Algorithms - Trie
Trie (aka Prefix Tree) stores keys at the bottom of the tree, in leaf nodes. The resulting data structure has a number of useful properties that can serve as the basis for number of effective search algorithms. We usually pronounce it as "try-ee" or just "try".
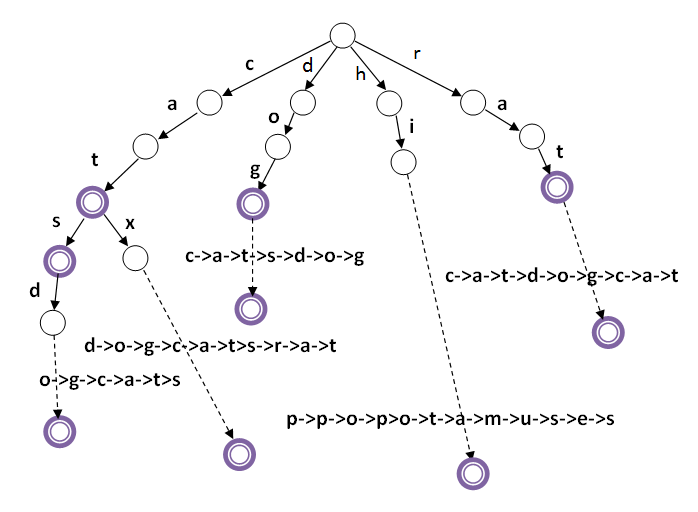
The code below has minimal code just for storing/seraching/listing. In the later section, I'll extend it to serve more general purpose or tailored to use for a specific application.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
Node() { mLetter = ' '; mTerminator = false; }
~Node() {}
void setLetter(char c) { mLetter = c; }
char getLetter() { return mLetter; }
void setTerminator() { mTerminator = true; }
bool hasTerminator() { return mTerminator; }
void appendChild(Node* child) { mChildren.push_back(child); }
Node* findChild(char c);
void printNode();
void printBranch(Node*, char *, int count);
vector<Node*> children() { return mChildren; }
private:
char mLetter;
bool mTerminator;
vector<Node*> mChildren;
};
Node* Node::findChild(char c)
{
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
if ( ptr->getLetter() == c )
{
return ptr;
}
}
return NULL;
}
void Node::printBranch(Node *node, char *word, int count)
{
if(node->mLetter!= ' ') {
word[count++] = node->mLetter;
}
if(node->hasTerminator()) {
cout << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
cout << word[i];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < (node->mChildren).size(); i++) {
printBranch((node->mChildren).at(i), word, count);
}
}
void Node::printNode()
{
char *word = new char[200];
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
printBranch(ptr, word, 0);
}
}
class Trie
{
public:
Trie();
void addWord(string s);
bool searchWord(string s);
void printTrie();
void printBranch(Node*);
private:
Node* root;
};
void Trie::printTrie()
{
root->printNode();
}
Trie::Trie()
{
root = new Node();
}
void Trie::addWord(string s)
{
Node* current = root;
if ( s.length() == 0 )
{
current->setTerminator();
return;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* child = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( child != NULL )
{
current = child;
}
else
{
Node* ptr = new Node();
ptr->setLetter(s[i]);
current->appendChild(ptr);
current = ptr;
}
if ( i == s.length() - 1 ) {
current->setTerminator();
}
}
}
bool Trie::searchWord(string s)
{
Node* current = root;
while ( current != NULL )
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( ptr == NULL )
return false;
current = ptr;
}
if ( current->hasTerminator() )
return true;
else
return false;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
Trie* trie = new Trie();
trie->addWord("cat");
trie->addWord("cats");
trie->addWord("catsdogcats");
trie->addWord("catxdogcatsrat");
trie->addWord("dog");
trie->addWord("dogcatsdog");
trie->addWord("hippopotamuses");
trie->addWord("rat");
trie->addWord("ratcatdogcat");
if ( !trie->searchWord("hippopotamus") )
cout << "Not Found hippopotamus" << endl;
if ( trie->searchWord("catsdogcats") )
cout << "Found catsdogcats" << endl;
if ( trie->searchWord("ratcatdogcat") )
cout << "Found ratcatdogcat" << endl;
trie->printTrie();
delete trie;
return 0;
}
Output:
Not Found hippopotamus Found catsdogcats Found ratcatdogcat cat cats catsdogcats catxdogcatsrat dog dogcatsdog hippopotamuses rat ratcatdogcat
The following code finds the two longest strings which are composed of other words. It is slightly modified from the previous version. Actually, isComposed() has been added to check whether a word is made from other words.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string longest[2];
int substringIndex[100];
class Trie;
class Node
{
public:
Node() { mLetter = ' '; mTerminator = false; }
~Node() {}
void setLetter(char c) { mLetter = c; }
char getLetter() { return mLetter; }
void setTerminator() { mTerminator = true; }
bool hasTerminator() { return mTerminator; }
void appendChild(Node* child) { mChildren.push_back(child); }
Node* findChild(char c);
void printNode(Trie*);
void setTrie(Trie* trie) {mTrie = trie;}
void printBranch(Node*, char *, int, int);
void storeThisWord(char *);
bool isComposed(string, int, bool);
vector<Node*> children() { return mChildren; }
private:
char mLetter;
bool mTerminator;
vector<Node*> mChildren;
Trie* mTrie;
};
class Trie
{
public:
Trie();
void addWord(string s);
bool searchWord(string s);
void searchComponents(string);
void printTrie();
void printBranch(Node*);
private:
Node* root;
};
void Node::storeThisWord(char *w)
{
int index = 0;
index = longest[0].size() < longest[1].size() ? 0 : 1;
if(strlen(w) > longest[index].size()) {
longest[index] = string(w);
}
}
Node* Node::findChild(char c)
{
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
if ( ptr->getLetter() == c )
{
return ptr;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool Node::isComposed(string inputStr, int sz, bool flag)
{
if(sz <= 0) return false;;
for(int i = 1; i < sz; i++) {
string left = inputStr.substr(0, i);
string right = inputStr.substr(i, inputStr.size());
if(mTrie->searchWord(left)) {
if(mTrie->searchWord(right)) {
if(flag) cout << left << endl << right << endl;
return true;
}
else {
if(isComposed(right, right.size(), flag)) {
if(flag) cout << left << endl;
return true;
}
}
}
if(isComposed(left, left.size(), flag) && isComposed(right, right.size(), flag)) return true;
}
return false;
}
void Node::printBranch(Node *node, char *word, int count, int terminator_count)
{
if(node->mLetter!= ' ') {
word[count++] = node->mLetter;
}
if(node->hasTerminator()) {
substringIndex[terminator_count] = count;
cout << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
cout << word[i];
}
if( (node->mChildren).size() == 0 && terminator_count >= 1) {
// check substring of a composite word
int st = substringIndex[terminator_count-1];
int end = substringIndex[terminator_count];
string str = string(word).substr(st, end-st);
if(isComposed(str, str.size(), false)) {
word[count] = '\0';
storeThisWord(word);
}
}
terminator_count++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < (node->mChildren).size(); i++) {
printBranch((node->mChildren).at(i), word, count, terminator_count);
}
}
void Node::printNode(Trie* trie)
{
// Let Node class have pointer to the trie
setTrie(trie);
char *word = new char[200];
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
printBranch(ptr, word, 0, 0);
}
}
void Trie::printTrie()
{
root->printNode(this);
}
Trie::Trie()
{
root = new Node();
}
void Trie::addWord(string s)
{
Node* current = root;
if ( s.length() == 0 )
{
current->setTerminator();
return;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* child = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( child != NULL )
{
current = child;
}
else
{
Node* ptr = new Node();
ptr->setLetter(s[i]);
current->appendChild(ptr);
current = ptr;
}
if ( i == s.length() - 1 ) {
current->setTerminator();
}
}
}
bool Trie::searchWord(string s)
{
Node* current = root;
while ( current != NULL )
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( ptr == NULL )
return false;
current = ptr;
}
if ( current->hasTerminator() )
return true;
else
return false;
}
return false;
}
void Trie::searchComponents(string s)
{
root->isComposed(s, s.size(), true);
}
int main()
{
Trie* trie = new Trie();
trie->addWord("cat");
trie->addWord("cats");
trie->addWord("catsdogcats");
trie->addWord("catxdogcatsrat");
trie->addWord("dog");
trie->addWord("dogcatsdog");
trie->addWord("hippopotamuses");
trie->addWord("rat");
trie->addWord("ratcatdogcat");
if ( !trie->searchWord("hippopotamus") )
cout << "Not found hippopotamus" << endl;
if ( trie->searchWord("catsdogcats") )
cout << "Found catsdogcats" << endl;
if ( trie->searchWord("ratcatdogcat") )
cout << "Found ratcatdogcat" << endl;
if ( trie->searchWord("cats") )
cout << "Found cats" << endl;
if ( !trie->searchWord("catsd") )
cout << "Not found catsd" << endl;
cout << endl << "All strings..." << endl;
trie->printTrie();
cout << endl;
cout << endl << "The two longest composite strings..." << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
cout << longest[i] << endl;
cout << "composed of the following words: " << endl;
trie->searchComponents(longest[i]);
cout << endl;
}
delete trie;
return 0;
}
Output is:
Not found hippopotamus Found catsdogcats Found ratcatdogcat Found cats Not found catsd All strings... cat cats catsdogcats catxdogcatsrat dog dogcatsdog hippopotamuses rat ratcatdogcat The two longest composite strings... ratcatdogcat composed of the following words: dog cat cat rat catsdogcats composed of the following words: dog cats cats
In this sample, a Trie was constructed after reading 173531 lines from a file. The file contains a sorted list of words (one word per line, no spaces, all lower case). Because the size of the words is much bigger than the previous example (also included in this section as a small test case), efficiency does matter.
After building the Trie, we search for the longest compound strings from the Trie. Also, we need to find the words that are used to get the compounds. To save the comprising words, multimap is used since it enables us to store several values for one key string.
Two class are constructed: Trie and Node.
The core of the code is isComposed() routine which finds out if a word is a compound. It tests every possible combination of the second part of the string. For example, if we have "microspectrophotometries", then the algorithm figures out we have already the first string (micro), and it only has to check the rest which is "spectrophotometries". This may be either a compound of other words or may be not.
Since we want to have only two longest compounds, it will expedite the speed of the search so that we only check the possibility of compound if the length is greater than or equal to the existing lengths of two compound strings.
Here are the files:
- C++ file: LongestCompound.cpp
- Input text: words for problem.txt.
Note that this is an input for Windows. For linux, we should open it and then save it in linux way. As you may already know, in Windows, lines end with both the carriage return and the line feed ASCII characters (\r\n), while Linux uses only a line feed (\n).
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class Trie;
class Node
{
public:
Node() { mLetter = ' '; mTerminator = false; }
~Node() {}
void setLetter(char c) { mLetter = c; }
char getLetter() { return mLetter; }
void setTerminator() { mTerminator = true; }
bool hasTerminator() { return mTerminator; }
void appendChild(Node* child) { mChildren.push_back(child); }
Node* findChild(char c);
void processNode(Trie*);
void setTriePointer(Trie* trie) {mTrie = trie;}
void processBranch(Node*, char *, int, int, int []);
void storeThisWord(char *, int);
bool isComposed(string, int, string, string);
vector<Node*> children() { return mChildren; }
private:
char mLetter;
bool mTerminator;
vector<Node*> mChildren;
Trie* mTrie;
};
class Trie
{
public:
Trie();
void addWord(string s);
bool searchWord(string s);
void processTrie();
vector<string>& getLongestStr() { return m_longestStr;}
int getSecondLongest() { return m_secondLongest; }
void setSecondLongest(int n) { m_secondLongest = n; }
multimap<string, string>& getMap() { return m_Map;}
private:
Node* m_root;
int m_secondLongest;
// key string for map
vector<string> m_longestStr;
// map for substring of a compount
multimap<string, string> m_Map;
};
void Node::storeThisWord(char *w, int sz)
{
int index = 0;
vector<string> longStr = mTrie->getLongestStr();
index = longStr[0].size() < longStr[1].size() ? 0 : 1;
if( sz > longStr[index].size()) {
mTrie->getLongestStr()[index] = string(w);
cout << "longestStr: " << longStr[0] << "(" << longStr[0].size() << ") "
<< longStr[1] << "(" << longStr[1].size() << ")" << endl;
mTrie->setSecondLongest(min(longStr[0].size(), longStr[1].size()));
}
}
Node* Node::findChild(char c)
{
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
if ( ptr->getLetter() == c )
{
return ptr;
}
}
return NULL;
}
/* Take the input string, and then recursively search through the trie to find words
which comprising the input string.
If the comprising words are found, put them into the stl multimap. */
/* INPUT
inputStr - string to check if it's compound
sz - size of the inputStr
keyStr - key string to be used as a key for multimap. This is the full string
originalStr - because this routine is recursive, we need keep this initial input string
*/
bool Node::isComposed(string inputStr, int sz, string keyStr, string originalStr)
{
if(sz <= 0) return false;
/* Some input words can be a complete word itself not comprised of any other words */
if(inputStr == originalStr) {
if(mTrie->searchWord(inputStr)) {
mTrie->getMap().insert(make_pair(keyStr,inputStr));
return true;
}
}
// loop through character by character making different words to see if it's compound
for(int i = 1; i < sz; i++) {
string left = inputStr.substr(0, i);
string right = inputStr.substr(i, inputStr.size());
if(mTrie->searchWord(left)) {
if(mTrie->searchWord(right)) {
// component of the compound, save it
mTrie->getMap().insert(make_pair(keyStr,left));
mTrie->getMap().insert(make_pair(keyStr,right));
return true;
}
else {
if(isComposed(right, right.size(), keyStr, originalStr)) {
// component of the compound, save it
mTrie->getMap().insert(make_pair(keyStr,left));
return true;
}
}
}
// repeat: recursive
if(isComposed(left, left.size(), keyStr, originalStr)
&& isComposed(right, right.size(), keyStr, originalStr))
return true;
}
return false;
}
/* Progress each branch, and check if the words in the subsequent node are compound word*/
void Node::processBranch(Node *node, char *word, int count,
int terminator_count, int substringIndex[])
{
if(node->mLetter!= ' ') {
word[count++] = node->mLetter;
}
if(node->hasTerminator()) {
substringIndex[terminator_count] = count;
if (count >= mTrie->getSecondLongest()) {
/* only the word with more than one terminator can be a candidate for a compound word */
if( (node->mChildren).size() == 0 && terminator_count >= 1) {
// check substring of a composite word
int st = substringIndex[terminator_count-1];
int end = substringIndex[terminator_count];
string str = string(word).substr(st, end-st);
string keyStr = string(word).substr(0, count);
mTrie->getMap().insert(make_pair(keyStr, string(word).substr(0, st)));
string originalStr = str;
// Check if compound. If it is, give it a try to be the longest compound */
if(isComposed(str, str.size(), keyStr, originalStr)) {
word[count] = '\0';
storeThisWord(word, count);
}
}
}
terminator_count++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < (node->mChildren).size(); i++) {
processBranch((node->mChildren).at(i), word, count, terminator_count, substringIndex);
}
}
/* process all the branches ('a'-'z') one by one */
void Node::processNode(Trie* trie)
{
// Let Node class have pointer to the trie
setTriePointer(trie);
char *word = new char[200];
int substringIndex[10];
for ( size_t i = 0; i < mChildren.size(); i++ )
{
char c = 'a' + i;
Node* ptr = mChildren.at(i);
cout << "Processing trie " << c << "..." << endl;
processBranch(ptr, word, 0, 0, substringIndex);
}
delete word;
}
/* This is the start of the process finding the longest compound */
void Trie::processTrie()
{
// pass the incidence
m_root->processNode(this);
}
// trie constructor
Trie::Trie()
{
m_root = new Node();
m_secondLongest = 1;
m_longestStr.push_back(" ");
m_longestStr.push_back(" ");
}
// add words to the trie
void Trie::addWord(string s)
{
Node* current = m_root;
if ( s.length() == 0 )
{
current->setTerminator();
return;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* child = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( child != NULL )
{
current = child;
}
else
{
Node* ptr = new Node();
ptr->setLetter(s[i]);
current->appendChild(ptr);
current = ptr;
}
if ( i == s.length() - 1 )
current->setTerminator();
}
}
// search a word from the trie
bool Trie::searchWord(string s)
{
Node* current = m_root;
while ( current != NULL )
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.length(); i++ )
{
Node* ptr = current->findChild(s[i]);
if ( ptr == NULL )
return false;
current = ptr;
}
if ( current->hasTerminator() )
return true;
else
return false;
}
return false;
}
enum CASES { REALCASE, SMALLCASE };
/* Two test cases: real test and very samll test cases */
int main()
{
Trie* trie = new Trie();
/* specify the case to run */
CASES run = REALCASE;
// CASES run = SMALLCASE;
switch (run)
{
case REALCASE:
{
ifstream myReader("words for problem.txt");
if(!myReader) {
cout << "Error in opening input file" << endl;
return -1;
}
int lineCount = 0;
cout << "Adding words to the Trie..." << endl;
cout << "\nPotential candidates are ..." << endl;
string line;
while(!myReader.eof()) {
getline(myReader, line);
trie->addWord(line);
lineCount++;
if(line.length() >= 25) {
cout << line << "(" << line.length() << ")" << endl;
}
}
cout << "\nA trie has been constructed after reading "
<< lineCount << " lines from a file." << endl;
myReader.close();
break;
}
case SMALLCASE:
{
trie->addWord("cat");
trie->addWord("cats");
trie->addWord("catsdogcats");
trie->addWord("catxdogcatsrat");
trie->addWord("dog");
trie->addWord("dogcatsdog");
trie->addWord("hippopotamuses");
trie->addWord("rat");
trie->addWord("ratcatdogcat");
break;
}
default:
cout << "No case is provided." << endl;
}
cout << endl << "Now, searching for longest compound strings from the Trie...\n\n";
// Loop through the trie from a-z to find the longest compound
trie->processTrie();
cout << "\n-----------------------------" << endl;
cout << "The two longest composite strings are: \n\n";
vector<string> longStr = trie->getLongestStr();
multimap<string, string>::iterator pos;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
cout << longStr[i] << "(" << longStr[i].size() << ")" << endl;
cout << " is composed of the following words =>" << endl;
cout << "[";
for(pos = trie->getMap().lower_bound(longStr[i]);
pos != trie->getMap().upper_bound(longStr[i]); ++pos) {
cout << pos->second << ", ";
}
cout << "]\n\n";
}
cout << "-----------------------------" << endl;
delete trie;
cout << "Just pause here, to see the outcome... " << endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
Output looks like this:
Adding words to the Trie... Potential candidates are ... electroencephalographically(27) ethylenediaminetetraacetate(27) ethylenediaminetetraacetates(28) immunoelectrophoretically(25) phosphatidylethanolamines(25) A trie has been constructed after reading 173531 lines from a file. Now, searching for longest compound strings from the Trie... Processing trie a... longestStr: (1) (1) longestStr: (1) aahed(5) longestStr: abacuses(8) aahed(5) longestStr: abacuses(8) abandoned(9) longestStr: abattises(9) abandoned(9) longestStr: abattises(9) abducentes(10) longestStr: abductores(10) abducentes(10) longestStr: abductores(10) aberrancies(11) longestStr: aberrational(12) aberrancies(11) longestStr: aberrational(12) abiogenically(13) longestStr: abortivenesses(14) abiogenically(13) longestStr: abortivenesses(14) abrasivenesses(14) longestStr: abortivenesses(14) absentmindednesses(18) longestStr: absorbabilities(15) absentmindednesses(18) longestStr: abstemiousnesses(16) absentmindednesses(18) longestStr: accommodativenesses(19) absentmindednesses(18) longestStr: accommodativenesses(19) adventuresomenesses(19) Processing trie b... Processing trie c... longestStr: accommodativenesses(19) antiferromagnetically(21) longestStr: chemotherapeutically(20) antiferromagnetically(21) Processing trie d... Processing trie e... longestStr: contemporaneousnesses(21) antiferromagnetically(21) longestStr: contemporaneousnesses(21) electrocardiographically(24) Processing trie f... Processing trie g... Processing trie h... Processing trie i... longestStr: electroencephalographically(27) electrocardiographically(24) Processing trie j... Processing trie k... Processing trie l... Processing trie m... Processing trie n... Processing trie o... Processing trie p... Processing trie q... Processing trie r... Processing trie s... Processing trie t... Processing trie u... Processing trie v... Processing trie w... Processing trie x... Processing trie y... Processing trie z... ----------------------------- The two longest composite strings are: electroencephalographically(27) is composed of the following words => [electroencephalographic, ally, ] immunoelectrophoretically(25) is composed of the following words => [immunoelectrophoretic, ally, ] ----------------------------- Just pause here, to see the outcome...
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization