of learning algorithms, but also many convenient functions such as preprocessing data, fine-tuning, and evaluating our models.
Most machine learning algorithms implemented in scikit-learn expect a numpy array as input X that has (n_samples, n_features) shape.
- n_samples: The number of samples.
- n_features: The number of features or distinct traits that can be used to describe each item in a quantitative manner.
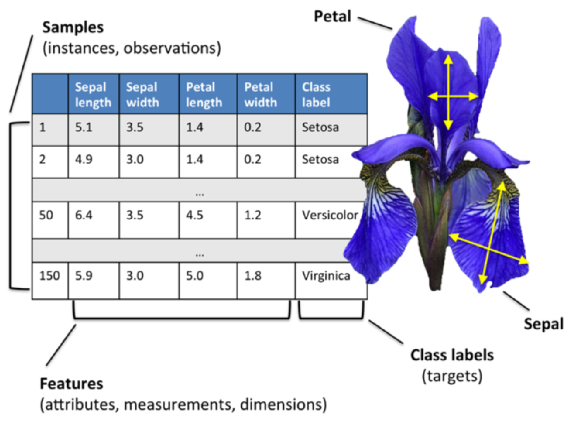
Picture credit: Python Machine Learning by Sebastian Raschka, 2015
The data set of this tutorial consists of 50 samples from each of three species of Iris (Iris setosa, Iris virginica and Iris versicolor).
Four features were measured from each sample: the length and the width of the sepals and petals, in centimeters. Based on the combination of these four features, Fisher developed a linear discriminant model to distinguish the species from each other." - Iris flower data set
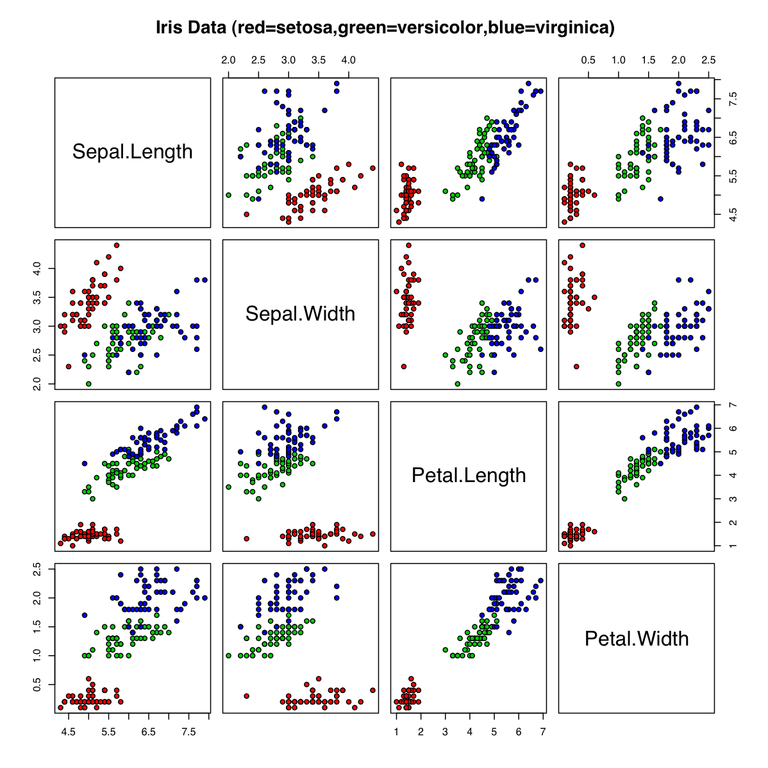
Picture source - Iris flower data set
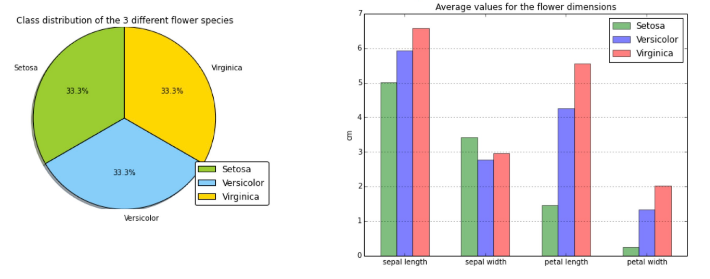
Picture source - Predictive modeling, supervised machine learning, and pattern classification
scikit-learn loads data from CSV file into numpy arrays:
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris >>> iris = load_iris()
The data attribute of the dataset stores the features of each sample flower:
>>> iris.data
array([[ 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.9, 3. , 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
...
[ 6.5, 3. , 5.2, 2. ],
[ 6.2, 3.4, 5.4, 2.3],
[ 5.9, 3. , 5.1, 1.8]])
>>>
>>> n_samples, n_features = iris.data.shape
>>> n_samples
150
>>> n_features
4
>>> iris.data.shape
(150, 4)
The target attribute of the dataset stores the information about the class of each sample:
>>> len(iris.target)
150
>>> iris.target
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
The target_names attribute stores the names of the classes:
>>> iris.target_names
array(['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'],
dtype='|S10')
If we just want a portion of dataset, for example, "Petal length" and "Petal width", we can extract like this:
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> import numpy as np
>>> iris = datasets.load_iris()
>>> X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
>>> X
array([[ 1.4, 0.2],
[ 1.4, 0.2],
[ 1.3, 0.2],
[ 1.5, 0.2],
...
[ 5. , 1.9],
[ 5.2, 2. ],
[ 5.4, 2.3],
[ 5.1, 1.8]])
If we do np.unique(y) to return the different class labels stored in iris. target, we can see Iris flower class names, Iris-Setosa, Iris-Versicolor, and Iris-Virginica, which are stored as integers ( 0 , 1 , 2 ):
>>> y = iris.target >>> np.unique(y) array([0, 1, 2])
Machine Learning with scikit-learn
scikit-learn installation
scikit-learn : Features and feature extraction - iris dataset
scikit-learn : Machine Learning Quick Preview
scikit-learn : Data Preprocessing I - Missing / Categorical data
scikit-learn : Data Preprocessing II - Partitioning a dataset / Feature scaling / Feature Selection / Regularization
scikit-learn : Data Preprocessing III - Dimensionality reduction vis Sequential feature selection / Assessing feature importance via random forests
Data Compression via Dimensionality Reduction I - Principal component analysis (PCA)
scikit-learn : Data Compression via Dimensionality Reduction II - Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
scikit-learn : Data Compression via Dimensionality Reduction III - Nonlinear mappings via kernel principal component (KPCA) analysis
scikit-learn : Logistic Regression, Overfitting & regularization
scikit-learn : Supervised Learning & Unsupervised Learning - e.g. Unsupervised PCA dimensionality reduction with iris dataset
scikit-learn : Unsupervised_Learning - KMeans clustering with iris dataset
scikit-learn : Linearly Separable Data - Linear Model & (Gaussian) radial basis function kernel (RBF kernel)
scikit-learn : Decision Tree Learning I - Entropy, Gini, and Information Gain
scikit-learn : Decision Tree Learning II - Constructing the Decision Tree
scikit-learn : Random Decision Forests Classification
scikit-learn : Support Vector Machines (SVM)
scikit-learn : Support Vector Machines (SVM) II
Flask with Embedded Machine Learning I : Serializing with pickle and DB setup
Flask with Embedded Machine Learning II : Basic Flask App
Flask with Embedded Machine Learning III : Embedding Classifier
Flask with Embedded Machine Learning IV : Deploy
Flask with Embedded Machine Learning V : Updating the classifier
scikit-learn : Sample of a spam comment filter using SVM - classifying a good one or a bad one
Machine learning algorithms and concepts
Batch gradient descent algorithmSingle Layer Neural Network - Perceptron model on the Iris dataset using Heaviside step activation function
Batch gradient descent versus stochastic gradient descent
Single Layer Neural Network - Adaptive Linear Neuron using linear (identity) activation function with batch gradient descent method
Single Layer Neural Network : Adaptive Linear Neuron using linear (identity) activation function with stochastic gradient descent (SGD)
Logistic Regression
VC (Vapnik-Chervonenkis) Dimension and Shatter
Bias-variance tradeoff
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE)
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
minHash
tf-idf weight
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Sentiment Analysis I (IMDb & bag-of-words)
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Sentiment Analysis II (tokenization, stemming, and stop words)
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Sentiment Analysis III (training & cross validation)
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Sentiment Analysis IV (out-of-core)
Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) using Cosine Distance (Cosine Similarity)
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
[Note] Sources are available at Github - Jupyter notebook files1. Introduction
2. Forward Propagation
3. Gradient Descent
4. Backpropagation of Errors
5. Checking gradient
6. Training via BFGS
7. Overfitting & Regularization
8. Deep Learning I : Image Recognition (Image uploading)
9. Deep Learning II : Image Recognition (Image classification)
10 - Deep Learning III : Deep Learning III : Theano, TensorFlow, and Keras
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization