Linux Drivers 1 - 2018

A kernel is an OS. In general, the OS is used to denote the entire package that controls resources of a computer such as GUI, file utilities, and command-line interpreters.
A kernel is a small version of OS, and it is a resource manager. Whether the resource being managed is a process, memory, or hardware device, the kernel manages the access to the resource between multiple competing users (both in the kernel and in user space).
Even though we can run a program without a kernel, but the very presence of a kernel greatly reduces the complexity of writing a program or using other programs. In other words, it increases the power and flexibility by providing a software layer to manage the limited resource of a machine. - from The Linux Programming Interface.
The Linux kernel executable typically resides at the pathname /boot/vmlinuz, or something similar (Fedora 18, it's /boot/vmlinuz-3.6.10-4.fc18.x86_64).
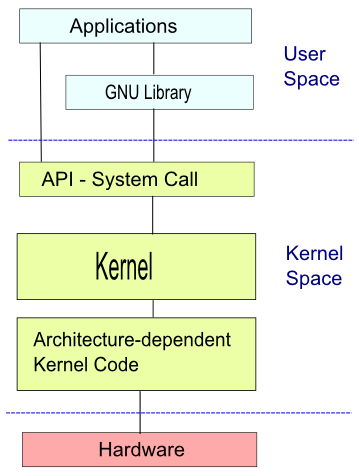
CPU can typically have at least two different modes: user mode and kernel mode. Hardware instructions allow switching from one mode to the other. Areas of virtual memory can be divided as user space or kernel space.
When running in user mode, the CPU can access only memory that is in user space, and attempting access memory in kernel space may result in a hardware exception. However, when running in kernel mode, the CPU can access both user and kernel memory space.
User Space
This is where the user applications are executed.GNU Library
This provides the system call interface that connects to the kernel and provides the mechanism to transition between the user-space application and the kernel.- This is important because the kernel and user application occupy different protected address spaces.
- While each user-space process occupies its own virtual address space, the kernel occupies a single address space.
Kernel Space
The Linux kernel can be further divided into three levels.- At the top is the system call interface, which implements the basic functions such as read and write.
- Below the system call interface is the kernel code, which can be more accurately defined as the architecture-independent kernel code. This code is common to all of the processor architectures supported by Linux.
- Below this is the architecture-dependent code, which forms what is more commonly called a BSP (Board Support Package). This code serves as the processor and platform-specific code for the given architecture.
The kernel is layered into a number of distinct subsystems.
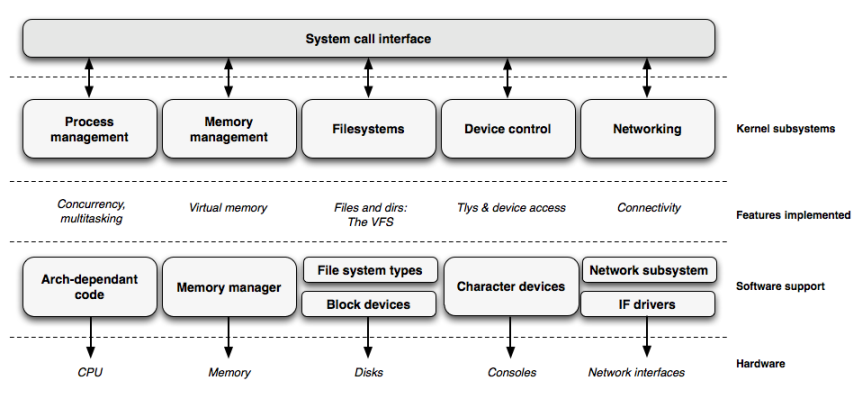
System Call Interface, API
Processes can request the kernel to do various tasks using kernel entry points which is known as system calls. This is a thin layer that provides the means to perform function calls from user space into the kernel.Process Management
A computer has one or more CPUs which execute program instructions. Linux OS is a preemptive multitasking OS. Multitasking means multiple processes can reside in memory simultaneously. Preemptive means that scheduling is determined by the kernel process scheduler rather than by the process themselves. - from The Linux Programming Interface.
Process management is focused on the execution of processes. In the kernel, these are called threads and represent an individual virtualization of the processor (thread code, data, stack, and CPU registers). In user space, the term process is typically used, though the Linux implementation does not separate the two concepts (processes and threads). The kernel provides an application program interface (API) through the SCI to create a new process (fork, exec, or Portable Operating System Interface [POSIX] functions), stop a process (kill, exit), and communicate and synchronize between them (signal, or POSIX mechanisms).
Also in process management is the need to share the CPU between the active threads. The kernel implements a novel scheduling algorithm that operates in constant time, regardless of the number of threads vying for the CPU. This is called the O(1) scheduler, denoting that the same amount of time is taken to schedule one thread as it is to schedule many. The O(1) scheduler also supports multiple processors (called Symmetric MultiProcessing, or SMP).
Memory Management
Another important resource that's managed by the kernel is memory. For efficiency, given the way that the hardware manages virtual memory, memory is managed in what are called pages (4KB in size for most architectures). Linux includes the means to manage the available memory, as well as the hardware mechanisms for physical and virtual mappings.Here is the technique that Linux employs:
- Processes are isolated from one another and from the kernel, so that one process cannot read or modify the memory of another process or the kernel.
- Only part of a process needs to be kept in memory, which can leads to effective CPU use.
But memory management is much more than managing 4KB buffers. Linux provides abstractions over 4KB buffers, such as the slab allocator. This memory management scheme uses 4KB buffers as its base, but then allocates structures from within, keeping track of which pages are full, partially used, and empty. This allows the scheme to dynamically grow and shrink based on the needs of the greater system.
Supporting multiple users of memory, there are times when the available memory can be exhausted. For this reason, pages can be moved out of memory and onto the disk. This process is called swapping because the pages are swapped from memory onto the hard disk.
File Systems
The file system provides a common interface abstraction for file systems. It provides a switching layer between the SCI and the file systems supported by the kernel.Device Drivers
The kernel provides programs with a interface that standardizes and simplified access to the devices (monitors, keyboards, disk, mice, and so on). The vast majority of the source code in the Linux kernel exists in device drivers that make a particular hardware device usable. The Linux source tree provides a drivers subdirectory that is further divided by the various devices that are supported, such as Bluetooth, I2C, serial, and so on.Networking
The kernel transmits and receives network messages on behalf of user processes including routing network packets to target system. The network stack, by design, follows a layered architecture modeled after the protocols themselves. Internet Protocol (IP) is the core network layer protocol that sits below the transport protocol (most commonly the Transmission Control Protocol, or TCP). Above TCP is the sockets layer, which is invoked through the System Call Interface.The sockets layer is the standard API to the networking subsystem and provides a user interface to a variety of networking protocols. From raw frame access to IP protocol data units (PDUs) and up to TCP and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), the sockets layer provides a standardized way to manage connections and move data between endpoints.
In this section, we will see how to develop our first Linux device driver, which will be introduced in the kernel as a module.
I'm using kernel 2.6.18:
$ uname -r 2.6.18-164.11.1.el5
Just out of curiosity, we can go into that directory, and open up Makefile:
VERSION = 2 PATCHLEVEL = 6 SUBLEVEL = 18 EXTRAVERSION = -164.11.1.el5 RHEL_MAJOR = 5 RHEL_MINOR = 4
We'll discuss what are those later.
Let's make a working directory, mydev, and make my_driver.c:
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
Makefile looks like this:
obj-m := my_driver.o
Put those two files into current working directory, mydev, in which we will build our module.
$ pwd /home/khong/mydev
One of the special thing about kernel makefile: we can have the kernel headers and source somewhere else and work in our own directory with just our source code, but build our module for the running kernel. If we want to modify some pre-existing kernel module we can download the kernel source code and copy the modules *.c to our working directory:
$ ls Makefile my_driver.c
It's necessary to compile the module using the same kernel that we're going to load and use the module with.
The make command required to build our module would be:
$ make -C /usr/src/kernels/2.6.18-164.11.1.el5-i686 M=~/mydev modules make: Entering directory `/usr/src/kernels/2.6.18-164.11.1.el5-i686' CC [M] /home/khong/mydev/my_driver.o Building modules, stage 2. MODPOST CC /home/khong/mydev/my_driver.mod.o LD [M] /home/khong/mydev/my_driver.ko make: Leaving directory `/usr/src/kernels/2.6.18-164.11.1.el5-i686'
Let's look at the working directory to see what files have been made:
$ ls Makefile Module.symvers my_driver.ko my_driver.mod.o Module.markers my_driver.c my_driver.mod.c my_driver.o
The most important file we are looking for is the *.ko file, or kernel object file. This is the file that we can load into our running kernel using modprobe or insmod.
This simple module belongs to kernel space and will form part of it once it's loaded.
After the module is built, we can load it into the kernel. The insmod does the job for us. The program loads the module code and data into the kernel, which, in turn, performs a function similar to that of ld. In other words, it links any unresolved symbol in the module to the symbol table of the kernel.
In user space, we can load the module as root by typing the following into the command line:
# /sbin/insmod my_driver.ko
We may use modprobe instead of insmod. Like insmod, modprobe loads a module into the kernel. It differs in that it will look at the module to be loaded to see whether it references any symbols that are not currently defined in the kernel.
It is possible to check that the module has been loaded correctly by looking at the list of modules currently loaded in the kernel:
# /sbin/lsmod Module Size Used by my_driver 5248 0 iptable_filter 7105 0 ip_tables 17029 1 iptable_filter nfs 229825 2 fscache 20321 1 nfs nfsd 204337 17 exportfs 9665 1 nfsd nfs_acl 7617 2 nfs,nfsd auth_rpcgss 43105 1 nfsd .... usb_storage 77473 0 mptsas 37321 2 mptscsih 37825 1 mptsas mptbase 80517 2 mptsas,mptscsih scsi_transport_sas 30529 1 mptsas sd_mod 25281 3 ext3 125001 2 jbd 57065 1 ext3 uhci_hcd 25421 0 ohci_hcd 24553 0 ehci_hcd 33869 0
Modules can be removed from the kernel with the rmmod command:
# /sbin/rmmod my_driver
Then, by issuing the lsmod command again, we can verify that the module is no longer in the kernel:
# /sbin/lsmod Module Size Used by iptable_filter 7105 0 ip_tables 17029 1 iptable_filter ...
Over the years, Unix systems have supported a handful of different special files. Linux supports four:
- block device files
- character device files
- named pipes
- Unix domain sockets
Device access in Unix systems is performed via device files. The device files may be opened, read from, and written to, allowing user space to access and manipulate devices on the system.
A character device is accessed as a linear queue of bytes. The device driver places bytes onto the queue, one by one, and user space reads the bytes in the order that they were placed on the queue. A keyborad is an example of a character device. When there are no more characters left to read, the device returns end-of-file (EOF). Character devices are accessed via character device files.
I'll start off from char drivers since they are easier to understand than block drivers or network drivers.
A block device is accessed by an array of bytes. The device driver maps the bytes over a seekable device, and user space is free to access any valid bytes in the array in any order. Hard disks, cd-rom etc. are examples of block devices. They are accessed via block device files.
Named pipes are an interprocess communications (IPC) mechanism that provides a communication channel over a file descriptor, accessed via a special file. Regular pipes are the method used to pipe the output of one program into the input of another; they are created in memory via a system call, and do not exist on any file system. Named pipes act like regular pipes, but are accessed via a file, called a FIFO special file. Unrelated processes can access this file and communicate.
Sockets are the final type of special file. Sockets are an advance form of IPC that allow for communication between two different processes, not only on the same machine but on two different machines. Actually, sockets form the basis of network and internet programming. They come in multiple varieties, including the Unix domain socket, which is the form of socket used for communication within the local machine. Whereas sockets communicating over the internet might use a hostname and port pair for identifying the target of communication, Unix domain sockets use a special file residing on a file system, often simply called a socket file.
This section will be based on a real device driver, scull (Simple Character Utility for Loading Localities). It is a char driver that works on a memory, allocated from the kernel as if it were a device. The scull is useful to demonstrate the interface between the kernel and char drivers.
Char devices are accessed through names in the filesystem, and they are called device files or nodes of the filesystem tree.
Let's do back to device thing, issue ls -l against /dev:
crw------- 1 root root 10, 62 Aug 16 2010 autofs ... crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1, 3 Aug 16 2010 null ... crw-rw---- 1 root tty 4, 9 Aug 16 2010 tty1 ... crw-rw---- 1 root uucp 4, 64 Aug 16 2010 ttyS0 ... crw------- 1 vcsa tty 7, 128 Aug 16 2010 vcsa crw------- 1 vcsa tty 7, 129 Aug 16 2010 vcsa1 ... crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1, 5 Aug 16 2010 zero
The char drivers are identified by a c in the first column while block devices are identified by a b.
There are two numbers separated by a comma, and these numbers are the major and minor device number for the device. The major numbers are 1,4,7, and 10, while the minors are 1,3,5,62,64,128, and 129.
The major number identifies the driver associated with the device. /dev/null and /dev/zero/ are managed by driver1, while virtual consoles and serial terminals are managed by driver 4. vsca and vsca1 devices are managed by driver 7.
The minor number is used by the kernel to determine which device is being referred to.
Linux - system, cmds & shell
- Linux Tips - links, vmstats, rsync
- Linux Tips 2 - ctrl a, curl r, tail -f, umask
- Linux - bash I
- Linux - bash II
- Linux - Uncompressing 7z file
- Linux - sed I (substitution: sed 's///', sed -i)
- Linux - sed II (file spacing, numbering, text conversion and substitution)
- Linux - sed III (selective printing of certain lines, selective definition of certain lines)
- Linux - 7 File types : Regular, Directory, Block file, Character device file, Pipe file, Symbolic link file, and Socket file
- Linux shell programming - introduction
- Linux shell programming - variables and functions (readonly, unset, and functions)
- Linux shell programming - special shell variables
- Linux shell programming : arrays - three different ways of declaring arrays & looping with $*/$@
- Linux shell programming : operations on array
- Linux shell programming : variables & commands substitution
- Linux shell programming : metacharacters & quotes
- Linux shell programming : input/output redirection & here document
- Linux shell programming : loop control - for, while, break, and break n
- Linux shell programming : string
- Linux shell programming : for-loop
- Linux shell programming : if/elif/else/fi
- Linux shell programming : Test
- Managing User Account - useradd, usermod, and userdel
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) I : key generation, private key and public key
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) II : ssh-agent & scp
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) III : SSH Tunnel as Proxy - Dynamic Port Forwarding (SOCKS Proxy)
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) IV : Local port forwarding (outgoing ssh tunnel)
- Linux Secure Shell (SSH) V : Reverse SSH Tunnel (remote port forwarding / incoming ssh tunnel) /)
- Linux Processes and Signals
- Linux Drivers 1
- tcpdump
- Linux Debugging using gdb
- Embedded Systems Programming I - Introduction
- Embedded Systems Programming II - gcc ARM Toolchain and Simple Code on Ubuntu/Fedora
- LXC (Linux Container) Install and Run
- Linux IPTables
- Hadoop - 1. Setting up on Ubuntu for Single-Node Cluster
- Hadoop - 2. Runing on Ubuntu for Single-Node Cluster
- ownCloud 7 install
- Ubuntu 14.04 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox I
- Ubuntu 14.04 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox II
- Windows 8 guest on Mac OSX host using VirtualBox I
- Ubuntu Package Management System (apt-get vs dpkg)
- RPM Packaging
- How to Make a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
- Linux Q & A
- DevOps / Sys Admin questions
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization