json.dump(s) & json.load(s)

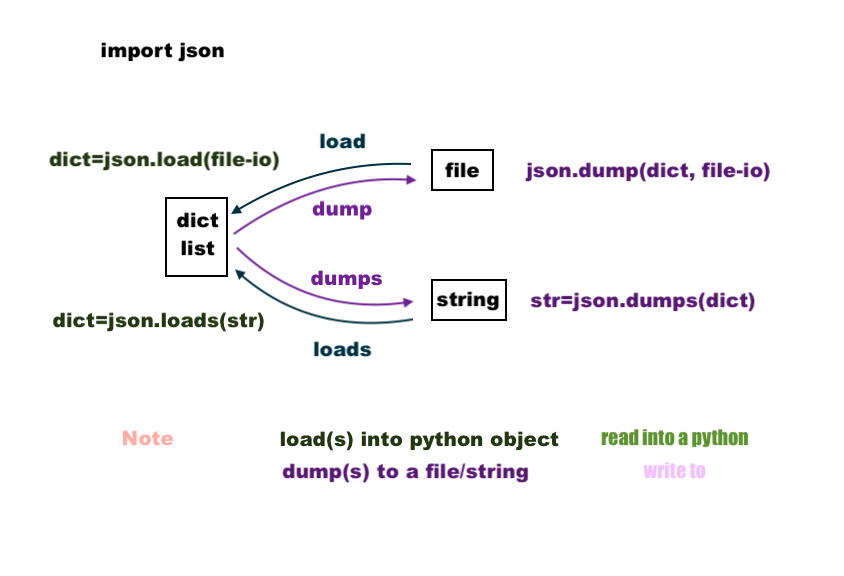
There are two ways of reading in (load/loads) the following json file, in.json:
{"alpha": 1, "beta": 2}
- string:
import json io = open("in.json","r") string = io.read() # json.loads(str) dictionary = json.loads(string) # or one-liner # dictionary = json.loads(open("in.json","r").read()) print(dictionary) - dictionary:
import json # json.load(_io) io = open("in.json","r") dictionary = json.load(io) # or one-liner # dictionary = json.load(open("in.json","r")) print(dictionary)
Both will print out:
{'alpha': 1, 'beta': 2}
Note that while the json.loads() requires string, load(s,...), the json.load() requires file descriptor, load(fp...).
Similarly, we can write a (dump/dumps) json file:
- string:
import json d = {'alpha': 1, 'beta': 2} s = json.dumps(d) open("out.json","w").write(s) - dictionary:
import json d = {'alpha': 1, 'beta': 2} json.dump(d, open("out.json","w"))
Note that the json.dump() requires file descriptor as well as an obj, dump(obj, fp...).
In the following example, we'll convert Python dictionary to JSON and write it to a text file. Then, we'll read in back from the file and play with it.
Initially we'll construct Python dictionary like this:
# Four Fundamental Forces with JSON
d = {}
d ["gravity"] = {
"mediator":"gravitons",
"relative strength" : "1",
"range" : "infinity"
}
d ["weak"] = {
"mediator":"W/Z bosons",
"relative strength" : "10^25",
"range" : "10^-18"
}
d ["electromagnetic"] = {
"mediator":"photons",
"relative strength" : "10^36",
"range" : "infinity"
}
d ["strong"] = {
"mediator":"gluons",
"relative strength" : "10^38",
"range" : "10^-15"
}
print(d)
The output looks like this:
{'electromagnetic': {'relative strength': '10^36', 'range': 'infinity', 'mediator': 'photons'}, 'strong': {'relative strength': '10^38', 'range': '10^-15', 'mediator': 'gluons'}, 'weak': {'relative strength': '10^25', 'range': '10^-18', 'mediator': 'W/Z bosons'}, 'gravity': {'relative strength': '1', 'range': 'infinity', 'mediator': 'gravitons'}}
Now, we want to convert the dictionary to a string using json.dumps:
import json data = json.dumps(d) print(type(data)) print(data)
Output:
<type 'str'>
{"electromagnetic": {"relative strength": "10^36", "range": "infinity", "mediator": "photons"}, "strong": {"relative strength": "10^38", "range": "10^-15", "mediator": "gluons"}, "weak": {"relative strength": "10^25", "range": "10^-18", "mediator": "W/Z bosons"}, "gravity": {"relative strength": "1", "range": "infinity", "mediator": "gravitons"}}
Note that the "json.dumps()" returns a string as indicated by the "s" at the end of "dumps". This process is called encoding.
Let's write it to a file:
import json
data = json.dumps(d)
with open("4forces.json","w") as f:
f.write(data)
Now that the file is written. Let's reads it back and decoding the JSON-encoded string back into a Python dictionary data structure:
# reads it back
with open("4forces.json","r") as f:
data = f.read()
# decoding the JSON to dictionay
d = json.loads(data)
Let's play with the dictionary a little bit.
What's the relative strength of electromagnetic compared to gravity?
print(d["electromagnetic"]["relative strength"]) 10^36
Who's the mediator for "strong" force?
print(d["strong"]["mediator"]) gluons
Ok, here is the full code:
# Four Fundamental Forces with JSON
d = {}
d ["gravity"] = {
"mediator":"gravitons",
"relative strength" : "1",
"range" : "infinity"
}
d ["weak"] = {
"mediator":"W/Z bosons",
"relative strength" : "10^25",
"range" : "10^-18"
}
d ["electromagnetic"] = {
"mediator":"photons",
"relative strength" : "10^36",
"range" : "infinity"
}
d ["strong"] = {
"mediator":"gluons",
"relative strength" : "10^38",
"range" : "10^-15"
}
import json
# encoding to JSON
data = json.dumps(d)
# write to a file
with open("4forces.json","w") as f:
f.write(data)
# reads it back
with open("4forces.json","r") as f:
data = f.read()
# decoding the JSON to dictionay
d = json.loads(data)
print(d)
If we prefer working with files instead of strings, we may want to use json.dump() / json.load() to encode / decode JSON data using the data from the previous example:
# write to a file
with open("4forces.json","w") as f:
json.dump(d, f)
# reads it back
with open("4forces.json","r") as f:
d = json.load(f)
Here is another example (json.dump()/json.load()) using simpler data:
import json
# in.json file - {"alpha":1, "beta":2}
with open("in.json","r") as fr:
out_dict = json.load(fr)
print(out_dict)
in_dict = {"a":1,"b":2}
with open("out.json","w") as fw:
json.dump(in_dict, fw)
# out.json file - {"a":1,"b":2}
Usage for string version: json.loads()/json.dumps():
import json
# string version of json load & dump
# in.json file - {"alpha":1, "beta":2}
with open("in.json", "r") as fr:
out_str = fr.read()
out_dict = json.loads(out_str)
# in_dict = {"a":1,"b":2}
in_str = json.dumps(in_dict)
with open("out.json","w") as fw:
fw.write(in_str)
# out.json file - {"a":1,"b":2}
Another example:
import json
# dict from a string : json.loads(string)
with open("bogo.json","r") as f:
a = f.read()
s_d = json.loads(a)
print(f"type(s_d) = {type(s_d)}, sd = {s_d}")
# dict from a file : json.load(file Pointer)
f_d = json.load(open("bogo.json","r"))
print(f"type(f_d) = {type(f_d)}, fd = {f_d}")
# dump dict as a string
d_s = json.dumps(s_d)
print(f"type(ds_) = {type(d_s)}, ds = {d_s}")
# dump dict as a file
json.dump(f_d, open("bogo_dumped.json","w"))
bogo.json:
{
"5-extinctions":
{
"1st": "Ordovician extinction",
"2nd": "Devonian extinction",
"3rd": "Permian extinction",
"4th": "Triassic extinction",
"5th": "K-T extinction"
}
}
Output:
type(s_d) =, sd = {'5-extinctions': {'1st': 'Ordovician extinction', '2nd': 'Devonian extinction', '3rd': 'Permian extinction', '4th': 'Triassic extinction', '5th': 'K-T extinction'}} type(f_d) = , fd = {'5-extinctions': {'1st': 'Ordovician extinction', '2nd': 'Devonian extinction', '3rd': 'Permian extinction', '4th': 'Triassic extinction', '5th': 'K-T extinction'}} type(ds_) = , ds = {"5-extinctions": {"1st": "Ordovician extinction", "2nd": "Devonian extinction", "3rd": "Permian extinction", "4th": "Triassic extinction", "5th": "K-T extinction"}}
The following example sends a syslog to logstash fargate containers behind AWS NLB:
import socket
import json
import sys
HOST = 'demo-NLB-.....elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com'
PORT = 6514
try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
except socket.error as error:
if error.errno == errno.ECONNREFUSED:
print(os.strerror(error.errno))
else:
raise
try:
sock.connect((HOST, PORT))
except socket.error as error:
if error.errno == errno.ECONNREFUSED:
print(os.strerror(error.errno))
else:
raise
msg = {'@message': 'May 11 10:40:48 scrooge disk-health-nurse[26783]: [ID 702911 user.error] m:SY-mon-full-500 c:H : partition health measures for /var did not suffice - still using 96% of partition space', '@tags': ['python', 'test']}
sock.send(json.dumps(msg).encode())
sock.close()
sys.exit(0)
note that for the HOST, we can also use FQDN instead of the NLB's domain name.
Also, as usual, instead of the long line of code, we may want to use a simple linux command, nc:
$ echo "message at $(date) from khong" | nc demo-NLB-.....elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com 6514
If the NLB listener protocol is TLS, we can use openssl echo to the TLS NLB:
$ echo "message at $(date) from khong's mac" | openssl s_client -connect demo-TSL-NLB-.....elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:6514 -ign_eof
Another example: AWS API response.
When we make an AWS API call, the response can be an invalid json due to datetime:
datetime.datetime(2021, 8, 25, 22, 45, 28, tzinfo = tzutc())
We need to serialize it (ow to overcome “datetime.datetime not JSON serializable”?).
Here is a boto3 code for an API call to EC2 describe:
import boto3
import json
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
response = ec2.describe_instances()
s = json.dumps(response, default=str)
open("r.json","w").write(s)
print(response)
The r.json with jq looks like this:
$ cat r.json | jq '.'
{
"Reservations": [
{
"Groups": [],
"Instances": [
{
"AmiLaunchIndex": 0,
"ImageId": "ami-083ac7c7ecf9bb9b0",
"InstanceId": "i-065ddf45930536083",
"InstanceType": "t2.micro",
"LaunchTime": "2021-08-25 22:45:28+00:00",
"Monitoring": {
"State": "disabled"
},
"Placement": {
"AvailabilityZone": "us-west-2a",
"GroupName": "",
"Tenancy": "default"
},
"PrivateDnsName": "ip-10-99-101-164.us-west-2.compute.internal",
"PrivateIpAddress": "10.99.101.164",
"ProductCodes": [],
"PublicDnsName": "ec2-34-219-168-233.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com",
"PublicIpAddress": "34.219.168.233",
"State": {
"Code": 16,
"Name": "running"
},
"StateTransitionReason": "",
"SubnetId": "subnet-0c28e356543ecb34f",
"VpcId": "vpc-02fda1ad9b61c51a2",
"Architecture": "x86_64",
"BlockDeviceMappings": [
{
"DeviceName": "/dev/xvda",
"Ebs": {
"AttachTime": "2021-08-25 22:45:29+00:00",
"DeleteOnTermination": true,
"Status": "attached",
"VolumeId": "vol-0632c2b714a0cec83"
}
}
],
"ClientToken": "",
"EbsOptimized": false,
"EnaSupport": true,
"Hypervisor": "xen",
"IamInstanceProfile": {
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::197828489041:instance-profile/AmazonSSMRoleForInstancesQuickSetup",
"Id": "AIPAVPSFGBEENL5E6UYJ7"
},
"NetworkInterfaces": [
{
"Association": {
"IpOwnerId": "amazon",
"PublicDnsName": "ec2-34-219-168-233.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com",
"PublicIp": "34.219.168.233"
},
"Attachment": {
"AttachTime": "2021-08-25 22:45:28+00:00",
"AttachmentId": "eni-attach-0e740740b080380ab",
"DeleteOnTermination": true,
"DeviceIndex": 0,
"Status": "attached",
"NetworkCardIndex": 0
},
"Description": "Primary network interface",
"Groups": [
{
"GroupName": "delete-me",
"GroupId": "sg-00bee859aca8c03ab"
}
],
"Ipv6Addresses": [],
"MacAddress": "02:06:a7:41:c0:73",
"NetworkInterfaceId": "eni-089753322166f05ab",
"OwnerId": "197828489041",
"PrivateDnsName": "ip-10-99-101-164.us-west-2.compute.internal",
"PrivateIpAddress": "10.99.101.164",
"PrivateIpAddresses": [
{
"Association": {
"IpOwnerId": "amazon",
"PublicDnsName": "ec2-34-219-168-233.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com",
"PublicIp": "34.219.168.233"
},
"Primary": true,
"PrivateDnsName": "ip-10-99-101-164.us-west-2.compute.internal",
"PrivateIpAddress": "10.99.101.164"
}
],
"SourceDestCheck": true,
"Status": "in-use",
"SubnetId": "subnet-0c28e356543ecb34f",
"VpcId": "vpc-02fda1ad9b61c51a2",
"InterfaceType": "interface"
}
],
"RootDeviceName": "/dev/xvda",
"RootDeviceType": "ebs",
"SecurityGroups": [
{
"GroupName": "delete-me",
"GroupId": "sg-00bee859aca8c03ab"
}
],
"SourceDestCheck": true,
"VirtualizationType": "hvm",
"CpuOptions": {
"CoreCount": 1,
"ThreadsPerCore": 1
},
"CapacityReservationSpecification": {
"CapacityReservationPreference": "open"
},
"HibernationOptions": {
"Configured": false
},
"MetadataOptions": {
"State": "applied",
"HttpTokens": "optional",
"HttpPutResponseHopLimit": 1,
"HttpEndpoint": "enabled",
"HttpProtocolIpv6": "disabled"
},
"EnclaveOptions": {
"Enabled": false
}
}
],
"OwnerId": "197828489041",
"ReservationId": "r-0b6752f9a69f3ba08"
}
],
"ResponseMetadata": {
"RequestId": "5cd271e5-3631-4e4c-a07d-78d169514e39",
"HTTPStatusCode": 200,
"HTTPHeaders": {
"x-amzn-requestid": "5cd271e5-3631-4e4c-a07d-78d169514e39",
"cache-control": "no-cache, no-store",
"strict-transport-security": "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains",
"content-type": "text/xml;charset=UTF-8",
"content-length": "7803",
"vary": "accept-encoding",
"date": "Thu, 26 Aug 2021 00:02:15 GMT",
"server": "AmazonEC2"
},
"RetryAttempts": 0
}
}
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization