Coding Questions VII - 2024

Given two srings, how can we tell if the two strings are anagrams (i.e., below = elbow, study = dusty, night = thing)?
def isAnagram(w1,w2):
sw1 = ''.join(sorted(w1))
sw2 = ''.join(sorted(w2))
if sw1 == sw2:
return True
return False
words = [("evil","vile"), ("pat","tap"),("mile","nile")]
for w in words:
print(w,isAnagram(w[0],w[1]))
First, convert the two strings into sorted lists and make them new strings. Then, compare the two strings if they are the same, which means they are anagrams.
Output:
(('evil', 'vile'), True)
(('pat', 'tap'), True)
(('mile', 'nile'), False)
Note: we used sorted(mylist) here. It returns a new list. We can also use mylist.sort() for in-place sorting and this returns None.
Alice is taking a cryptography class and finding anagrams to be very useful. We consider two strings to be anagrams of each other if the first string's letters can be rearranged to form the second string. In other words, both strings must contain the same exact letters in the same exact frequency For example, bacdc and dcbac are anagrams, but bacdc and dcbad are not.
Alice decides on an encryption scheme involving two large strings where encryption is dependent on the minimum number of character deletions required to make the two strings anagrams. Can you help her find this number?
Given two strings, a and b, that may or may not be of the same length, determine the minimum number of character deletions required to make a and b anagrams. Any characters can be deleted from either of the strings.
For example, if a=cde and b=dcf, we can delete 'e' from string a and 'f' from string b so that both remaining strings are anagrams.
Problem source - https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges
Here is the code:
def make_ana(x,y):
if len(x) != len(y):
return -1
# construct dictionary { ch:frequent }
xd = dict((ch, x.count(ch)) for ch in x)
yd = dict((ch, y.count(ch)) for ch in y)
print(xd); print(yd)
count = 0
for k,v in xd.items():
# The key is not in yd
if k not in yd.keys():
count += 1
# The key is also in yd but the frequency is different
else:
if v - yd[k] > 0:
count += v - yd[k]
for k,v in yd.items():
# The key is not in xd
if k not in xd.keys():
count += 1
# The key is also in xd but the frequency is different
else:
if v - xd[k] > 0:
count += v - xd[k]
return count
x1 = 'cde'
y1 = 'abc'
rm = make_ana(x1,y1)
print(rm)
x2 = 'cde'
y2 = 'dcf'
rm = make_ana(x2,y2)
print(rm)
x2 = 'aaaaab'
y2 = 'bbbbba'
rm = make_ana(x2,y2)
print(rm)
Output:
{'c': 1, 'd': 1, 'e': 1}
{'a': 1, 'b': 1, 'c': 1}
4
{'c': 1, 'd': 1, 'e': 1}
{'d': 1, 'c': 1, 'f': 1}
2
{'a': 5, 'b': 1}
{'b': 5, 'a': 1}
8
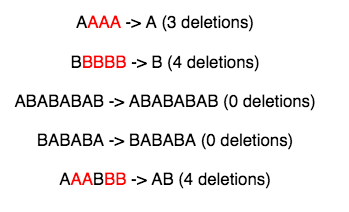
We are given a string containing characters A and B only. Our task is to change it into a string such that there are no matching adjacent characters. To do this, we are allowed to delete zero or more characters in the string.
Our task is to find the minimum number of required deletions.
Here is the code:
def alt_char(mystr):
alt = []
count = 0
for c in mystr:
if len(alt) == 0:
alt.append(c)
else:
if alt[-1] != c:
alt.append(c)
else:
count += 1
pass
return count
mystr = ['AAAA','BBBBB','ABABABAB','BABABA','AAABBB']
for s in mystr:
c = alt_char(s)
print('%s : %d' %(s,c))
Output:
AAAA : 3 BBBBB : 4 ABABABAB : 0 BABABA : 0 AAABBB : 4
Similar code:
def ndel(word):
prev = word[0]
count = 0
for i in range(1,len(word)):
if word[i] == prev:
count += 1
else:
prev = word[i]
return count
mystr = ['AAAA','BBBBB','ABABABAB','BABABA','AAABBB']
for s in mystr:
print('%s: %d characters to delete ' %(s, ndel(s)))
Output:
AAAA: 3 characters to delete BBBBB: 4 characters to delete ABABABAB: 0 characters to delete BABABA: 0 characters to delete AAABBB: 4 characters to delete
A string is said to be a special palindromic string if either of two conditions is met:
- All of the characters are the same, e.g. aaa.
- All characters except the middle one are the same, e.g. aadaa.
In other words, a substring is called special palindromic substring if all the characters in the substring are same or only the middle character is different for odd length. For example, "aabaa" and "aaa" are special palindromic substrings but "abcba" is not a special palindromic substring.
Given a string, determine how many special palindromic substrings can be formed from it.
Here is the code:
def special_palindrome(st):
pal = []
for i in range(len(st)):
j = i + 1
while j < len(st):
sub = st[i:j]
if sub == sub[::-1]:
pal.append(sub)
j += 1
return pal
mystr = ['asasd','mnonopoo','abcbaba','aaaa']
for st in mystr:
pal = special_palindrome(st)
print('%s, %s, %d' %(st, pal,len(pal)))
Output:
asasd, ['a', 'asa', 's', 'sas', 'a', 's'], 6 mnonopoo, ['m', 'n', 'non', 'o', 'ono', 'n', 'o', 'opo', 'p', 'o'], 10 abcbaba, ['a', 'abcba', 'b', 'bcb', 'c', 'b', 'bab', 'a', 'b'], 9 aaaa, ['a', 'aa', 'aaa', 'a', 'aa', 'a'], 6
We consider a string to be valid if all characters of the string appear the same number of times. It is also valid string if he can remove just 1 character in a string and the remaining characters will occur the same number of times.
For example, "abbca" is valid because by removing 'c' we can make it "abba" (both of 'a' and 'b' appear two times). But "aabbcd" is not because need to remove at least two characters ('c' and 'd'), not just one character.
Given a string s, determine if it is valid. If so, return True, otherwise return False.Problem source - https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges
Here is the code:
def isValid(st):
d = dict([(c,st.count(c)) for c in st])
mn = min(d.values())
mx = max(d.values())
if mx - mn == 0:
return d, True
elif mx - mn == 1:
freq = {}.fromkeys([mn,mx],0)
for k,v in d.items():
freq[v] += 1
print('freq=',freq)
if 1 in freq.values():
return d, True
else:
return d, False
else:
return d, False
mystr = ['abc','abcc','aabbcd','aabbccddeefghi','abcdefghhgfedecba','abbccc']
for st in mystr:
d, ret = isValid(st)
print('%s - %s %s' %(st, d, ret))
print()
Output:
abc - {'a': 1, 'b': 1, 'c': 1} True
freq= {1: 2, 2: 1}
abcc - {'a': 1, 'b': 1, 'c': 2} True
freq= {1: 2, 2: 2}
aabbcd - {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 1, 'd': 1} False
freq= {1: 4, 2: 5}
aabbccddeefghi - {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 2, 'd': 2, 'e': 2, 'f': 1, 'g': 1, 'h': 1, 'i': 1} False
freq= {2: 7, 3: 1}
abcdefghhgfedecba - {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 2, 'd': 2, 'e': 3, 'f': 2, 'g': 2, 'h': 2} True
abbccc - {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} False
Another code:
def isValid(st):
d = {w:st.count(w) for w in st}
print('st = %s, d = %s' %(st, d))
freq = [v for k,v in d.items()]
sfreq = list(set(freq))
# freqency : should be 1 or 2 but not greater than 2
if len(sfreq) > 2:
return False, '# of frequencies > 2'
if len(sfreq) == 1:
return True, ' already has the same number of chars'
# max & min freq
fmx = max(sfreq)
fmn = min(sfreq)
fmx_count = 0; fmn_count = 0
for f in freq:
if f == fmx:
fmx_count += 1
else:
fmn_count += 1
if fmx_count == 1 or fmn_count == 1:
return True, 'can remove 1 char'
else:
return False, ' at least 2 chars should be removed'
mystr = ['abc','abcc','aabbcd','aabbccddeefghi','abcdefghhgfedecba','abbccc']
for s in mystr:
print('%s: %s ' %(isValid(s)))
print()
Output:
st = abc, d = {'a': 1, 'b': 1, 'c': 1}
True: already has the same number of chars
st = abcc, d = {'a': 1, 'b': 1, 'c': 2}
True: can remove 1 char
st = aabbcd, d = {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 1, 'd': 1}
False: at least 2 chars should be removed
st = aabbccddeefghi, d = {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 2, 'd': 2, 'e': 2, 'f': 1, 'g': 1, 'h': 1, 'i': 1}
False: at least 2 chars should be removed
st = abcdefghhgfedecba, d = {'a': 2, 'b': 2, 'c': 2, 'd': 2, 'e': 3, 'f': 2, 'g': 2, 'h': 2}
True: can remove 1 char
st = abbccc, d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
False: # of frequencies > 2
A string is said to be a child of a another string if it can be formed by deleting 0 or more characters from the other string. Given two strings of equal length, what's the longest string that can be constructed such that it is a child of both?
For example, ABCD and ABDC have two children with maximum length 3, ABC and ABD. They can be formed by eliminating either the D or C from both strings. Note that we will not consider ABCD as a common child because we can't rearrange characters and ABCD !=ABDC.
Problem source - https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges
Here is the code:
def isCommonChild(st1,st2):
# construct new strings from the input, only with common characters
common1 = ''.join([c for c in st1 if c in st2])
common2 = ''.join([c for c in st2 if c in st1])
# no common chars, then just return with []
if not common1 or not common2:
return common1
# O(n^2)
# try every substring (with initial order of chars) of common1
# if it's a substring of common2.
# If it is, construct list of substrings
subcommon = []
mx = 0
for i in range(len(common1)):
j = i
while (j < len(common1)):
sub = common1[i:j+1]
if sub in common2:
subcommon.append(sub)
j += 1
print('subcommon=',subcommon)
# find the longes substring, and return it.
mxsub = max(subcommon, key=len)
return mxsub
mystr = [('ABCD','ABDC'), ('HARRY','SALLY'),('AA','BB'),('SHINCHAN','NOHARAAA'),('ABCDEF','FBDAMN')]
for st in mystr:
print(st)
ret = isCommonChild(st[0],st[1])
print(ret, len(ret))
print()
Output:
('ABCD', 'ABDC')
subcommon= ['A', 'AB', 'B', 'C', 'D']
AB 2
('HARRY', 'SALLY')
subcommon= ['A', 'AY', 'Y']
AY 2
('AA', 'BB')
0
('SHINCHAN', 'NOHARAAA')
subcommon= ['H', 'N', 'NH', 'NHA', 'H', 'HA', 'A', 'N']
NHA 3
('ABCDEF', 'FBDAMN')
subcommon= ['A', 'B', 'BD', 'D', 'F']
BD 2
HackerLand National Bank has a simple policy for warning clients about possible fraudulent account activity. If the amount spent by a client on a particular day is greater than or equal to 2x the client's median spending for a trailing number of days, they send the client a notification about potential fraud. The bank doesn't send the client any notifications until they have at least that trailing number of prior days' transaction data.
Given the number of trailing days d and a client's total daily expenditures [10,20,30,40,50] for a period of d days, find and print the number of times the client will receive a notification over all d days.
For example, d=3 and expenditures [10,20,30,40,50]. On the first three days, they just collect spending data. At day 4, we have trailing expenditures of [10,20,30]. The median is 20 and the day's expenditure is 40. Because 40 >= 20x2, there will be a notice. The next day, our trailing expenditures are [20,30,40] and the expenditures are 50. This is less than 2x30 so no notice will be sent. Over the period, there was one notice sent.
Problem source - https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges
Here is the code:
def isFraud(sp, days):
import statistics
notice = 0
for i in range(len(sp)):
if i >= days:
med = statistics.median(sp[i-days:i])
if sp[i] >= med*2:
notice += 1
return notice
# input ([spending], trainling days)
spending = [([10,20,30,40,50],3),([2,3,4,2,3,6,8,4,5],5),([1,2,3,4,4],4)]
for sp in spending:
notice = isFraud(sp[0],sp[1])
print("%s : %s " %(sp, notice))
Output:
([10, 20, 30, 40, 50], 3) : 1 ([2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 6, 8, 4, 5], 5) : 2 ([1, 2, 3, 4, 4], 4) : 0
There are a number of different toys, tagged with their prices. We have only a certain amount to spend, and we wants to maximize the number of toys we buy with this money.
Here is the code:
def isFraud(toys, money):
# sort prices of toy
st = sorted(toys)
nt = []
total = 0
for s in st:
total += s
if total <= money:
nt.append(s)
return nt
# input ([prices], money)
toys_money = [([1,2,3,4],7),([1,12,5,111,200,1000,10],50)]
for t in toys_money:
toys = isFraud(t[0],t[1])
print("%s : - %s, number of toys = %s" %(t, toys, len(toys)))
Output:
([1, 2, 3, 4], 7) : - [1, 2, 3], number of toys = 3 ([1, 12, 5, 111, 200, 1000, 10], 50) : - [1, 5, 10, 12], number of toys = 4
It must return an array of integers representing the maximum minimum value for each window size from 1 to n.
Please see https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges for the detailed description of the problem.
Here is the code:
def maxmin(a):
size = 1
mxwindows = []
# size variation from 1 to s
while size <= len(a):
windows = []
# looping the given array for a specfic size windows
for i in range(len(a)-size+1):
s = 0
window = []
# make a list - size of s
while s < size:
window.append(a[i+s])
s += 1
# attach a min size to windows list
windows.append(min(window))
size += 1
# get max from all mins of windows
mxwindows.append(max(windows))
return mxwindows
# input
arr = ([6,3,5,1,12],[2,6,1,12],[1,2,3,5,1,13,3],[3,5,4,7,6,2])
for a in arr:
val = maxmin(a)
print("%s : max of mins = %s" %(a, val))
Output:
[6, 3, 5, 1, 12] : max of mins = [12, 3, 3, 1, 1] [2, 6, 1, 12] : max of mins = [12, 2, 1, 1] [1, 2, 3, 5, 1, 13, 3] : max of mins = [13, 3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1] [3, 5, 4, 7, 6, 2] : max of mins = [7, 6, 4, 4, 3, 2]
There are a number of plants in a garden. Each of these plants has been treated with some amount of pesticide. After each day, if any plant has more pesticide than the plant on its left, being weaker than the left one, it dies.
We are given the initial values of the pesticide in each of the plants. Print the number of days after which no plant dies, i.e. the time after which there are no plants with more pesticide content than the plant to their left.
For example, pesticide levels p = [3,6,2,7,5]. Using a 1-indexed array, day 1 plants 2 and 4 die leaving p=[3,2,5]. On day 2, plant 3 of the current array dies leaving p=[3,2]. As there is no plant with a higher concentration of pesticide than the one to its left, plants stop dying after day 2.
It must return an integer representing the number of days until plants no longer die from pesticide.
Please see https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges for the detailed description of the problem.
Here is the code:
def plants(a):
alive = a
day = 1
while True:
die = []
for i in range(1, len(alive)):
current = alive[i]
if current > alive[i-1]:
die.append(i)
if not die:
return alive,day
else:
alive = [alive[i] for i in range(len(alive)) if i not in die]
print('plants alive at day %d is %s' %(day, alive))
day += 1
# input
level = [[3,6,2,7,5],[6,5,8,4,7,10,9]]
for l in level:
alive, day = plants(l)
print("%s : plants alive = %s Plants no longer die at day %d" %(l, alive, day))
Output:
plants alive at day 1 is [3, 2, 5] plants alive at day 2 is [3, 2] [3, 6, 2, 7, 5] : plants alive = [3, 2] Plants no longer die at day 3 plants alive at day 1 is [6, 5, 4, 9] plants alive at day 2 is [6, 5, 4] [6, 5, 8, 4, 7, 10, 9] : plants alive = [6, 5, 4] Plants no longer die at day 3
Initial code with O(n^2)-using list:
def common(arr1,arr2):
com = []
for a in arr1:
if a in arr2:
com.append(a)
return com
a = [1,3,5,7]
b = [3,5,8,9]
print(common(a,b)) # [3,5]
Same but more compact code:
def common(arr1,arr2):
return [x for x in arr2 if x in arr1]
a = [1,3,5,7]
b = [3,5,8,9]
print(common(a,b)) # [3,5]
The code is basically looping through to for loops, so in the worst case, the complexity becomes n^2.
To improve the performance, we may want to use set() which is implemented based on hash (similar to dict).
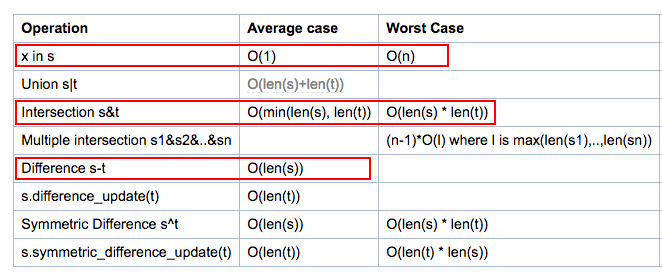
Pic from https://wiki.python.org/moin/TimeComplexity#set
First improvement can be achieved by converting the "list" to "set" while keeping the two loops (1 < complexity < n^2):
def common(arr1,arr2):
com = [x for x in set(arr2) if x in set(arr1)]
return com
a = [1,3,5,7]
b = [3,5,8,9]
print(common(a,b))
Additional improvements by using the set-difference:
def common(arr1,arr2):
s1 = set(arr1)
s2 = set(arr2)
com = s1 - (s1-s2)
return com
a = [1,3,5,7]
b = [3,5,8,9]
print(common(a,b)) # {3,5}
Now we have O(len(arr1)) by using set instead of O(n^2).
Note that we do not have nested loops. Well, converting a list to a set at least requires O(n) and adding hash to each element is O(1). So, not having nested for loop is the big thing here.
We may be tempted to use "set1.intersection(set2)", but it appears to be expensive than finding the difference of sets.
def common(arr1,arr2):
s1 = set(arr1)
s2 = set(arr2)
com = s1.intersection(s2)
return com
a = [1,3,5,7]
b = [3,5,8,9]
print(common(a,b)) # {3,5}
Using a decorator, write a code to measure execution time for a function. We can start from this:
from functools import wraps
def decorator_name(a_func):
@wraps(a_func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
a_func()
return a_func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
@decorator_name
def a_func_needs_decorator():
pass
# now "a_func_needs_decorator" is wrapped by the wrapper() function
a_func_needs_decorator()
Here is the code:
from functools import wraps
from time import time
def decorator_name(a_func):
@wraps(a_func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
st = time()
result = a_func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time()
print('{} - elapsed time: {}'.format(a_func.__name__, end-st))
return result
return wrapper
@decorator_name
def a_func_needs_decorator(r):
for _ in range(r):
pass
# now "a_func_needs_decorator" is wrapped by the wrapper() function
a_func_needs_decorator(10000000)
Output:
a_func_needs_decorator - elapsed time: 0.4498329162597656
For more on decorators, check http://book.pythontips.com/en/latest/decorators.html
Additional examples are available from here as well:
We have a Hello() function returning a string, "Hello World". Now, we want to make it lowercase and split it with space delimiter.
But we do not want to modify the Hello() and does it all with two decorators: lowercase_decorator and split_decorator. Here is the code:
def lowercase_decorator(func):
def wrapper():
f = func()
lowercase = f.lower()
return lowercase
return wrapper
def split_decorator(func):
def wrapper():
f = func()
split = f.split()
return split
return wrapper
@split_decorator
@lowercase_decorator
def Hello():
return "Hello World"
print(Hello())
Output:
['hello', 'world']
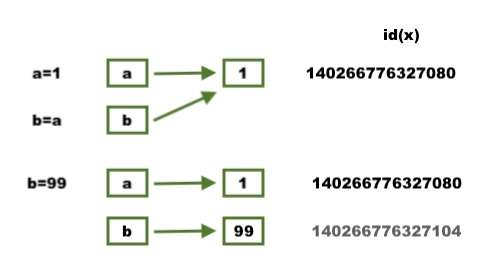
In the following code, Python selects a memory location for a and saves the integer value 1 at a=1.
At b=a Python lets b point to the memory location of a. So, a and b will have the same value of 1.
b=99, unlike C and C++ code where a will be changed to 99, b gets its own memory location, containing 99 and a still retains 1.
>>> a=1 >>> b=a >>> a 1 >>> b 1 >>> b=99 >>> a 1 >>> b 99 >>>
When we use assign (=) operator, user may think that this creates a new object. However, it doesn’t. It only creates a new variable that shares the reference of the original object.
For collections that are mutable or contain mutable items, a copy is sometimes needed so one can change one copy without changing the other.
The copy module provides generic shallow (copy.copy()) and deep copy (copy.deepcopy()) operations.
First, let's look into the assign (=) operator:
a = [1,2,3,[4,5,6],7]
b = a
a[0] = 11
b[1] = 22
print("a = %s" %a)
print("b = %s" %b)
Output:
a = [11, 22, 3, [4, 5, 6], 7] b = [11, 22, 3, [4, 5, 6], 7]
As we can see the a and b are the same object. Changing one is reflected on the other object. We can check it with id():
id(a) = 4547344288 id(b) = 4547344288
Building off of the previous example, modifying b will modify a if we don't create a shallow copy:
import copy
a = [1,2,3,[4,5,6],7]
b = a
c = copy.copy(a)
a[0] = 11
b[1] = 22
c[2] = 33
print("a = %s" %a)
print("b = %s" %b)
print("c = %s" %c)
print("id(a) = %s" %id(a))
print("id(b) = %s" %id(b))
print("id(c) = %s" %id(c))
Output:
a = [11, 22, 3, [4, 5, 6], 7] b = [11, 22, 3, [4, 5, 6], 7] c = [1, 2, 33, [4, 5, 6], 7] id(a) = 4305529528 id(b) = 4305529528 id(c) = 4305600312
Now, we have a copied object stored at different address from the original object.
Shallow copy - is a bit-wise copy of an object. The copied object created has an exact copy of the values in the original object. If either of the values are references to other objects, just the reference addresses for the same are copied:
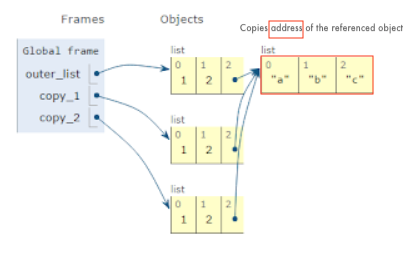
Deep copy - copies all values recursively from source to target object, i.e. it even duplicates the objects referenced by the source object:
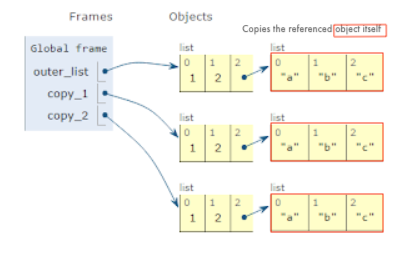
Picture source: Copying lists (shallow copy vs. deep copy)
Here is another sample code that shows the difference between the shallow copy and the deep copy. Note that the difference appears when dealing with nested list:
import copy
a = [1,2,3,[4,5,6],7]
c = copy.copy(a)
d = copy.deepcopy(a)
c[3][0] = 44
c[3][1] = 55
d[3][0] = 444
d[3][1] = 555
d[3][2] = 666
print("a = %s" %a)
print("c = %s" %c)
print("d = %s" %d)
Output:
a = [1, 2, 3, [44, 55, 6], 7] c = [1, 2, 3, [44, 55, 6], 7] d = [1, 2, 3, [444, 555, 666], 7]
Let's check the objects' ids:
id(a) = 4469032256 id(c) = 4469032320 id(d) = 4468978944 id(a[3]) = 4462313152 id(c[3]) = 4462313152 id(d[3]) = 4469055744
We can see a, c, and d are all different objects.
But the nested list, [4,5,6], of the deep copied is different from the original and from the shallow copied. So, if we want to make some changes to the nested list while keeping the original, we need to use the deep copy.
A generator object is an iterator. A generator yields the values one at a time, which requires less memory and allows the caller to get started processing the first few values immediately.
Show how to create a Fibonacci sequence using next() of generator.
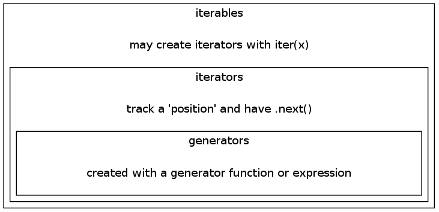
Picture source : Iterables, Iterators and Generators: Part 1
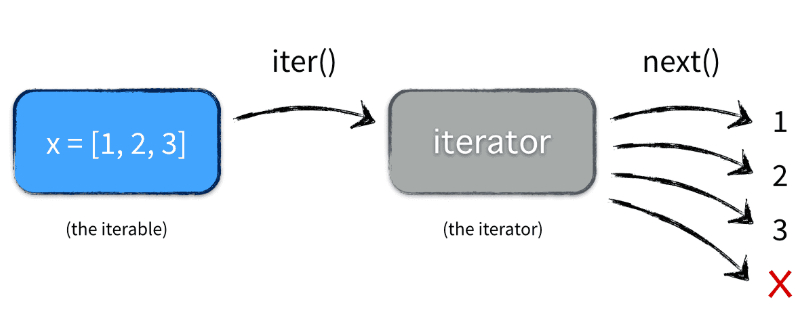
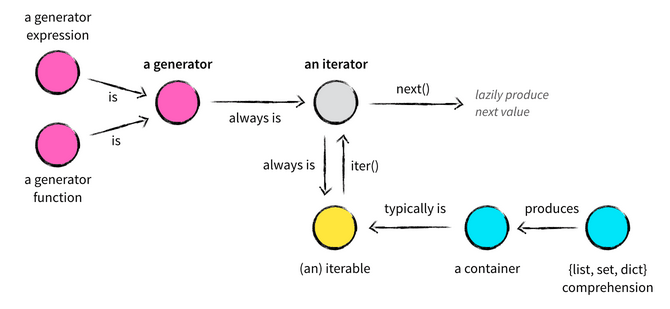
Picture source : Iterables vs. Iterators vs. Generators
def fib(n): p, q = 0, 1 while (p < n): yield p p, q = q, p+q # iterationg loop for i in fib(10): print(i) # create generator object g = fib(10) # iterating using next(g), for Python2, use __next__() print(next(g)) # output => 0 print(next(g)) # output => 1 print(next(g)) # output => 1 print(next(g)) # output => 2 print(next(g)) # output => 3 print(next(g)) # output => 5 print(next(g)) # output => 8 print(next(g)) # error StopIteration
Output:
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/kihyuckhong/Documents/TEST/t.py", line 24, in <module>
print(next(g)) # error StopIteration
StopIteration
Iterators are objects with which we can iterate over iterable objects like lists, strings, etc.
Write an iterator class and demonstrate how we can build our own iterator using __iter__() and next() methods.
- __iter__() method initializes an iterator.
- next() method which returns the next item in iteration and points to the next element.
Upon reaching the end of iterable object next() must return
StopIterationexception.
class myList:
def __init__(self, data):
self.arr = data
def __iter__(self):
self.pos = 0
return self
def next(self):
if(self.pos < len(self.arr)):
self.pos += 1
return self.arr[self.pos - 1]
else:
raise StopIteration
def __str__(self):
return str(self.arr)
array_obj = myList([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(array_obj) # output: 1,2,3,4,5
it = iter(array_obj)
print(next(it)) # output: 1
print(next(it)) # output: 2
print(next(it)) # output: 3
print(next(it)) # output: 4
print(next(it)) # output: 5
print(next(it))
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
1
2
3
4
5
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/kihyuckhong/Documents/TEST/deco.py", line 32, in <module>
print(next(it))
StopIteration
Find the 2nd smalles element from a = [1, -4, 2, 1, -4, -3, -3, 0, 0].
Note that it has duplicate elements.
a = [1, -4, 2, 1, -4, -3, -3, 0, 0] uniq = list(set(a)) uniq.sort() print(uniq[1]) # -3
We may want to use *args when we're not sure how many arguments might be passed to our function, i.e. it allows us to pass an arbitrary number of arguments to our function.
For an arbitrary number of keyword arguments, we use **kargs.
What is the output of the following code?
def f(a,b=2,c=3,*args, **kargs):
print("a=%s, b=%s, c=%s, args=%s, kargs=%s" %(a,b,c,args,kargs))
f(1)
f(1,2)
f(1,2,3,4,5)
f(1,2,30,40,50,x=100,y=200)
f(1,2,[11,22,33], x=111, y=222, z=333)
f(1,2,[11,22,33],[44,55,66],x=111, y=222, z=333)
def f2(*args):
print("args=", args)
f2(1,2)
f2([1],[1,2],[1,2,3])
def f3(*args, **kargs):
print("args=",args, "kargs=",kargs)
f3(1,2)
f3(1,2,[1],[1,2],[1,2,3])
f3(1,2,[1],[1,2],[1,2,3], x=100, y=200)
Output:
a=1, b=2, c=3, args=(), kargs={}
a=1, b=2, c=3, args=(), kargs={}
a=1, b=2, c=3, args=(4, 5), kargs={}
a=1, b=2, c=30, args=(40, 50), kargs={'y': 200, 'x': 100}
a=1, b=2, c=[11, 22, 33], args=(), kargs={'y': 222, 'x': 111, 'z': 333}
a=1, b=2, c=[11, 22, 33], args=([44, 55, 66],), kargs={'y': 222, 'x': 111, 'z': 333}
('args=', (1, 2))
('args=', ([1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3]))
('args=', (1, 2), 'kargs=', {})
('args=', (1, 2, [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3]), 'kargs=', {})
('args=', (1, 2, [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3]), 'kargs=', {'y': 200, 'x': 100})
Write a funciton, fn('x','y',3) that returns a list, ['x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2', 'x3', 'y3'].
def fn(a,b,n):
ans = []
for i in range(1,n+1):
ans.append(a+str(i))
ans.append(b+str(i))
return ans
print(fn('x','y',3))
Given two lists as its input, write a funciton fn(list1, list2) that returns True if list1 is a sublist of list2 otherwise return False.
Note that while [3 ,4] is a sublist of [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] but [3, 5] is not.
def fn(x,y): xs = ''.join([str(e) for e in x]) ys = ''.join([str(e) for e in y]) return xs in ys a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] b = [3 ,4] c = [3, 5] d = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] print(fn(b,a)) # T print(fn(c,a)) # F print(fn(a,d)) # T print(fn(d,a)) # F
any(): if any of the elements in a list is a even number.
all(): if all of the elements in a list are even numbers.
a = [1,3,5] b = [2,3] c = [2,4] print( any(x % 2 == 0 for x in a) ) print( any(x % 2 == 0 for x in b) ) print( any(x % 2 == 0 for x in c) ) print( all(x % 2 == 0 for x in a) ) print( all(x % 2 == 0 for x in b) ) print( all(x % 2 == 0 for x in c) )
Output:
False True True False False True
Convert [[1,2,3],[4,5],[6]] => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]:
import itertools a = [[1,2,3],[4,5],[6]] flattened = list(itertools.chain(*a)) print(flattened)
Or we can use list comprehension:
a = [[1,2,3],[4,5],[6]] b = [y for x in a for y in x] print(b)
Unlike the previous sample list, not all the elements of following list are not list. So, we better use plain if-else:
a = [0,1,[2,3],4,5,[6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
b = []
for x in a:
if isinstance(x, list): # checking if x is a list
for y in x:
b.append(y)
else:
b.append(x)
print(b) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
Random selection of an element of a = [4,5,6,1,2,3]:
import random a = [4,5,6,1,2,3] print(random.choice(a)) print(random.choice(a)) print(random.choice(a))
Check whether two lists are circularly identical - a with b, and a with c:
a1 = [1,2,3,4,5] a2 = [3,4,5,1,2] a3 = [1,2,3,5,4] a1_str = ' '.join(map(str,a1)) a2_str = ' '.join(map(str,a2*2)) a3_str = ' '.join(map(str,a3*2)) print(a1_str in a2_str) # True print(a1_str in a3_str) # False
One trick is create the second list (b or c) as a cloned string and check if the first string is in the second string. Also, to convert the numbers to strings we used the map(str,).
Find the difference between two lists, a and b.
def f1(a,b): d1 = list(set(a)-set(b)) d2 = list(set(b)-set(a)) return d1 + d2 def f2(a,b): d1 = [x for x in a if x not in b] d2 = [y for y in b if y not in a] return d1 + d2 a = [1,2,3] b = [2,3,4] print(f1(a,b)) # [1,4] print(f2(a,b)) # [1,4]
Find the intersection of two lists, a and b.
def f1(a,b): return list(set(a) & set(b)) def f2(a,b): return [x for x in a if x in b] a = [1,2,3] b = [2,3,4] print(f1(a,b)) # [2,3] print(f2(a,b)) # [2,3]
The simplest way of getting reversed list is using slicing: a[::-1]. Here is other ways: reverse() reverses the list in place and reversed() returns an iterable of the list in reverse order.
Initial code:
a = [1,2,3,4,5] ar = [] for i in range(len(a)): ar.append(a[len(a)-1-i]) print(ar) # [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Another code using reverse() or reversed():
import copy
a = [1,2,3,4,5]
ac = copy.copy(a)
ac.reverse()
a_iterable = reversed(a)
ar = [x for x in a_iterable]
print("a = %s" %a) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print("ac = %s" %ac) # [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
print("ar = %s" %ar) # [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Step = 4, a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] => [[1, 5, 9, 13], [2, 6, 10, 14], [3, 7, 11, 15], [4, 8, 12]]:
def f(a, step): return [a[i::step] for i in range(step)] a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] print(f(a,4))
Chunks = 4, a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] => [[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8], [9,10,11,12], [13,14,15]]:
def f(a,n): return [a[i:i+n] for i in range(0,len(a),n)] a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] chunks = 4 print(f(a,chunks))
Note: range([start], stop[, step])!
Remove duplicate consecutive elements from a list and leave only on if they are duplicates:
a = [0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 2, 2]
b = []
prev = None
for x in a:
if x != prev:
b.append(x)
prev = x
print(b) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2]
From the two lists, a = ["kingdom","by"] and b = ["the", "sea"], produce a list, ['kingdom the', 'kingdom sea', 'by the', 'by sea']:
a = ["kingdom","by"] b = ["the", "sea"] c = [ x +' '+ y for x in a for y in b ] print(c)
Or:
a,b = ["kingdom","by"], ["the", "sea"]
c = []
for x in a:
for y in b:
c.append(' '.join([x,y]) )
From the two list a = [1,2,3,4], b = [10,20,30,40], generate the following output:
(1, 40) (2, 30) (3, 20) (4, 10)
The code looks like this:
a = [1,2,3,4] b = [10,20,30,40] c = [(x,y) for x,y in zip(a,b[::-1])] for e in c: print(e)
Or we can convert the zip to tuple:
a = [1,2,3,4] b = [10,20,30,40] for t in tuple(zip(a,b[::-1])): print(t)
Add a sublist [8, 9, 10] to [1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7], 11], 12], 13, 14] and make it looks [1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], 11], 12], 13, 14]
a = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7], 11], 12], 13, 14] b = [8, 9, 10] a[2][1][2].extend(b) print(a)
Output:
[1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], 11], 12], 13, 14]
If we leave the original list untouched, we should use copy.deepcopy().
Note the simple copy.copy() won't do the job because it is still referencing the original nested list not creating a new list:
import copy
a = [1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7], 11], 12], 13, 14]
b = [8,9,10]
print('original a=%s' %a)
copy_a = copy.copy(a)
deepcopy_a = copy.deepcopy(a)
copy_a[2][1][2].extend(b)
deepcopy_a[2][1][2].extend(b)
print('a=%s' %a)
print('copy_a=%s' %copy_a)
print('deepcopy_a=%s' %deepcopy_a)
Output:
original a=[1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7], 11], 12], 13, 14] a=[1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], 11], 12], 13, 14] copy_a=[1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], 11], 12], 13, 14] deepcopy_a=[1, 2, [3, [4, 5, [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], 11], 12], 13, 14]
Given a = [3,6,9,12,15,18,21,15,15], find 15 and replace it with 1515, but only the first occurence:
find = 15
replace = 1515
found = False
a = [3,6,9,12,15,18,21,15,15]
new_a = []
for x in a:
if x == find and not found:
new_a.append(replace)
found = True
else:
new_a.append(x)
print('a = %s' %a)
print('new_a = %s' %new_a)
Output:
a = [3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 15, 15] new_a = [3, 6, 9, 12, 1515, 18, 21, 15, 15]
Or we can use index():
find = 15 replace = 1515 a = [3,6,9,12,15,18,21,15,15] i = a.index(find) a[i] = replace print(a) # [3, 6, 9, 12, 1515, 18, 21, 15, 15]
Given two lists, sort the values of one list using the second priority list:
a = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i'] b = [ 0,1,1,0,1,2,2,0,1] z = zip(a,b) sz = sorted(z, key=lambda x:x[1]) print(sz) sa = [x[0] for x in sz] print(sa)
Output:
[('a', 0), ('d', 0), ('h', 0), ('b', 1), ('c', 1), ('e', 1), ('i', 1), ('f', 2), ('g', 2)]
['a', 'd', 'h', 'b', 'c', 'e', 'i', 'f', 'g']
Given two nest matrix (nested list), mat1 = [ [1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8] ], mat2 = [ [1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8] ], find the transposes of the two matrices.
mat1 = [ [1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8] ] t = [ [r[i] for r in mat1] for i in range(len(mat1[0])) ] print(t) # [[1, 5], [2, 6], [3, 7], [4, 8]] mat2 = [ [1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8] ] t = [ [r[i] for r in mat2] for i in range(len(mat2[0])) ] print(t) # [[1, 3, 5, 7], [2, 4, 6, 8]]
Not using comprehension:
mat1 = [ [1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8] ] transposed = [] for i in range(len(mat1[0])): transposed_row = [] for r in mat1: transposed_row.append(r[i]) transposed.append(transposed_row) print(transposed)
Another way is using zip(*iterables):
mat1 = [ [1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8] ] mat2 = [ [1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8] ] t_mat1 = list(zip(*mat1)) t_mat2 = list(zip(*mat2)) print(t_mat1) # [(1, 5), (2, 6), (3, 7), (4, 8)] print(t_mat2) # [(1, 3, 5, 7), (2, 4, 6, 8)]
Note that the '*' is to unzip the matrix. So, the following two lines of code are equivalent:
t_mat1 = list(zip(*mat1))
t_mat1 = list(zip(mat1[0],mat1[1]))
To see how the zip() works. check zip(*iterables):
x = [1,2,3] y = [4,5,6] zipped = list(zip(x,y)) print(zipped) # [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)] x2, y2 = zip(*zip(x,y)) print(x2,y2) # (1, 2, 3) (4, 5, 6) print(list(x2),list(y2)) # [1, 2, 3] [4, 5, 6]
- Python Coding Questions I
- Python Coding Questions II
- Python Coding Questions III
- Python Coding Questions IV
- Python Coding Questions V
- Python Coding Questions VI
- Python Coding Questions VII
- Python Coding Questions VIII
- Python Coding Questions IX
- Python Coding Questions X
List of codes Q & A
- Merging two sorted list
- Get word frequency - initializing dictionary
- Initializing dictionary with list
- map, filter, and reduce
- Write a function f() - yield
- What is __init__.py?
- Build a string with the numbers from 0 to 100, "0123456789101112..."
- Basic file processing: Printing contents of a file - "with open"
- How can we get home directory using '~' in Python?
- The usage of os.path.dirname() & os.path.basename() - os.path
- Default Libraries
- range vs xrange
- Iterators
- Generators
- Manipulating functions as first-class objects
- docstrings vs comments
- using lambdda
- classmethod vs staticmethod
- Making a list with unique element from a list with duplicate elements
- What is map?
- What is filter and reduce?
- *args and **kwargs
- mutable vs immutable
- Difference between remove, del and pop on lists
- Join with new line
- Hamming distance
- Floor operation on integers
- Fetching every other item in the list
- Python type() - function
- Dictionary Comprehension
- Sum
- Truncating division
- Python 2 vs Python 3
- len(set)
- Print a list of file in a directory
- Count occurrence of a character in a Python string
- Make a prime number list from (1,100)
- Reversing a string - Recursive
- Reversing a string - Iterative
- Reverse a number
- Output?
- Merging overlapped range
- Conditional expressions (ternary operator)
- Packing Unpacking
- Function args
- Unpacking args
- Finding the 1st revision with a bug
- Which one has higher precedence in Python? - NOT, AND , OR
- Decorator(@) - with dollar sign($)
- Multi-line coding
- Recursive binary search
- Iterative binary search
- Pass by reference
- Simple calculator
- iterator class that returns network interfaces
- Converting domain to ip
- How to count the number of instances
- Python profilers - cProfile
- Calling a base class method from a child class that overrides it
- How do we find the current module name?
- Why did changing list 'newL' also change list 'L'?
- Constructing dictionary - {key:[]}
- Colon separated sequence
- Converting binary to integer
- 9+99+999+9999+...
- Calculating balance
- Regular expression - findall
- Chickens and pigs
- Highest possible product
- Implement a queue with a limited size
- Copy an object
- Filter
- Products
- Pickle
- Overlapped Rectangles
- __dict__
- Fibonacci I - iterative, recursive, and via generator
- Fibonacci II - which method?
- Fibonacci III - find last two digits of Nth Fibonacci number
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time A
- Write a Stack class returning Max item at const time B
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 1
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 2
- Finding duplicate integers from a list - 3
- Reversing words 1
- Parenthesis, a lot of them
- Palindrome / Permutations
- Constructing new string after removing white spaces
- Removing duplicate list items
- Dictionary exercise
- printing numbers in Z-shape
- Factorial
- lambda
- lambda with map/filter/reduce
- Number of integer pairs whose difference is K
- iterator vs generator
- Recursive printing files in a given directory
- Bubble sort
- What is GIL (Global Interpreter Lock)?
- Word count using collections
- Pig Latin
- List of anagrams from a list of words
- lamda with map, filer and reduce functions
- Write a code sending an email using gmail
- histogram 1 : the frequency of characters
- histogram 2 : the frequency of ip-address
- Creating a dictionary using tuples
- Getting the index from a list
- Looping through two lists side by side
- Dictionary sort with two keys : primary / secondary keys
- Writing a file downloaded from the web
- Sorting csv data
- Reading json file
- Sorting class objects
- Parsing Brackets
- Printing full path
- str() vs repr()
- Missing integer from a sequence
- Polymorphism
- Product of every integer except the integer at that index
- What are accessors, mutators, and @property?
- N-th to last element in a linked list
- Implementing linked list
- Removing duplicate element from a list
- List comprehension
- .py vs .pyc
- Binary Tree
- Print 'c' N-times without a loop
- Quicksort
- Dictionary of list
- Creating r x c matrix
- Transpose of a matrix
- str.isalpha() & str.isdigit()
- Regular expression
- What is Hashable? Immutable?
- Convert a list to a string
- Convert a list to a dictionary
- List - append vs extend vs concatenate
- Use sorted(list) to keep the original list
- list.count()
- zip(list,list) - join elements of two lists
- zip(list,list) - weighted average with two lists
- Intersection of two lists
- Dictionary sort by value
- Counting the number of characters of a file as One-Liner
- Find Armstrong numbers from 100-999
- Find GCF (Greatest common divisor)
- Find LCM (Least common multiple)
- Draws 5 cards from a shuffled deck
- Dictionary order by value or by key
- Regular expression - re.split()
- Regular expression : re.match() vs. re.search()
- Regular expression : re.match() - password check
- Regular expression : re.search() - group capturing
- Regular expression : re.findall() - group capturin
- Prime factors : n = products of prime numbers
- Valid IPv4 address
- Sum of strings
- List rotation - left/right
- shallow/deep copy
- Converting integer to binary number
- Creating a directory and a file
- Creating a file if not exists
- Invoking a python file from another
- Sorting IP addresses
- Word Frequency
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - I. Clock-wise
- Printing spiral pattern from a 2D array - II. Counter-Clock-wise
- Find a minimum integer not in the input list
- I. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer
- II. Find longest sequence of zeros in binary representation of an integer - should be surrounded with 1
- Find a missing element from a list of integers
- Find an unpaired element from a list of integers
- Prefix sum : Passing cars
- Prefix sum : count the number of integers divisible by k in range [A,B]
- Can make a triangle?
- Dominant element of a list
- Minimum perimeter
- MinAbsSumOfTwo
- Ceiling - Jump Frog
- Brackets - Nested parentheses
- Brackets - Nested parentheses of multiple types
- Left rotation - list shift
- MaxProfit
- Stack - Fish
- Stack - Stonewall
- Factors or Divisors
- String replace in files 1
- String replace in files 2
- Using list as the default_factory for defaultdict
- Leap year
- Capitalize
- Log Parsing
- Getting status_code for a site
- 2D-Array - Max hourglass sum
- New Year Chaos - list
- List (array) manipulation - list
- Hash Tables: Ransom Note
- Count Triplets with geometric progression
- Strings: Check if two strings are anagrams
- Strings: Making Anagrams
- Strings: Alternating Characters
- Special (substring) Palindrome
- String with the same frequency of characters
- Common Child
- Fraudulent Activity Notifications
- Maximum number of toys
- Min Max Riddle
- Poisonous Plants with Pesticides
- Common elements of 2 lists - Complexity
- Get execution time using decorator(@)
- Conver a string to lower case and split using decorator(@)
- Python assignment and memory location
- shallow copy vs deep copy for compound objects (such as a list)
- Generator with Fibonacci
- Iterator with list
- Second smallest element of a list
- *args, **kargs, and positional args
- Write a function, fn('x','y',3) that returns ['x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2', 'x3', 'y3']
- sublist or not
- any(), all()
- Flattening a list
- Select an element from a list
- Circularly identical lists
- Difference between two lists
- Reverse a list
- Split a list with a step
- Break a list and make chunks of size n
- Remove duplicate consecutive elements from a list
- Combination of elements from two lists
- Adding a sublist
- Replace the first occurence of a value
- Sort the values of the first list using the second list
- Transpose of a matrix (nested list)
- Binary Gap
- Powerset
- Round Robin
- Fixed-length chunks or blocks
- Accumulate
- Dropwhile
- Groupby
- Simple product
- Simple permutation
- starmap(fn, iterable)
- zip_longest(*iterables, fillvalue=None)
- What is the correct way to write a doctest?
- enumerate(iterable, start=0)
- collections.defaultdict - grouping a sequence of key-value pairs into a dictionary of lists
- What is the purpose of the 'self' keyword when defining or calling instance methods?
- collections.namedtuple(typename, field_names, *, rename=False, defaults=None, module=None)
- zipped
- What is key difference between a set and a list?
- What does a class's init() method do?
- Class methods
- Permutations and combinations of ['A','B','C']
- Sort list of dictionaries by values
- Return a list of unique words
- hashlib
- encode('utf-8')
- Reading in CSV file
- Count capital letters in a file
- is vs ==
- Create a matrix : [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
- Binary to integer and check if it's the power of 2
- urllib.request.urlopen() and requests
- Game statistics
- Chess - pawn race
- Decoding a string
- Determinant of a matrix - using numpy.linalg.det()
- Revenue from shoe sales - using collections.Counter()
- Rangoli
- Unique characters
- Valid UID
- Permutations of a string in lexicographic sorted order
- Nested list
- Consecutive digit count
- Find a number that occurs only once
- Sorting a two-dimensional array
- Reverse a string
- Generate random odd numbers in a range
- Shallow vs Deep copy
- Transpose matrix
- Are Arguments in Python Passed by Value or by Reference?
- re: Is a string alphanumeric?
- reversed()
- Caesar's cipher, or shift cipher, Caesar's code, or Caesar shift
- Every other words
- re: How can we check if an email address is valid or not?
- re: How to capture temperatures of a text
- re.split(): How to split a text.
- How can we merge two dictionaries?
- How can we combine two dictionaries?
- What is the difference between a generator and a list?
- Pairs of a given array A whose sum value is equal to a target value N
- Adding two integers without plus
- isinstance() vs type()
- What is a decorator?
- In Python slicing, what does my_list[-3:2:-2] slice do?
- Revisit sorting dict - counting chars in a text file
- re: Transforming a date format using re.sub
- How to replace the newlines in csv file with tabs?
- pandas.merge
- How to remove duplicate charaters from a string?
- Implement a class called ComplexNumber
- Find a word frequency
- Get the top 3 most frequent characters of a string
- Just seen and ever seen
- Capitalizing the full name
- Counting Consequitive Characters
- Calculate Product of a List of Integers Provided using input()
- How many times a substring appears in a string
- Hello, first_name last_name
- String validators
- Finding indices that a char occurs in a list
- itertools combinations
Python tutorial
Python Home
Introduction
Running Python Programs (os, sys, import)
Modules and IDLE (Import, Reload, exec)
Object Types - Numbers, Strings, and None
Strings - Escape Sequence, Raw String, and Slicing
Strings - Methods
Formatting Strings - expressions and method calls
Files and os.path
Traversing directories recursively
Subprocess Module
Regular Expressions with Python
Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet
Object Types - Lists
Object Types - Dictionaries and Tuples
Functions def, *args, **kargs
Functions lambda
Built-in Functions
map, filter, and reduce
Decorators
List Comprehension
Sets (union/intersection) and itertools - Jaccard coefficient and shingling to check plagiarism
Hashing (Hash tables and hashlib)
Dictionary Comprehension with zip
The yield keyword
Generator Functions and Expressions
generator.send() method
Iterators
Classes and Instances (__init__, __call__, etc.)
if__name__ == '__main__'
argparse
Exceptions
@static method vs class method
Private attributes and private methods
bits, bytes, bitstring, and constBitStream
json.dump(s) and json.load(s)
Python Object Serialization - pickle and json
Python Object Serialization - yaml and json
Priority queue and heap queue data structure
Graph data structure
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
Prim's spanning tree algorithm
Closure
Functional programming in Python
Remote running a local file using ssh
SQLite 3 - A. Connecting to DB, create/drop table, and insert data into a table
SQLite 3 - B. Selecting, updating and deleting data
MongoDB with PyMongo I - Installing MongoDB ...
Python HTTP Web Services - urllib, httplib2
Web scraping with Selenium for checking domain availability
REST API : Http Requests for Humans with Flask
Blog app with Tornado
Multithreading ...
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : A Basics
Python Network Programming I - Basic Server / Client : B File Transfer
Python Network Programming II - Chat Server / Client
Python Network Programming III - Echo Server using socketserver network framework
Python Network Programming IV - Asynchronous Request Handling : ThreadingMixIn and ForkingMixIn
Python Coding Questions I
Python Coding Questions II
Python Coding Questions III
Python Coding Questions IV
Python Coding Questions V
Python Coding Questions VI
Python Coding Questions VII
Python Coding Questions VIII
Python Coding Questions IX
Python Coding Questions X
Image processing with Python image library Pillow
Python and C++ with SIP
PyDev with Eclipse
Matplotlib
Redis with Python
NumPy array basics A
NumPy Matrix and Linear Algebra
Pandas with NumPy and Matplotlib
Celluar Automata
Batch gradient descent algorithm
Longest Common Substring Algorithm
Python Unit Test - TDD using unittest.TestCase class
Simple tool - Google page ranking by keywords
Google App Hello World
Google App webapp2 and WSGI
Uploading Google App Hello World
Python 2 vs Python 3
virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper
Uploading a big file to AWS S3 using boto module
Scheduled stopping and starting an AWS instance
Cloudera CDH5 - Scheduled stopping and starting services
Removing Cloud Files - Rackspace API with curl and subprocess
Checking if a process is running/hanging and stop/run a scheduled task on Windows
Apache Spark 1.3 with PySpark (Spark Python API) Shell
Apache Spark 1.2 Streaming
bottle 0.12.7 - Fast and simple WSGI-micro framework for small web-applications ...
Flask app with Apache WSGI on Ubuntu14/CentOS7 ...
Fabric - streamlining the use of SSH for application deployment
Ansible Quick Preview - Setting up web servers with Nginx, configure enviroments, and deploy an App
Neural Networks with backpropagation for XOR using one hidden layer
NLP - NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) ...
RabbitMQ(Message broker server) and Celery(Task queue) ...
OpenCV3 and Matplotlib ...
Simple tool - Concatenating slides using FFmpeg ...
iPython - Signal Processing with NumPy
iPython and Jupyter - Install Jupyter, iPython Notebook, drawing with Matplotlib, and publishing it to Github
iPython and Jupyter Notebook with Embedded D3.js
Downloading YouTube videos using youtube-dl embedded with Python
Machine Learning : scikit-learn ...
Django 1.6/1.8 Web Framework ...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization